An Approach to *Bad Blood* AKA acute leukemia
advertisement

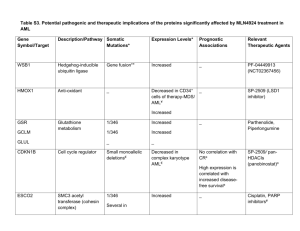
AN APPROACH TO “BAD BLOOD” AKA ACUTE LEUKEMIA Arif Ali Awan – R2 JGH November 27th, 2014 IM Teaching DISCLAIMER Just a Resident CASE 52F Nurse, 3 sisters PMHx: HTN, hysterectomy Meds: Hctz 12.5; NKDA No family history Presents with 6 week history of intermittent fever (upto 38.5), sore throat, malaise, muscle pains, mild dyspnea went to GP, given NSAID’s and antibiotics Developed small red dots especially on legs, gingival bleeding, worsening fatigue Presented to Santa Cabrini WBC 279,000, Hgb 80 MCV = 90, Plat 25; 60% peripheral blasts Transferred to JGH. THE FIRST THINGS YOU HAVE TO DO Make sure patient not in DIC, TLS Symptomatic leukostasis! AML/APL or ALL ACUTE LEUKEMIA A disease in which immature heterogenous white blood cells multiply or accumulate uncontrollably Circulating “clonal” white blood cells. Need to distinguish between AML (60-70%)/APL (5-8% of AML), ALL (~20%) Hematologic emergency: fatal in weeks to months (Infection, bleeding) AML: 16000 cases yearly in US, median age 70 y, 3-5/100,000 person-yr ALL: total 6000 cases yearly in US, minority in adults HISTORY Common: fatigue, infection, bruising, bleeding Leukostasis: Neuro (CN, altered MS), Resp, CVS MSK: bone pain Cardiac history, co-morbidities Prior transfusions and pregnancies: allo antibodies Drug allergies Prior herpes simplex: prophylaxis Pregnancy/menses: OCP; fertility preservation Siblings? Extramedullary: anywhere, gingiva Skin (leukemia cutis or Sweet syndrome) Performance status RISK FACTORS Risk factors: MDS Myeloproliferative disorder Prior chemotherapy IR Trisomy 21 Rare congenital syndromes (Klinefelter’s, Fanconi, dyskeratosis congenita) Smoking RR 1.4 CT scans RR 1.2-1.7 Family history Not cell phones! PHYSICAL EXAM Fever: treat as infection Eyes: hemorrhages and or exudates up to half have ocular involvement. Oropharynx: gingival involvement, dental caries, oral thrust Organomegaly and LNs: uncommon in AML - think of ALL or CML in blast crises Neuro: CN palsies, Altered MS. Skin: pallor, infiltrative lesions, petechiae and echymoses, leukemia cutis (10-15%), Sweet Syndrome LEUKEMIA CUTIS SWEET SYNDROME AKA ACUTE FEBRILE NEUTROPHILIC DERMATOSIS AML CNS INVOLVEMEMENT uncommon ( 5-7%): high circulating blast count, M5 defer LP if high blast count and asymptomatic to avoid contamination defer LP to consolidation IDENTIFYING LINEAGE: AML/APL, ALL Morphology not always helpful Flow cytometry Immunostains Cytogenetics AML DIAGNOSIS Blood and marrow (aspirate and biopsy) Auer rods: rod like filaments of aggregated primary azurophilic granules (most seen in M1 and M2) > 20% blasts in BM/peripheral or recurrent cytogenetic abnormality Special stains distinguish myeloid (MPO) from lymphoid (TdT) Flow cytometry: help to distinguish lymphoid from myeloid (CD13, 33, 34, 117); establishes maturation DO CYTOGENETICS! ROUTINE LAB TESTING CBC with differential and blood film BUN, creatinine, lytes, uric acid, glucose Liver enzymes, LDH calcium profile PT, PTT, fibrinogen, FDPs or D dimers flow cytometry if blasts in blood Beta-HCG Type and Screen Defer HSCT testing: HLA, CMV, Hep A/B/C/HIV/HTLV LABORATORY FINDINGS WBC: 20% > 100,000, 50% normal or reduced Pancytopenia Watch out for tumor lysis syndrome (hypoCA, HyperPhos, Acidosis, hyperK, increased LDH, increased Uric Acid, renal failure). ADDITIONAL INTERVENTIONS CXR ECG TTE if