New England Colonies
(1620-1700)
I.
II.
III.
IV.
Intro
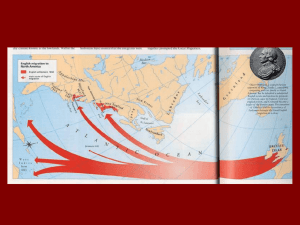
Why?
Plymouth (1620)
Massachusetts Bay
A. Founding (1630)
B. Dissenters
• Witches
V. New England Society
A. Community
B. Family
•
•
•
•
•
•
Key Terms
Puritans
Pilgrims
John Winthrop
Roger Williams
Anne Hutchinson
Salem Witch Trials
Two Dominant Religions In England
Roman Catholic
Anglican
(Church of England)
Puritans: Purify Church of all
Catholic influences
Pilgrims: “Radical” Puritans
who wanted to
separate from
Anglican Church
Major Religions
In Europe
(ca. 1560)
Netherlands =
Religious Freedom
Image Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Pilgrims Land At Plymouth
(November, 1620)
• Included
about 100
settlers
• About half
died within
six months
First Thanksgiving
(1621)
• Thanksgiving = Indians
& Pilgrims work
together
Pilgrim’s Legacy
1. First permanent
English settlement in
New England
2. Pilgrims = VERY
small in number
Massachusetts Bay Colony
(1630)
• John Winthrop
delivers “City on a Hill
Sermon”
• Included 11 ships;
700 passengers
Great Puritan Migration
(1610-1660)
• Persecution in
England led to
dramatic
increase in
settlement
• By 1700
population was
93,000 in ALL of
New England
Massachusetts Bay Colony
• Influential leader
• Governor of the colony
13 of its first 19 years
• Church & State were
closely intertwined:
– “Blue Laws”
John Winthrop
(1588-1649)
Dissenter
Roger Williams
(1603-1683)
• Minister who called for
separation of Church & State.
• Declared the colony had no
legal right to own land.
• Banished in 1635; moved to
“Providence” and began his
own colony.
• Rhode Island practiced
religious toleration.
Dissenter
• A mother of 14 children
• Challenged the authority
of ministers
• Declared she had direct
revelations from God
• Put on trial and
banished; later killed by
Indians
Anne Hutchinson
(1591-1643)
Williams & Hutchinson
• Puritans did NOT
necessarily support freedom
of religion; they supported
the right to practice their
religion freely.
Salem Witch Trials
(1692)
• In April, several girls began
to act strangely
• Tituba, an African slave, and
two others were accused of
witchcraft; accusations grew
• Over 300 were accused of
witchcraft & 20 were executed
Rev Cotton Mather’s Book
Provided Brief Trial Narratives
Image Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Petition For Bail From Accused
Witches (1692)
Pattern
• Accusation = Guilty
Verdict
• Guilty Verdict = Execution
• To avoid execution, a
confession was needed
Image Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Salem Witch Trials
(How Could This Happen?)
• Economics: social class & income conflict
• Puritan’s Goal: “City Upon a Hill”
New England: Community Life
• The Meeting House was the “center.”
• Homes were close to one another; 150 acre plots
were for farming (not necessarily next to home)
• High population density = Watchfulness
– 500 people per sq. mile
New England: Community Life
Farm-land
Farm-land
Farm-land
Farm-land
Farm-land
Farm-land
Boston Common Today
Land Divisions
• Homes in clusters with
Meeting House in center
• Town Commons =
grazing land
• One person (John
Goodnow) grew crops
in five separate spots
Sudbury, MA 1639-1656
New England: Family Life
•
Family = Backbone of community
Stability
–
–
80% of children reach adulthood
Life expectancy was 15-20 years longer than
in Virginia
• Family Organization
– Father: “True head” of family
– Mother: Managed households; often became
“deputy husbands”
– Children: Provided labor force
• Sex = Natural & ok; but acceptable only in….
Marriage
New England Colonies
(1620-1700)
I.
II.
III.
IV.
Intro
Why?
Plymouth (1620)
Massachusetts Bay
A. Founding (1630)
B. Dissenters
• Witches
V. New England Society
A. Community
B. Family
•
•
•
•
•
•
Key Terms
Puritans
Pilgrims
John Winthrop
Roger Williams
Anne Hutchinson
Salem Witch Trials