Exam 3 Study Guide
advertisement

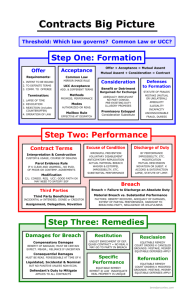
Business Law Study Guide- Test 3 *- written on the board. Possible List/For sure test Question Chapter 17 * Statute of Frauds- certain classes of contracts to be enforceable must be evidenced by 1. a writing and 2. signed by the person sought to be bound. Found in contracts where lying was a problem so now it needs to be written down to be enforceable. Contracts under the statute of frauds are VOIDABLE. *Required In:(List) Classes of Contracts Required in Statute of Frauds • *Evidence and interest in Real Property (sale or lease of land) • *Contracts exceeding one year (by terms of contract) • *Promises to answer for debts of another (collateral contracts) • *Promises of executor to pay estate claims from personal funds(if someone dies with debt and you have written down you will pay out of pocket to avoid from liquidating estate) • *Promise in consideration of marriage (prenuptial) • *U.C.C. Contracts exceeding 500 dollars. Exceptions To Statute Of Frauds:Be able to apply these 1.Partial Performance 2.Part Payment – UCC 3.Judicial Admission Effective Non-Compliance: Majority of states hold that a contract that does not comply with the statute of frauds is unenforceable. Suretyship- undertaking to pay the debt or be liable for the default of another. Parole Evidence Rule- Based on idea that there was never an oral agreement prior to contract/or the parties’ abandoned original contract when they began negotiating. Parole or external evidence will not be allowed into evidence to add or modify a contract that is fully integrated or complete on its face. Exceptions (when parole evidence doesn’t apply) • When a contract is ambiguous. If the contract may have two or more meanings, parole evidence helps to clarify. • When fraud, duress, or mistake has occurred. If provisions should have been included but were fraudulently left out. • Modification of a contract- if a contract was modified after completion or terminated, that is allowed in. • Ambiguity 3 Types of Contract 1. Complete 2. Integrated 3. Merged. Rules of Construction- How do you interpret the language? Ordinary words are to be interpreted based on ordinary meaning. Contract Construction- Always look at the entire agreement. Law exercises good faith and applies contract to the better party if one is worse. Whole Contract Rule-The provisions of a contract must be construed as a whole so that every party is given effect. Every word is equally important. Incorporation by Reference- Contract consisting of both the original document and the detailed document that covers missing terms in the original. *Strict Construction Against Drafting Party- ambiguity is held against the drafting party because they are the ones in power. *Interpreting Contradictory Contracts- (What part takes precedence over others) *1. Handwritten (most like an actual discussion) is over… *2. Type Written is over … *3. Pre-Printed *Implied Terms: Law will fill in the blanks when there is something you have left out. Such as using such skills necessary to perform work. Also reasonable time is implied. There is an implied covenant of good faith (absence of any problems). *Implied Term and Determining Intent (Hierarchy ) Contract Provisions *1. Course of Performance- Contract over time. was there earlier performance (same parties same contract?) *2. Course of dealing (allows prior evidence) - earlier dealing between same party but not same cotract *3. Custom and Usage of Trade (what is the standard in the community). Cannot override expressed provisions of a contract however. Standard from the dealing party Ex. Bring in floral company to see if flowers dealt meet typical standards Avoidance of Hardship - if there are two ways of interpreting a contract, one way will benefit both and one will cause hardhip to another, choose one that does not cause hardship Chapter 18 *3 types of Third Parties: • *3rd Party Beneficiary- 3 people and none are added. Contracts ends with 3 • *Assignments- Beginning with 2 people, then add 1. Ends with 3 • *Novation-Substation for an old contract with new one. Starts with 2 then adds 1 and subtracts 1. Ends with 2. Third Party Beneficiary- Third person whom the parties to a contract intend to benefit from the making of the contract. *3 Types of 3rd Party Beneficiaries: • *Creditor- 3rd party who was going to collect can sue b for breach of contract. Enforceable Rights • *Donee- Life insurance. Beneficiary can sue. Enforceable Rights. • *Incidental- If there was no intent to benefit this 3rd party can’t sue. Non Enforceable. • A(Obligee, Assignor, Claims