Cells: structure & function
advertisement

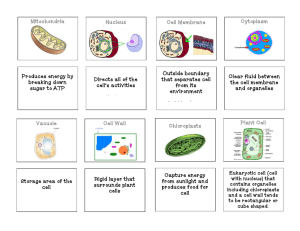
CELLS: STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Biology ATAR Unit 2 Text: Chapter 7 Pages 160-163; 175-177 Keywords Organelles Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body (apparatus) Lysosome Mitochondria Nucleus Plastid Ribosome Vacuole Making connections Every cell in an organism is connected in some way to every other cell. Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs and organs work together as systems. Cells are the basic unit of life. They are extremely complex machines with many interdependent parts. Understanding how a cell works is the first step to understanding how organisms function. LEARNING OUTCOMES Describe and explain the function of the different organelles Relate the structure of organelles to their function Describe and understand the difference between plant and animal cells CELL THEORY Cells are the smallest living units of organisms All cells come from pre-existing cells. Each organism is made of one or more cells. CELL STRUCTURE Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell membrane Cytosol Organelles Cytoskeleton the skin the fluid the machines the bones Cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles CELL STRUCTURE Organelles are the internal structure of cells. Cells from all sorts of organisms have at least some, if not all, of these structures. Cell membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies (apparatus) Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosomes ANIMAL CELLS Centrioles Lysosomes PLANT CELLS Cell wall Chloroplasts Vacuoles CELL MEMBRANE Structure Is a bilayer of phospholipids molecules enclosing the cytoplasm in all cells Function It controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell It contains receptor proteins that allow it to communicate with other cells ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Structure A network of intracellular membranes that links with the plasma membrane and other membranous organelles. Endoplasmic reticulum may be rough (associated with ribosomes) or smooth (lacking ribosomes). Function It is involved with the production, processing, transport and storage of materials within the cell. GOLGI BODIES (GOLGI APPARATUS) Structure A stack of flat membrane sacs linked to the endoplasmic reticulum. Function The golgi bodies package proteins into membranebound vesicles before they are secreted from the cell. ANIMAL CELLS: LYSOSOMES Structure Membrane-bound vesicles containing powerful enzymes Function The enzymes break down debris and foreign material Structure The nucleus is a large organelle that is surrounded by a porous membrane. The nucleus contains genetic material (DNA) Function The nucleus controls all cellular activity NUCLEUS MITOCHONDRIA Structure Mitochondria are composed of many folded layers of membrane Function The mitochondria are involved in energy production RIBOSOMES Structure Tiny organelles located in the cytosol, sometimes associated with endoplasmic reticulum. Function They are sites of production of proteins. ANIMAL CELLS: CENTRIOLES Structure A pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules. Function They are involved in the separation of chromosomes during cell division in animal cells and protists. They are not found in plant cells. PLANT CELLS: CELL WALL Structure The cell wall is found in plant cells It is made of cellulose and surrounds the cell membrane Lignin is present in the cell wall of the xylem of woody plants to give them further support Function provides support prevents expansion of the cell allows water and dissolved substances to pass freely through it PLANT CELLS: CHLOROPLASTS Structure Found mostly in plant leaf cells Contains chlorophyll – a green pigment that absorbs light energy Function photosynthesis PLANT CELLS: VACUOLE Structure A vacuole is found in most plant cells They may contain food, enzymes and waste products Function Vacuoles are filled with fluid and provide physical support SUMMARY: CELL STRUCTURES Structure Function Cell membrane •Border patrol: controls movement of substances in and out of the cell •Enables chemical communication between cells Centrioles •Separate chromosomes during cell division (protista and animalia only) Endoplasmic •Processing and transport centre reticulum •Rough (+ribosomes) or smooth (-ribosomes) Golgi bodies •Packaging & export centre – vesicles Lysosomes •Recycling & waste disposal centre (animalia only) Mitochondria •Power supply centre SUMMARY: CELL STRUCTURES Structure Function Nucleus •DNA – blueprint for building specifications Ribosomes •Assembly line – manufacture of proteins Vacuoles •Storage centre – food or enzymes •Support – fluid (plantae) Contractile vacuole •Osmoregulation (maintaining fluid balance) •Protists and unicellular algae PLANT CELLS ALSO CONTAIN: Cell wall •Structure and support Chloroplasts •Food manufacturing centre - photosynthesis Plastids Class of organelles which include: •Chloroplasts •Amyloplasts (starch storage) •Chromoplasts (pigmentation organelles) CONTRACTILE VACUOLE