CHAPTER 15
Distributing
Products
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2015 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Explain the concept of marketing channels and their
value.
2. Demonstrate how intermediaries perform the six
marketing utilities.
3. Identify the types of wholesale intermediaries in the
distribution system.
15-2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
4. Compare the distribution strategies retailers use.
5. Explain the various kinds of nonstore retailing.
6. Explain the various ways to build cooperation in
channel systems.
7. Describe logistics and outline how intermediaries
manage the transportation and storage of goods.
15-3
REED HASTINGS
Netflix
• Almost singlehandedly
ended the era of brick and
mortar video rentals.
• In college, Hastings spent
his summers training with
the Marines and joined the
Peace Corps.
• Was inspired to start Netflix
after racking up a $40 late
fee.
15-4
NAME that COMPANY
This U.S. company is known for having low prices
all the time. One way it keeps prices low is by
eliminating as many wholesalers as possible and
doing all the wholesale function itself.
Name that company!
15-5
WHAT are MARKETING
INTERMEDIARIES?
LO 15-1
• Marketing Intermediaries -- Organizations that
assist in moving goods and services from businesses
to businesses (B2B) and from businesses to
consumers (B2C).
• They are called intermediaries because they’re in
the middle of a series of firms that distribute
goods.
15-6
WHAT are MARKETING
INTERMEDIARIES?
LO 15-1
• Channel of Distribution -- A group of marketing
intermediaries that joining together to transport and
store goods from producers to consumers.
15-7
ANSWER MAY BE BLOWING
in the WIND
• IKEA was looking to cut down on shipping costs
and to focus on renewable energy.
• It has plans to construct a wind farm in Illinois with
49 wind turbines to generate electricity for 34,000
homes.
• Started using paper pallets that weigh 90% less
than the wood and can be recycled.
• IKEA officials are not satisfied with the new pallets
already and are looking for a new option.
15-8
TYPES of MARKETING
INTERMEDIARIES?
LO 15-1
• Agents and Brokers -- Intermediaries who bring
buyers and sellers together and assist in negotiating
an exchange but do not take title to the goods.
• Wholesaler -- An intermediary that sells products to
other organizations such as retailers, manufacturers,
and hospitals.
• Retailer -- An organization that sells products to
ultimate customers.
15-9
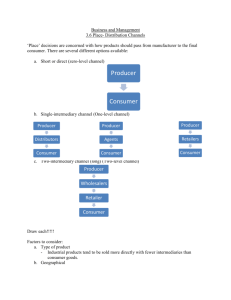
SELECTED CHANNELS of
DISTRIBUTION
LO 15-1
15-10
WHY MARKETING NEEDS
INTERMEDIARIES
LO 15-1
• Intermediaries perform marketing tasks faster
and cheaper than most manufacturers could
provide them.
• Marketing
intermediaries make
markets more
efficient by reducing
transactions and
contacts.
15-11
HOW INTERMEDIARIES CREATE
EXCHANGE EFFICIENCY
LO 15-1
15-12
THREE KEY FACTS ABOUT
MARKETING INTERMEDIARIES
LO 15-1
1) Marketing intermediaries can be eliminated but
their activities cannot.
2) Intermediaries perform marketing functions
faster and cheaper than other organizations can.
3) Marketing intermediaries add costs to products
but they are generally offset by the values they
provide.
15-13
DISTRIBUTION’S EFFECT on
YOUR FOOD DOLLAR
LO 15-1
15-14
INTERMEDIARIES
CREATE UTILITY
LO 15-2
• Utility -- The want-satisfying ability, or value, that
organizations add to goods and services by making
them more useful or accessible to consumers.
• Six types of utilities:
1. Form
2. Time
3. Place
4. Possession
5. Information
6. Service
15-15
HOW MARKETERS USE UTILITY
LO 15-2
• Form Utility -- Changes raw materials into useful
products; producers generally provide form utility.
- Starbucks makes coffee the way the customers want it.
- Dell assembles computers according to customer needs.
• Time Utility -- Makes products available when
customers want them.
- Many Walgreens stores are open 24-hours a day.
- Colleges offer day and evening classes.
15-16
HOW MARKETERS USE UTILITY
LO 15-2
• Place Utility -- Adds value to products by placing
them where people want them.
- Banks place ATMs at convenient locations.
- 7-11 stores are found in easy-to-reach locations.
• Possession Utility -- Helps transfer ownership from
one party to another, including providing credit.
- Pay for lunch at McDonalds with your Visa card.
- A savings and loan office offers loans to home/car buyers.
15-17
HOW MARKETERS USE UTILITY
LO 15-2
• Information Utility -- Opens two-way flows of
information between marketing participants.
- Websites offer advice to shoppers.
- Local government maps show tourist locations.
• Service Utility -- Provides service during and after a
sale and teaches customers how to best use
products.
- Apple offers classes to help computer buyers.
- College placement offices help students find jobs.
15-18
TEST PREP
• What is a channel of distribution and what
intermediaries participate in it?
