Mitosis Virtual Lab http://bio.rutgers.edu/~gb101/lab2_mitosis/index2
advertisement

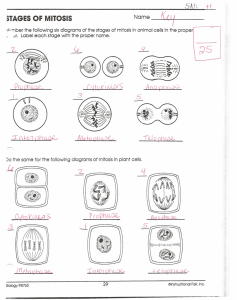
Mitosis Virtual Lab http://bio.rutgers.edu/~gb101/lab2_mitosis/index2.html Introduction to the Lab: The emphasis of this laboratory period will be on mitosis. Mitosis is the sequence of events by which the nuclear material of one cell is distributed, by a process involving chromosomes, into two equal parts. At the right is a longitudinal section through an onion (Allium) root tip. The root tip is responsible for the downward growth of the root and therefore, is one of the regions in the plant where cells are actively dividing and elongating. Because of this, the root tip is an excellent system in which to study the process of cell division (cytokinesis) and nuclear division (mitosis) Furthermore, the chromosomes are fairly large and distinct, and this species has a relatively small number of chromosomes. Click on Begin Assignment Part 1. a. Click on the root tip to magnify the image. Can you find dividing cells in the onion root tip? b. What differences can you see when you compare the nucleus of a dividing cell with that of a nondividing cell? Part 2. a. Review the diagrammatic summary of cell division in your notebook before you begin. b. View a video of mitosis in an animal cell Part 3. Microscopy Lab Now that you have seen how nuclei divide, you can begin the microscope exercises. Go back to the image of the root tip. Click on the image to magnify the root tip. Use the scroll bars to move around the root tip. Identify at least one cell in each of the stages of division summarized in the review. Place the cursor over a dividing cell and click once. Identify the stage of division. When you have identified at least one cell in each stage, proceed to the next section. Part 4. Mitosis in an Animal Cell. Click to begin Slides of whitefish blastulae will be used to show mitosis and cell division in animal cells. Although the result of these processes and many of the events are the same or very similar to that of the plant cells, there are some differences. See what differences you can detect. Click on any of the slides at the right to magnify. Use the scroll bars to move around the slide. Place the cursor over a dividing cell and click once. Identify the stage of division. Identify at least one cell in each stage.