Chapter04b
advertisement

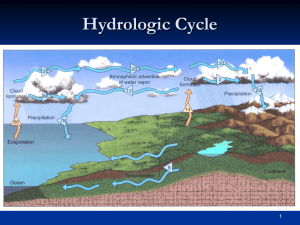
Atmospheric Moisture: Relative Humidity and Dew Point RECAP • • • Absolute Humidity: the mass of water vapor in a fixed • • Water mixing ratio: the mass of water vapor in a fixed • • Hydrological cycle: transport of water and energy. Humidity: the water content in the air. volume of air, i.e. the water vapor density. Specific Humidity: the mass of water vapor in a fixed total mass of air. mass of the remaining dry air. Actual vapor pressure: the amount of water vapor in terms of the amount of pressure exerted by the water vapor molecules alone. Dalton’s law. Saturation vapor pressure: the pressure that the water vapor molecules would exert if the air were saturated, i.e. the maximal vapor pressure at a given temperature T. • • Humidity Humidity: the amount of water in the air. Absolute humidity: the mass of water vapor in a unit volume of air. AH mass of water vapor volume of air • compared to the total mass of the air parcel. Specific humidity: the mass of the water vapor SH mass of water vapor total mass of air • Water (mass) mixing ratio: The mass of water vapor compared to the mass of the rest of the air parcel. MR mass of water vapor mass of dry air Vapor pressure • Partial pressure: the pressure of each gaseous component in a mixture of gases. • Dalton’s law of partial pressure: the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of each gas component. P P1 P2 P3 ... P P( N2 ) P(O2 ) P( Ar) ... P( H 2O) ... • Vapor pressure: the partial pressure of H O vapor. 2 ♦ What is the H2O vapor pressure if 1% of the air is H2O and the total air pressure is 1bar? • The pressure of a gas is proportional to the number of molecules and to the temperature of the gas. P nT • • Saturation Vapor Pressure What is it? ♦ This is the partial pressure of H2O when the air is saturated. ♦ This is the maximum H2O partial pressure before the H2O molecules condense out. Supersaturation: P(H2O)>Ps ♦ It is an unstable condition ♦ It occurs in the absence of condensation nuclei. Saturation Vapor Pressure saturated • The saturation vapor • pressure Ps, depends on the temperature. It increases with temperature. Ps over water is larger than it is over an ice surface at the same temperature. Supersaturated unsaturated • • Definition: Relative Humidity Description: how close the air is to being saturated. water vapor content RH water vapor capacity P ( H 2O ) RH 100% Ps ( H 2O) • RH=100% :the air is saturated. (clouds, fog, rain) • • • If we add water vapor to the air, RH is increasing. If • RH<100% :the air is not saturated. RH>100% :the air is supersaturated-clean air with no condensation nuclei (rare) we remove water vapor from the air RH is decreasing. An increase in temperature results in a decrease of RH, and a decrease of T results in an increase in RH. Relative Humidity and Temperature • • Watering the plants is more effective when RH is high: less • RH is usually maximum in the morning (low T) and minimum during the afternoon (high T). evaporation from the ground (morning, evening hours). The air’s total vapor content is ~ constant during the day P ( H 2O ) RH 100% Ps ( H 2O) Specific Humidity (g/kg) Variation of SH and RH with latitude. SH SH mass of water vapor total mass of air P ( H 2O ) RH 100% Ps ( H 2O) RH Dew Point • The temperature to which the air has to be cooled (with no change in the air pressure or water content) for saturation to occur. • If the air is saturated saturated ♦ How much is RH? ♦ What is the air T? • The dew point is a measure of the water vapor content in the atmosphere. A high dew point temperature corresponds to high H2O content. • Adding water vapor increases the dew point and removing water vapor decreases the dew point. Supersaturated unsaturated US Dew Point Map • • • Examples of Weather Conditions The Gulf area has high dew point but also high temperature => RH is not so high. High dew point does not mean high RH! Fog and precipitation are associated with high RH. • California / Florida Why is the weather in California much drier than the weather in Florida? • Humidity in Your Home Cold climate (winter in upstate NY). The water content is the same inside and outside the house.The RH inside is much lower than RH outside. T=-15 C Tdew=-15 C RH=100% The outside air is heated and as it enters the house T = 20 C Tdew=-15 C RH=8% • air down, the air becomes saturated, the excess H O vapor condenses Hot and humid climate (summer Florida). The air conditioner cools the 2 in the cooling unit. As a result the air inside the house has lower water content (lower dew point). The relative humidity in the house decreases as the cooled saturated air from the cooling unit is mixed with the warm unsaturated air in the room. • Hot and dry climate (summer in Arizona). Evaporative cooling systems: The hot dry air from outside flows across pads saturated with water. Water is evaporated, the air cools down because it provides the energy needed for the evaporation. As a result the air in the house becomes cooler, with higher dew point and RH. How humid is “VERY” humid? • (evaporation of body liquids from the skin surface). • The human body cools down through perspiration • • If the relative humidity is high, the evaporation is inhibited and we cannot cool efficiently. The body temperature rises. Heat Index: shows what the air temperature feels like. It takes into account the humidity and the actual temperature of the air. Humans feel comfortable if HI<80 F. Heat index above 90 F is uncomfortable. HI>100 F is dangerous. Heat Index The weight of humid air • Mean molecular mass of dry air: gas m % mass of the gas mixture -------------------------------------------N2 28 78% 28x78/100+32x21/100=28.6 O2 32 21% • Mean molecular mass of wet air. gas m % mass of the gas mixture --------------------------------------------Dry air 28.6 90% 28.6x90/100+18x10/100=27.5 H2O 18 10% • Moist air is lighter and less dense than dry air at the same temperature. • Moist air rises more readily. Evaporation enhances convection in the atmosphere.