• Why do we need intermediaries? Illustrate how
intermediaries create exchange efficiency.
• How would you defend intermediaries to
someone who said getting rid of them would save
consumers millions of dollars?
• Give examples of the utilities intermediaries
create and how they provide them.
15-19
WHOLESALE INTERMEDIARIES
LO 15-3
• Wholesalers normally make B2B sales, however,
stores like Staples and Costco also have retail
functions.
- Retail sales are sales of goods and services to customers
for their own use.
- Wholesale sales are sales of goods and services to other
businesses for use in the business or resale.
• Consumers are more familiar with retailers than
wholesalers.
15-20
TYPES of WHOLESALE
INTERMEDIARIES
LO 15-3
• Merchant Wholesalers -- Independently owned
firms that take title to the goods they handle. There
are two types:
1. Full-service wholesalers perform all distribution
functions.
2. Limited-function wholesalers perform only selected
distribution functions.
15-21
TYPES of LIMITED-FUNCTION
WHOLESALERS
LO 15-3
• Rack Jobbers -- Furnish racks or shelves of
merchandise such as music and magazines for
retailers for display and sell them on consignment.
• Cash-and-Carry Wholesalers -- Serve mostly
smaller retailers with a limited assortment of
products.
• Drop Shippers -- Take orders from retailers and
other wholesalers and have the merchandise shipped
from producer to buyer.
15-22
ROLES of AGENTS
and BROKERS
LO 15-3
• Agents generally maintain long-term relationships
with the clients they represent.
- Manufacturer’s agents
represent several
manufacturers in a specific
territory.
- Sales agents represent a
single client in a larger territory.
• Brokers usually represent
clients on a temporary
basis.
15-23
RETAILING in the U.S.
LO 15-4
• There are over 2 million retailers in the U.S., not
including websites.
• Retailers in the U.S.
employ about 5 million
people and operate
under many different
structures.
15-24
TRUCKIN’ ON
with SOCIAL MEDIA
• Today, over 3 million trucks cruise around the U.S.
with lots of specialty items.
• The food truck craze hit around the same time as
Twitter and Facebook blew up.
• Social media sites and food truck-specific apps
help link up hungry mouths with the nearest trucks.
15-25
FASTEST GROWING RETAIL
CATEGORIES
LO 15-4
• Video games
• Sports and fitness
• Home, garden, and
furniture
• Event tickets
• Consumer electronics
15-26
HOW to PREVENT
COUPON FRAUD
LO 15-4
• Make sure your coupons
are unique.
• Have clear expiration
dates and rules.
• Train staff on how to spot
fraudulent coupons.
Source: Entrepreneur, www.entrepreneur.com, accessed November 2014.
Photo Credit: Walmart Stores
15-27
HOW to PREVENT
RETURN POLICY FRAUD
LO 15-4
• Always require receipts for
returns.
• Shred receipts so they cannot be
used to return stolen goods.
• Check for tampering.
• Have customers fill out a return
form and check details.
Photo Credit: Bill Ballentyne
Source: Entrepreneur, www.entrepreneur.com, accessed November 2014.
15-28
TYPES of RETAIL STORES
Types
LO 15-4
Examples
Department Store
Sears, JC Penney, Nordstom
Discount Store
Wal-Mart, Target
Supermarket
Safeway, Kroger, Albertson’s
Warehouse Club
Costco, Sam’s Club
Convenience Store
7-Eleven
Category Killer
Toys-R-Us, Bass Pro Shops, Office
Depot
Outlet Store
Nordstrom Rack, TJ Maxx, Nike
Outlet
Specialty Store
Jewelry store, shoe stores, bicycle
shops
15-29
RETAIL DISTRIBUTION
STRATEGIES
LO 15-4
• Intensive Distribution -- Puts products into as
many retail outlets as possible.
• Selective Distribution -- Uses only a preferred
group of the available retailers in an area.
• Exclusive Distribution -- The use of only one
retail outlet in a given geographic area.
15-30
PICK a STRATEGY…
LO 15-4
What’s the Correct Retail Strategy for These Products?
• Ralph Lauren Polo Shirts
• Diet Pepsi
• Rolls Royce Automobiles
• Calloway Golf Clubs
• Snickers Candy Bars
• Steinway Pianos
15-31
TEST PREP
• Describe the activities of rack jobbers and drop
shippers?
• What kinds of products would call for each of the
different distribution strategies: intensive,
selective, and exclusive?
15-32
FORMS of NON-STORE
RETAILING
LO 15-5
• Electronic Retailing -- Selling goods and services
to ultimate consumers online.
• Telemarketing -- The sale of goods and services
via the telephone.
• Vending machines dispense
convenience goods when
consumers deposit sufficient
money.
15-33
FORMS of NON-STORE
RETAILING
LO 15-5
• Social Commerce – A form of electronic
commerce that involves using social media, online
media that supports social interaction, and user
contributions to assist in the online buying and selling
of products.
