Presentation1.Finished
advertisement

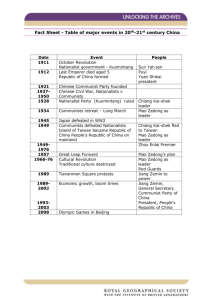
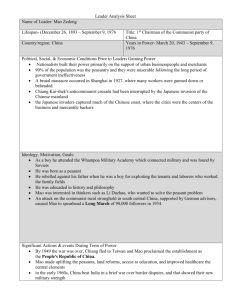
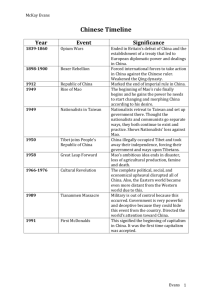
Communist China By: ShaneQuis behanan Mao Zedong *1893–1976, founder of the People's Republic of China. * From 1928 until 1931 Mao, with Zhu De and others, established rural soviets in the hinterlands, and built the Red Army. * Mao was one of the most prominent Communist theoreticians and his ideas on revolutionary struggle and guerrilla warfare have been extremely influential, especially among Third World revolutionaries. *MAO Zedong was born on December 26 in the small village of Shaoshan in the province of Hunan -Southeast China. While Mao spent much of his childhood working on the family farm, he developed a passion for learning during his brief primary education. At the age of sixteen, Mao left Shaoshan and traveled to the city of Changsha, the provincial capital, where he enrolled in middle school. Mao was born at a time of great social, political, and cultural change. China was feeling the pressure of imperialism and many scholars, government officials, and others were pushing for modernizing reforms. rosenblumtv.wordpress.com The Great Leap Forward * The Great Leap Forward planned to develop agriculture and industry. Mao believed that both had to grow to allow the other to grow. Industry could only prosper if the work force was well fed, while the agricultural workers needed industry to produce the modern tools needed for modernization. To allow for this, China was reformed into a series of communes. history.cultural-china.com Cultural Revolution *The movement that became known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution represented an attempt by Mao to go beyond the party rectification campaigns, of which there had been many since 1942, and to devise a new and more radical method for dealing with what he saw as the bureaucratic degeneration of the party. *During the early 1960s, tensions with the Soviet Union convinced Mao that the Russian revolution had gone astray, which in turn made him fear that China would follow the same path. Programs carried out by his colleagues to bring China out of the economic depression caused by the Great Leap Forward made Mao doubt their revolutionary commitment and also resent his own diminished role. Tiananmen Square *Tiananmen (translated from Chinese: The Gate of Heavenly Peace) is the original gate of the Imperial Palace, commonly known as the Forbidden City. It is now one of the entrances for tourists visiting the Forbidden City. *in the middle of Tiananmen Square sits the Renmin Yinxiong Jinian Bei, or Monument to the People's Heroes, which can be seen in the foreground. Dedicated to the men and women who died in the struggles to make China an independent nation in the century before the Communists came to power, it has acted as a lightning rod for dissent. After the start of the Falungong demonstrations, it was cordoned off from the public. latinamericangrid.org Chinese Economy *The People's Republic of China which was established in 1949 under the leadership of Mao Zedong, is today a rapidly developing nation of a billion people; on present trends it is poised to emerge as the largest economy in the world in about two decades (by the year 2015), overtaking both Japan and the USA. The counter-revolution in the USSR and its rapid economic and social collapse since 1990 under the regime of "market reforms", lends a special interest to the sharply contrasting scenario in the world's largest remaining socialist state. The question inevitably arises: what were the characteristics of that growth strategy which permitted rapid development during the three decades 1949- 79; and what is the relation of that strategy to the apparently very different policies the Chinese planners themselves call, socialist market economy. lucys6.blogspot.com Bibliography *"Mao Zedong — Infoplease.com." Infoplease: Encyclopedia, Almanac, Atlas, Biographies, Dictionary, Thesaurus. Free Online Reference, Research & Homework Help. — Infoplease.com. Columbia University Press, 2007. Web. 23 Mar. 2011. <http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/people/A0831663.html>. *"The Economic Ideas of Mao Zedong: Agricultural Transformation - Utsa Patnaik." Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts - Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Kala Kendra - इंदिरा गााँधी राष्ट्रीय कला केंद्र . Web. 25 Mar. 2011. <http://www.ignca.nic.in/ks_41032.htm>. *"Tiananmen Square." Infoplease: Encyclopedia, Almanac, Atlas, Biographies, Dictionary, Thesaurus. Free Online Reference, Research & Homework Help. — Infoplease.com. Web. 25 Mar. 2011. <http://www.infoplease.com/spot/tiananmen.html>. *1974, July. "The Cultural Revolution." Free Hosting, Web Hosting, Domain Names and Web Design | Fortunecity. Web. 25 Mar. 2011. <http://www.fortunecity.com/victorian/riley/787/China/Cultural/Cultural.html>. *"Mao Zedong — Infoplease.com." Infoplease: Encyclopedia, Almanac, Atlas, Biographies, Dictionary, Thesaurus. Free Online Reference, Research & Homework Help. — Infoplease.com. Web. 25 Mar. 2011. <http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/people/A0831663.html>. boston.com