Stoichiometry
advertisement

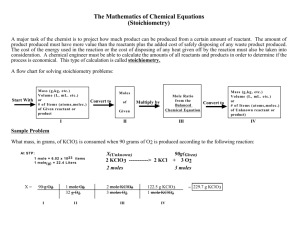
WHAT IS STOICHIOMETRY? Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants used and the products formed by a chemical reaction Stoichiometry is based on the Law of Conservation of Mass Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products WHAT IS STOICHIOMETRY USED FOR? Stoichiometry is used to tell chemists: 1. How much product will be produced 2. How much reactant is needed to make a product STOICHIOMETRY AND THE BALANCED EQUATION Coefficients in a balanced chemical equation can tell us: 1. The # of individual particles: (atoms, molecules, or FUN) 2. The # of moles of particles 3. The mass of reactants and products (Found using the molar mass (MM) of the compounds) EXAMPLE Balance the Following Equation: ___ Fe(s) + ___ O2(g) ___ Fe2O3(s) EXAMPLE ANSWER Balance the Following Equation: 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Fe2O3(s) FILL IN THE TABLE Fill in the table below: Reactants Name: Iron + Formula: Fe + Products Oxygen Gas O2 Iron (III) Oxide Fe2O3 _____atoms of Fe + _____ molecules O2 _____ formula units Fe2O3 _____ moles Fe + _____ moles O2 _____ moles Fe2O3 + _____ grams O2 _____ grams Fe2O3 ____ grams reactants _____ grams products _____ grams Fe MOLE RATIO (COEFFICIENT RATIO) Mole Ratio (coefficient ratio) – the ratio between the numbers of moles of any 2 substances in a balanced chemical equation Ex. Balance the following equation and determine all mole ratios: 1. ____ N2(g) + ____ H2(g) ____ NH3(g) 2. ____ Fe(s) + ____ H2O(l) ____ Fe3O4(s) + ____ H2(g)