risk factors LP if symptomatic BM asp and biopsy with cytogenetics and flow cytometry (subclassification, prognosis, tailoring treatment): KIT, FLT3, NPM1, CEBPA Broviac placement Fertility preservation Dentistry consultation if poor oral hygiene Oncology/transplant nurse Psychosocial support AML - FAB FAB subgroups based on the predominant cell type and to define the leukemia’s cell position in the maturation sequence of that specific lineage, less common use nowadays M0-M7 M0 Minimal differentiation (3%) M1 Without maturation (15–20%) M2 Maturation (25–30%) M3 Acute promyelocytic leukemia (5–10%) M4 Acute myelomonocytic leukemia (20%) M4Eo Acute myelomonocytic leukemia with abnormal eosinophils (5–10%) M5 Acute monocytic leukemia (2–9%) M6 Erythroleukemia (3–5%) M7 Acute megakaryocytic leukemia (5%) AML WHO AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities t(8;21)- AML/ETO With abnormal bone marrow eosinophils and inv16 or t(16;16) 11q23 abnormalities AML with multilineage dysplasia AML and MDS-therapy related AML not otherwise categorized ++ atleast 20 different subtypes AML TREATMENT Goal: stabilize patient and then rapid restoration of normal BM function. Induce Remission: Induction: reduces leukemia cell population from 1012 to 109 (MRD) Prevent Relapse: Consolidation: 1-3 or more courses of chemo or BMT to eradicate residual leukemia and allow for cure Complete Remission: normal blood counts (ANC>1000, plt > 100,000, no pRBC transfusion needs) and BM cellularity with < 5% blasts without leukemic phenotype Cure?: relapse and death rates low after 3-4 years remission; 40% age < 60 Clinical trials AML TREATMENT INDUCTION 7+3 1) Cytarabine (Ara C ) -continuous infusion x 7 days -<60 yo 200 mg/m2; >60 yo 100 mg/m2 - Myelosuppresion: biphasic nadir 7-9 D, 15-24D, Rash, conjunctivitis, Mod. N/V, increased LFT’s, ulceration, neurotoxicity (cerebellar dysfunction) 2) Anthracycline -Daunorubicin 60-90 mg/m2 IV x 3 days -Dose reduce with hepatic dysfunction (bilirubin) - Myelosuppresion: nadir 10-14 D, cardiac toxicity, mucositis, red/orange urine, Mod. N/V, increased LFT’s, ?? D14 Marrow SUPPORTIVE CARE DURING INDUCTION Febrile Neutropenia: treat find source otherwise prophylaxis (Levofloxacin) RR 0.66 reduced mortality. NNT 30’ 60% identified source, 6% mortality (15% of cases fungal, 15% mixed, 5% bacteria) IPA prophylaxis posaconazole NNT 20 mortality Herpes Simplex Prophylaxis Nutrition HLA matched CMV neg, irradiated, leukodepleted transfusions (plt > 50000 APL) ?G-CSF no survival benefi TLS: Allopurinal nearly all; Rasburicase if WBC > 100,000, T-ALL but not if G6PD def. Beware transfusions with leukostasis. Psychosocial AML TREATMENT CONSOLIDATION High dose cytarabine/Ara-C (HiDAC) 3g/m2 x 6 doses For 3-4 cycles No proven role for maintenance therapy in AML compared to ALL If relapse: salvage chemotherapy, re-induction, clinical trial, ?autologous transplant HSCT/TRANSPLANT Allogenic matched related donor better than unrelated donor Unfavourable prognosis – 20% increased survival 27 vs 7 % at 5 year Intermediate risk – 6 to 10% increased survival COMPLICATIONS: LEUKOSTASIS WBC > 50,000 (AML > ALL) Neurological: visual disturbance, headache/dizziness, TIA/CVA CVS: MI Resp: dyspnea, infiltrate on chest X-ray Treatment: hydroxyurea, chemo, leukapheresis TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME ALL > AML First sign incr. LDH, low Ca Then hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, increased