Writing Specifications
advertisement

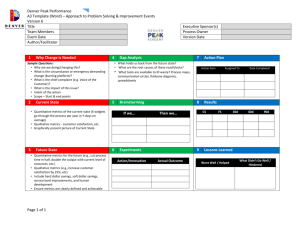
Writing Target and Final Specifications translating customer words… into … realizable engineering specifications Rationale for Specs • Need to know when you’re done. • Need to know what is ‘good’. • Agree on target specs before design development begins. • Refine and validate final specs before detail design begins. • Use specs to prevent scope creep! Process for Target Specs 1. Create a list of customer needs. (by-product of client interview) 2. Prioritize customer needs (by importance). 3. Prepare a needs-metrics matrix. 4. Compile a benchmarking chart. 5. Establish ideal as well as marginally acceptable values. 6. Set appropriate target values. Tips on Customer Needs • Use interviews, observations, and experiential information (based on client visit/interview) • Asses functional performance, human factors, physical requirements, reliability, life-cycle concerns, resource concerns, fabrication requirements (based on project learning) • Play these back to your client for their comment/clarification/approval! Process for Target Specs 1. Create a list of customer needs. (by-product of client interview) 2. Prioritize customer needs (by importance). 3. Prepare a needs-metrics matrix. 4. Compile a benchmarking chart. 5. Establish ideal as well as marginally acceptable values. 6. Set appropriate target values. Tips on Selecting Metrics • • • Ideally each customer need would correspond to a single metric, and the value of that metric would correlate perfectly with meeting that need. In practice, several metrics may be necessary. Metrics should be dependent, not independent, variables. Specs indicate what the product must do, but not how the specs will be achieved. Show a table of metrics at the Oct 14 Snapshot. Tips on Selecting Metrics • • • Metrics should be practical (ie measured with available equipment). Some needs cannot easily be translated into quantifiable metrics. Indicate these by ‘subj’, meaning that they should be interrogated by an expert or focus group. Metrics should include popular criteria for comparison in the marketplace. Seek out metrics cited in trade magazines/catalogs. Process for Target Specs 1. Create a list of customer needs. (by-product of client interview) 2. Prioritize customer needs (by importance). 3. Prepare a needs-metrics matrix. 4. Compile a benchmarking chart. 5. Establish ideal as well as marginally acceptable values. 6. Set appropriate target values. Tips on Selecting Target Values 5 ways to express target values… - At least X - At most X - Between X and Y - Exactly X - A set of discrete values Validate metrics and target values in your conceptual design review and again in your detail design review! Process for Final Specs 1. Develop technical models of the product. 2. Develop a cost model of the product. 3. Refine target specifications, making well documented trade-offs as necessary. 4. Flow down specifications for overall system into sub-systems. 5. Set appropriate values for final specs. Summary • Specifications are typically established at least twice. Immediately after identifying the customer needs, the team sets target specifications. After concept selection and testing, the team develops final specifications. • Final specifications are developed by thoroughly assessing actual technological constraints and production costs. They should be based on rigorous analytical and physical modeling. Helpful References Ulrich and Eppinger, Product Design and Development, 5th Edition, McGraw Hill, 2012. Hatley and Pirbhai, Strategies for Real-Time System Specification, Dorset House, 1998. Rechtin and Maier, The Art of Systems Architecting, 2nd Edition, CRC Press, 2000.