Benefit)<-------contract-------- B( Obligor,Promisor, Debtor) Assignment Of Rights C (Assignee, Creditor)- can collect from B after assignment. *Assignee is Subject To: • Claims or Cause of Action(a right to payment) • Defenses (a reason not to pay) • Set Offs • If A has a reason not to pay B, they have a reason not to pay C also Assignments- Transfer of a right, generally rights to receive payment. Courts encourage ability to assign because it promotes commerce *2 Types of Assignments 1. Assignment of Rights (More common) 2. Delegation of Duties (more limited) *Contracts That Aren’t assignable (delegation): • *Prohibits Assignment in Contracts Body • *Personal Services- (Providing lessons or teaching. Would be involuntary servitude) • *Involves Credit-(Cant assign credit to someone else) • *Assignment that materially increases burden. Warranty of Assignor- Assignor is the owner of the claim or the right assigned. Delegation of Duties- Transfer of duties by a contracting party to another party that will perform them. Contracting party remains liable in case of default even with delegation. Chapter 19 Discharge- action releasing you from completion of contract. *Parts of a Contract• *Covenant/Promise- Gives rise to damages when breached. • *Condition- stipulation or prerequisite in a contract. Triggering events *Condition Precedent- Condition that must occur before a party to a contract has an obligation to perform under contract. Contract created once certain event happens. *Condition Subsequent- event whose occurrence or lack thereof terminates a contract. Ex-If something happens, failed drug test, then you will be fired. Contract created but if something happens after, its over *Condition Concurrent- Mutual duties of the contract are to take place simultaneously. (right to payment) *Time (Tender) Of Performance- If time is of the essence (time is material). This is specified in contact. If not specified then it would be reasonable performance. Depends on facts of given contract. Tender- An offer to perform something. If someone tenders payment you still owe principal. 2 types: A) Cash B) Check aka conditional payment. Law of Perfect Tender- Having to accept anything but exactly what was ordered. Right to get what you asked for. Get 0000 *Substantial Performance Doctrine- (Adequacy of Performance) Exception to the rule of perfect tender. Equitable rule that if good faith attempt to perform does not precisely meet the terms of the agreement, the agreement will still be considered complete if the essential purpose accomplished. *For this to apply the breach has to be Neither(Non): • Material • Intentional *8 Ways a Contract Is Discharged By Agreement:(Context in true false, know definitions p 404) • Mutual cancelation- both parties agree to cancel and walk away. No repayment. • Mutual recession- both parties agree to cancel and go back to status quo (original standing). Give back item and money. Trade back • Substitution- agree to new agreement between same contracting parties. Same parties new agreement. • Novation- substitution for an old contract with a new one that either replaces an existing obligation or replaces an original party with a new party. Different parties same agreement. • Accordant Satisfaction- agreement after having differing views on different performance. Change the amount of payment because of unsatisfactory work. • Settle- dispute and agreement to release claim for less • Release- 1 party letting the other party off. • Waiver- release or relinquishment of a known right or objection or specific part of contract. *Impossibility- Objective. Based on the fact that the thing cannot be done due to external conditions. Common law. Terminates contract *Temporary Impossibility- Suspends the duty to perform. Does not terminate contract. Common Law. Weather is in this category. *Frustration of Purpose- Because of change in circumstances the purpose of the contract must have no value (frustration must be complete) to the party entitled to receive performance. This discharges a contract. Has to complete destroy the purpose of the contract. Example- Guys getting hotel room to watch parade, parade route changes, the room is now useless. *Commercial Impracticability- U.C.C. Applies to sales. Imposed to deal with the harsh rule that a party must perform its contracts unless it is absolutely impossible. However, not all impractabilities are excuses for nonperformance. Does not require same level of frustration. Expanded frustration of purpose. Tangible movable personal property. *Discharge By Operation of Law- Discharging a contract when (P 410 True/False) 