key terms updated instructions
advertisement

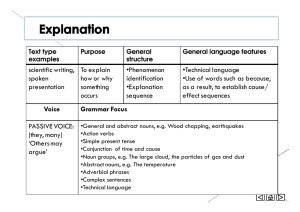
Key Terms, Tab 3 Key Terms: Updated Instructions A. The terms must be hand-written on a separate sheet of paper B. Number the terms in each group C. Examples should be used for most terms (or if it is more helpful for a term you can put an illustration of the term instead of an example) D. Examples should be placed on the next line, after the definition (and should say “Ex:” or “Example:”) E. Highlight each key term F. Leave at least three lines between each group G. Translate the definitions into your own words so they are more meaningful for you- this will help you A LOT more on the unit exam! H. Label each group (YOU come up with the label after you define the terms) DIFFUSION 1. Distance decay-as distance from the hearth increases the intensity of the cultural trait decreases; has become less significant with modern technology Example: The further you get from the German border the less likely German is going to be the dominant language 2. Spatial diffusion-the spread of a phenomenon across space Example: expansion (hierarchical, stimulus, contagious) and relocation are types of diffusion 3. Hierarchical diffusion-the spread of a phenomenon from people or places of greater prominence without regard to distance and then ultimately to people or places of lesser prominence Example: fashion trends 4. Stimulus diffusion-in order for a phenomenon to continue to spread to new people and places it changes as it encounters cultural barriers to be accepted Example: McDonald’s has modified menus to gain acceptance in other countries such as India 5. Contagious diffusion-the spread of a phenomenon across space based upon proximity Example: Tuberculosis 6. Relocation diffusion-the movement of a phenomenon across space, but without an increase in the phenomenon Example: I bring my accent with me from Kentucky to Texas, but the accent isn’t “caught” by anyone in my new location 7. Space-physical area REGIONS 1. Spatial organization/spatial association- how things can be grouped across space/what things are similarly distributed across space Example: examining where populations who speak Spanish are the majority in the United States 2. Regionalization/regional analysis- grouping places together based upon similar characteristics Example: examining all countries where Islam is dominant as one region 3. Formal region- an area where there is a unifying characteristic or set of characteristics Example: the Corn Belt 4. Functional region- a region with boundaries created based upon the extent of influence of a place or an activity Example: metro Louisville 5. Perceptual region- a region that is based on identity and individualized experiences; some of the basis of the region could be seen as formal, but it is also layered with phenomena that have a degree of subjectivity Example: “The South”