15-34
WHAT ONLINE STORES NEED
LO 15-5
Important Features on E-Commerce Web Sites
• Convenient return
policies
• Established brands
• User reviews
• Professional site design
• Alternative payment
options
Source: GSI Commerce; Harris Interactive.
15-35
FORMS of NON-STORE
RETAILING
LO 15-5
• Direct Selling -- Selling goods
and services to customers in
their homes or workplaces.
• Multilevel marketing uses
salespeople who work as
independent contractors.
• Direct Marketing -- Any
activity that directly links
manufacturers or intermediaries
with ultimate customers.
15-36
The FOUR SYSTEMS of
CHANNEL RELATIONSHIPS
LO 15-6
1. Corporate Distribution Systems
2. Contractual Distribution Systems
3. Administered Distribution Systems
4. Supply Chains
15-37
CORPORATE DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEMS
LO 15-6
• Corporate Distribution Systems -- Exist
when one firm owns all the organizations in a
channel of distribution.
• Examples:
- Goodyear
- Sherwin Williams
Photo Credit: Doug Wilson
15-38
CONTRACTUAL DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEMS
LO 15-6
• Contractual Distribution Systems -- Exist when
members are bound to cooperate through contractual
agreements.
• Forms of Contractual Systems:
- Franchise Systems: McDonald’s, Baskin-Robbins
- Wholesale-Sponsored Chains: IGA, Ace Hardware
- Retail Cooperatives: Associated Grocers, True Value
15-39
ADIMINISTERED DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEMS
LO 15-6
• Administered Distribution Systems -Exist when producers manage all the marketing
functions at the retail level.
• Examples:
- Kraft
- Ralph Lauren
Photo Credit: Stephen Boisvert
15-40
SUPPLY CHAINS
LO 15-6
• Supply Chain -- All the linked activities various
organizations must perform to move goods and
services from the source of raw materials to ultimate
consumers.
• Supply Chain Management -- The process of
managing the movement of raw materials, parts,
work in progress, finished goods, and related
information through all the organizations in the supply
chain.
15-41
The SUPPLY CHAIN
LO 15-6
15-42
WEAK LINKS CAN BREAK a CHAIN
• When nothing goes wrong, supply chains
can be a smashing success.
• But, natural disasters can wreak havoc
and cause billions of dollars in damage.
• Managing the integrity of products
throughout the whole chain is difficult too
• These weak links could cause a chain to
break.
15-43
USING LOGISTICS
LO 15-7
• Logistics -- The planning, implementing and
controlling of the physical flow of material, final goods
and related information from points of origin to points
of consumption.
• Firms outsource to
others specializing in
trade compliance to
determine what is
needed to market
products to global
customers.
15-44
LOGISTICS APPLICATIONS
LO 15-7
• Inbound Logistics -- Brings raw materials,
packaging, other goods and services and information
from suppliers to producers.
• Materials Handling -Movement of goods
within a warehouse,
from warehouse to the
factory floor and from
the factory floor to
workstations.
15-45
LOGISTICS APPLICATIONS
LO 15-7
• Outbound Logistics -- Manages the flow of
finished products and information to business buyers
and consumers.
• Reverse Logistics -- Brings goods back to the
manufacturer because of defects or for recycling.
15-46
COMPARING
TRANSPORTATION MODES
LO 15-7
Mode
Cost
Speed
Dependability
Flexibilit
y
Frequency
Reach
Rail
Med.
Slow
Medium
High
Low
High
Trucks
High
Fast
High
Medium
High
Highest
Pipeline
Low
Medium
Highest
Lowest
Highest
Lowest
Ships
Lowest
Slowest
Lowest
Highest
Lowest
Low
Air
Highest
Fastest
Low
Low
Medium
Medium
15-47
LOGISTICS SPECIALISTS
LO 15-7
• Freight Forwarder -- Puts many small shipments
together to create a single large shipment that can be
transported cost-effectively by truck or train.
• Intermodal Shipping -Uses multiple modes of
transportation to complete a
single long-distance
movement of freight.
15-48
TYPES of
INTERMODAL SHIPPING
LO 15-7
• Piggybacking: Truck
trailers placed on
trains
• Fishybacking: Truck
trailers placed on
ships
• Birdybacking: Truck
trailers placed on
planes
15-49
GET YOUR PRODUCT THERE
LO 15-7
Most Popular Modes of Freight Transport
Method
% of Distributors
Trucks
69%
Trains
15%
Pipelines
10%
Ships
6%
Air
Under 1%
Source: U.S. Freight Transportation Forecast.
15-50
STORAGE WAREHOUSES
LO 15-7
• Storage warehouses hold products for a relatively
long period of time.
• Distribution warehouses are
used to gather and
redistribute products such as:
- Beer and soft drinks
- Package deliveries
15-51
TEST PREP
• What four systems have evolved to tie together
members of the channel of distribution?
• How does logistics differ from distribution?
• What are inbound logistics, outbound logistics,
and reverse logistics?
15-52