1) An alteration or change is made by a party 2) The destruction of written contract with intent to discharge it 3) Bankruptcy 4) Operation of statute of limitations 5) contractual limitations. If an event takes place it has effect. Bankruptcy- Surrendering all assets when one is unable to pay debts results in discharge for unpaid balance of debt. Statute of Limitations- Statute that restricts the period of time in which a lawsuit can be brought against someone. The maximum period for judgments of record is 10-20 years. A contract cannot be discharged by unilateral action unless authorized by the act itself or by statute. Chapter 20 Breach-failure to act or to perform in the manner called for in a contract. Frees material party from contract. If it is a quasi contract- there are equitable remedies (status quo ante to prevent unjust enrichment) instead of damages. Law gives rise to damages to give nonbreaching party the benefit of the bargain. • Material- Major Breach • Non Material- Minor Breach • Damages- Law • Remedy- Equity *Anticipatory Breach- When a party expressly declares that performance will not be made when required. Can result in repudiation (undoing of the contract). Refers to time of the contract. *2 Types Anticipatory Breaches Can Occur • *Expressly- “I am not going to do it” • *Conduct- If a farmer only has a certain crop and sells it to another party prior to contracting parties date, then contract is impossible to carry out and is reputed. If adequate insurance wasnt given, Repudiation- result of a buyer or seller refusing to perform the contract as stated. *Anticipatory Repudiation- Can occur if there is a material breach. Result of the buyer or seller refusing contract made in advance of time of performance. **Mitigate- U.C.C. calls it cover. The injured party is required to try and reduce damages if reasonably possible. After a major breach, anticipatory breach, occurs. * List-5 Classes of Damages • *Compensatory- sum of money that compensates party for the damages incurred as result of breach. Contract Price Vs. Market Price. • *Consequential- does not necessarily flow from type of breach but arise from foreseeable consequences. • *Punitive- (treble)damages designed to punish. Excess of compensatory damages imposed on defendant because of the particular wrongdoing. Keeps people from being able to force to sell smoething by increasing the punishment. Only if statute is set. • *Nominal- sum awarded to plaintiff in order to establish legal rights have been violated but are damages in name only. 1 dollar. Used for attorneys fees. • *Liquidated- Preagreed upon sum that is applied based on days it is not completed. If building could generate revenue and was not done on time, builder has to pay. *Equitable Remedies- Arise from Quasi contracts when there is a material breach. • *Restitution- status quo ante. Back to original standing. • *Recession- mutual mistake of fact. Annul contract. Money back to original standing. • *Reformation- contract says the wrong thing so you can both rewrite it. • *Injunction- (injoin) Order from court to refrain from doing a specified act. See it when an activity lacks utiity or usefullness. Abating a nuesense • *Specific Performance- Chattel (unique items). This is allowed for unique chattel of money or other compensation wouldn’t be adequate because of unique nature of the chattel. This is also true in terms of land. * Curative Tender, Cure- The act of righting a `breach through curative tender. If time is not of the essence and there is still time to perform under U.C.C. we allow individuals making defective tender to cure their breach. Second chance for a seller to make proper tender. Limited Damages Clause- specification to exact compensation in case of breach of contract. Injured party cannot collect more then the specified amount. Limitation of Liability Clause- provision in a contract stating that one of the parties shall not be liable for damages in breach of contract. Business people are allowed to do this. However, there are no waivers to personal injury. Chapter 21- Personal Property- property that is movable or intangible. Such as possessions or intellectual property. Real Property- Means land and things embedded in the land such as oil tanks. Fixtures are things added to a building. Title- Right to ownership Gift- Title to a personal property that is voluntarily transferred by a party not receiving anything in exchange. *2 Types of Gifts: • *Gift Inter Vivos- Any transaction that takes place between living person and creates rights prior to the death of any of them. • *Gifts in Causa Mortis- Gift by donor in