4.1: Radian and Degree Measure
advertisement

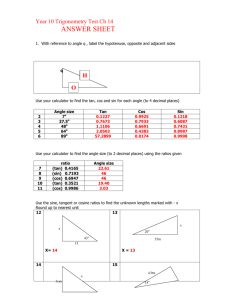
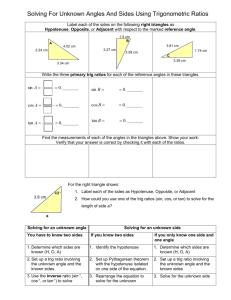
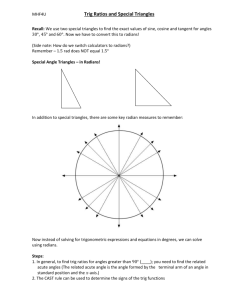
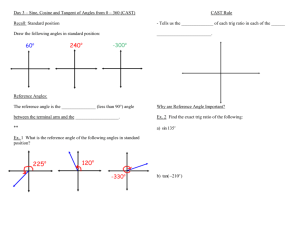
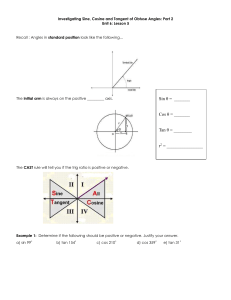
4.1: Radian and Degree Measure Objectives: •To use radian measure of an angle •To convert angle measures back and forth between radians and degrees •To find coterminal angle We are going to look at angles on the coordinate plane… An angle is determined by rotating a ray about its endpoint Starting position: Initial side (does not move) Ending position: Terminal side (side that rotates) Standard Position: vertex at the origin; initial side coincides with the positive x-axis Positive Angle: rotates counterclockwise (CCW) Negative Angle: rotates clockwise (CW) Negative Angle Positive Angles 1 complete rotation: 360⁰ Angles are labeled with Greek letters: α (alpha), β (beta), and θ (theta) Angles that have the same initial and terminal sides are called coterminal angles RADIAN MEASURE (just another unit of measure!) Two ways to measure an angle: radians and degrees For radians, use the central angle of a circle r s=r •s= arc length intercepted by angle •One radian is the measure of a central angle, Ѳ, that intercepts an arc, s, equal to the length of the radius, r • One complete rotation of a circle = 360° • Circumference of a circle: 2r • The arc of a full circle = circumference s= 2r Since s= r, one full rotation in radians= 2 =360 ° 2 6.28 , so just over 6 radians in a circle 2 360 (1 revolution) ½ a revolution = ¼ a revolution 1/6 a revolution= 1/8 a revolution= Quadrant 2 2 3 2 Quadrant 3 Quadrant 1 0 2 3 2 2 Quadrant 4 Coterminal angles: same initial side and terminal side Name a negative coterminal angle: 2 3 2 You can find an angle that is coterminal to a given angle by adding or subtracting 2 Find a positive and negative coterminal angle: 1. 6 2. 3 2 3. 3 7 4. 2 Degree Measure 360 2 180 So……… 1 rad 180 180 1rad deg Converting between degrees and radians: 1. Degrees →radians: multiply degrees by 180 180 2. Radians → degrees: multiply radians by Convert to Radians: 1. 320° 2. 45 ° 3. -135 ° 4. 270 ° 5. 540 ° Convert to Radians: 1. 2 2 .3 6 3. 5 5 4. 4 Sketching Angles in Standard Position: Vertex is at origin, start at 0° 1. 3 4 2. 60° Sketch the angle 3. 13 6 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: • Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles • Evaluate trig functions with a calculator • Use trig functions to model and solve real life problems Right Triangle Trigonometry Side opposite θ hypotenuse θ Side adjacent to θ Using the lengths of these 3 sides, we form six ratios that define the six trigonometric functions of the acute angle θ. sine cosine tangent cosecant secant cotangent *notice each pair has a “co” Trigonometric Functions • Let θ be an acute angle of a right triangle. opp sin hyp adj cos hyp opp tan adj RECIPROCALS csc hyp opp hyp sec adj adj cot opp Evaluating Trig Functions • Use the triangle to find the exact values of the six trig functions of θ. hypotenuse 4 θ 3 Special Right Triangles 45-45-90 30-60-90 45° 60° 2 1 2 1 45° 1 30° 3 Evaluating Trig Functions for 45° • Find the exact value of sin 45°, cos 45°, and tan 45° Evaluating Trig Functions for 30° and 60° • Find the exact values of sin60°, cos 60°, sin 30°, cos 30° 60° 30° Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Special Angles 1 sin 30 sin 6 2 0 p 1 sin 45 = sin = 4 2 0 3 sin 60 sin 3 2 0 3 cos 30 cos 6 2 0 p 1 cos 45 = cos = 4 2 0 cos 600 cos 3 1 2 tan 300 tan tan 450 tan tan 60 tan 0 6 4 3 1 3 1 3 Trig Identities • Reciprocal Identities 1 sin csc csc 1 sin 1 cos sec sec 1 cos 1 tan cot cot 1 tan Trig Identities (cont) • Quotient Identities sin tan cos cot cos sin Evaluating Using the Calculator • sin 63° • tan (36°) • sec (5°) Applications of Right Triangle Trigonometry • Angle of elevation: the angle from the horizontal upward to the object • Angle of depression: the angle from the horizontal downward to the object Word Problems • A surveyor is standing 50 feet from the base of a large tree. The surveyor measure the angle of elevation to the top of the tree as 71.5°. How tall is the tree? • You are 200 yards from a river. Rather than walk directly to the river, you walk 400 yards along a straight path to the river’s edge. Find the acute angle θ between this path and the river’s edge. • Find the length c of the skateboard ramp.