uric acid, renal failure, cardiac arrhythmias AML PROGNOSIS Age (> or <60); > 60 worse secondary AML blast count > 100,000 response to induction chemotherapy APL better prognosis CYTOGENETICS Favourable Intermediate Poor Karyotype t(15,17), t(8,21); inv(16)/t(16:16) Molecular modifications NPM1 (FLT3 neg), CEBPA (biallelic) Normal; includes -y, +8, +21, +22, CEBPA -5/del(5q), -7/del (7q), t(6,9), FLT3 11q23, 3 or more abnormalities Over 23 genes mutated AML PROGNOSIS 55-70% achieve CR with induction 50-70% will relapse during the first 18-24 months allogeneic transplant an option in select few with sibling (preferable) no role for maintenance chemotherapy APL Excellent prognosis once treatment started (higher mortality prior), younger ~ 30’s Remember DIC/severe thrombocytopenia/CNS bleeding t (15;17); t(11;17): PML-RAR α aberrant fusion protein blocks myeloid differentiation. Treated with: Induction: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) + anthracycline (nearly all patients CR) Consolidation: ATRA or Arsenic trioxide (ATO) Maintainence: ATRA, 6-Mercapto-purine, oral methotrexate Auto-HSCT if relapse. APL - 2 Watch out for differentiation syndrome (25-40%): fever, edema, stomatitis, Hypotension dyspnea, ARDS renal/liver failure Treated with high dose steroids (Dex 10 mg IV BID), temporary cessation ATRA/ATO Other AE: electrolyte imbalances, QT prolongation, rash, pain, increased LFT’s, hearing loss (ATO) ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA (ALL) Only ~ 1000 adult cases/year in US Similar presentation to AML Hepatosplenomegaly and LNs more common Leukocytosis less common CNS involvement (15%) and relapse more common Mediastinal mass in T cell ALL: CXR, CT chest TLS more common than AML, can be spontaneous TdT stain (ALL), MPO (AML) LP, testicular exam Philadelphia chromosome ALL B-cells (~80%): CD10, 19, 20 L1=Early Precursor B-ALL subtype represents 25-30% of adult cases L2= Pre-B ALL representing 70% of cases L3/Burkitt’s=B-ALL subtype accounts for 1-2% of adult cases T-ALL (~ 20%): CD2, 3, 5, 7, 4, 8, 38 Particularly aggressive ALL TREATMENT Borrowed from pediatric protocols Overall survival 40% PH chromosome ALL in 30%: poor prognosis treatment 4 components over 2-3 years: Induction, consolidation, CNS prophylaxis and maintenance Mainly outpatient Allo BMT for PH + ALL or relapsed disease Prognosis: Good: children, pre-B WBC < 30,000, T-ALL < 100,000, rapid CR, t(12,21), hyperdiploidy Bad: Ph chromosome changing with TKI-inhibitors, t(4,11), MLL/11q34 translocation BACK TO OUR PATIENT AML with leukemia cutis, FLT3 negative, intermediate cytogenetics Given hydroxyurea (4g/day) initially LP positive blasts Induction chemotherapy complicated by: 1) Febrile neutropenia secondary CLA-BSI with VRE bacteremia 2) Severe Mucositis: MMW, pink lady, dilaudid 3) 15% weight loss: nutrition 4) Mild increased in liver enzymes Day 28 bone marrow: CR Received consolidation Awaiting Allo-HSCT FUTURE DIRECTIONS Autologous Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells targeting CD19 Used in relapsed/refractory ALL: CR 90%, sustained response 67% of patients and response seen up to 24 months. SUMMARY Acute leukemia: emergency AML/APL vs ALL Leukostasis: symptomatic ?urgent treatment Treatment: Feb. Neut, TLS, transfusions, Anti-microbial prophylaxis Watch out for adverse effects due to chemotherapy REFERENCES DynaMed: AML, ALL, APL Pocket Oncology 2014