the belief that death was immediate and impending that is revoked under certain circumstances. Have to be completed by death. Revoked if 1) the donor does not die 2) the donor revokes prior to death 3) the donee dies before the donor. *2 Elements to a Gift• *Donative Intent- intent to give the gift. • *Delivery Actual-handing the item over Constructive- Symbolic Delivery of goods such as a key or papers. Lost Property- Not entitled to a reward or compensation without a contract specifying. Person finding property acquires possession but not title. If it is lost in public place where the person could find it, there is no possession by the finder. • Treasure Trove • Abandoned- Belongs to whoever claims it • Mislaid • Lost Escheat- Common law word referring to the property that returns to the government. Transfer to the state the title of a person’s property when a descendant does not claim or person is not survived by an heir. Happens with insurance payments, refunds, and dividends most often. Conversion - wrongful taking of property. Civil stealing *4 Types of Joint Tenancy• *Joint Tenancy with Right of Survivorship- On death of 1 tenant, the remaining tenant takes the share of the deceased. After first death everyone becomes tenants in common. If three people recieve something due to death, and one dies the other two split it. If another dies his kids split it. • *Tenants in Common- The interest of the tenant is transferred or inherited thus making the taker a new tenant in common. • *Tenancy by entirety- Exists only from husband to wife. Transfer of property completely to one or the other. Right of survivorship cannot be trumped and spouse gets it. • *Community Property- Property acquired during the time of marriage. Some states provide right of survivorship other provide half to widow and half to heirs on death. Bailment- Relationship that exists when personal property is delivered into the possession of another under an agreement that identical property will be returned in accordance with agreement. Has 2 parts 1. Contract to Bail 2. Actual Bailing of Property. *Ask 2 questions for Bailment: 1. Distinguish from rental 2. Who has burden of proof? (Generally plaintiff) • *Based on Contract- Becomes a tort liability claim. • Exclusive rental of Space is not bailment. Storage spaces are not bailments. • Using part of space/sharing space with others is bailment. Liability issues are different. *3 Types of Bailments and Burden of Proof. • Sole Benefit of the Bailor- Keeping books at a friend’s house over the summer. Must be liable only for gross negligence for a damages to be collected • Mutual Benefit- Commercial. Requires ordinary negligence. • Benefit of Bailee- Loaning a person your Les Paul guitar. Bailee benefits more. Liable in slight negligence. Gratuitous Bailment. - Bailment in which the bailee does not receive any compensation or advantage Constructive Bailment- bailment imposed by law as apposed to one created by contract, whereby the bailee must preserve the property and redeliver it to the owner. Baliment Bailor/ Baliee Express - Make an agreement Implied in fact - Actions express it Constructive - Test::: Ch. 17 Know statue of frauds and 6 types of contract subject to its terms Writing and signature Parole Evidence rule - need to know excetions 367 Contruction and interpretation whole contract rule and priorities rule Incorporation by reference 372 Para C - contrued against the drafting party Custom and conduct - course of performance/ dealing custom and usage of trade 3rd party beneficiary - law on assignment Know three types creditor donee incidental - if incidental don’t have enforcabel rights Assignments - assignee takes contract subject to claims defenses and setoffs Kinds of contracts that rights cannot be assigned - 387 Personal services Warantees of the assignor - 389 19 Conditions - concurent precent subsequent Tender of payment/performance Doctrine of curitive tender Time is of the essence Adequecy of performane - substantial perfomance doctrine - if substantial get your money if defect is neither intential nor major Discharge by agreement - 404 listing of 8 know in context Depth discharges Three concepts from UCC - Curitive tender, Cover, Doctrine of commercial impracticability Impossibiliy has to be objective not subjective Bankruptcy - 410 Ch 20 Know types of damages and equitable remedies No direct damages Anticipatory repudiation CH 21 Personal property on gifts - types and elements Lost property - lost mislaid and aboandoned Escheat - gov Joint tendancies Survivorship Bailment, bailor bailee Read thrugh para 15 on how lawsuits conducted 451