With Mrs. Love
advertisement

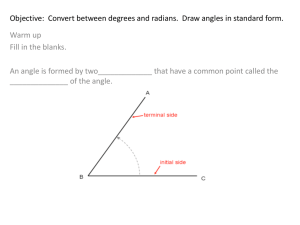
Calculus Prerequisite Knowledge 0.1: Angles and Radian Measure Learning Goals: •Review angle measure •Define radians as another angle measure. © 2008 Roy L. Gover (www.mrgover.com) Definition Terminal Side y Vertex A Initial Side x Angle A is in standard position Definition y A x If the terminal side moves counterclockwise, angle A is positive Definition y A x If the terminal side moves counterclockwise, angle A is positive Definition y A x If the terminal side moves counterclockwise, angle A is positive Definition y A x If the terminal side moves clockwise, angle A is negative Definition y A x If the terminal side moves clockwise, angle A is negative Definition y A x If the terminal side moves clockwise, angle A is negative Definition y A x If the terminal side moves clockwise, angle A is negative Definition y A If the terminal side is on x an axis, angle A is a quadrantel angle Definition y A If the terminal side is on x an axis, angle A is a quadrantel angle Definition y A If the terminal side is on x an axis, angle A is a quadrantel angle Definition y If the terminal side is on A x an axis, angle A is a quadrantel Is this an angle? angle Try This What kind of angle is this? (hint: where is the terminal side?) quadrantal angle Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. -90° b. -45° c. -270° d. -360° Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. -90° b. -45° c. -270° d. -360° Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. 0° b. 45° c. 90° d. 120° e. 180° Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. 0° b. 45° c. 90° d. 120° e. 180° Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. -90° b. -45° c. -270° d. -360° Try This What is the measure of this angle? a. -90° b. -45° c. -270° d. -360° Try This What is the measure of this quadrantal angle? 0° y x Try This If a 143° y angle is in standard position, determine the quadrant in which the terminal side lies. x 2 Try This If a 280° y angle is in standard position, determine the quadrant in which the terminal side lies. x 4 Important Idea There are two units of measure for angles: •degrees: used in geometry •radians: used in calculus In Precal, we use degrees and radians. Definition y Radian: The length of the arc above the angle divided by the radius of the circle. 1 r -1 s 1 x -1 s , in radians (rads) r Definition y Unit Circle: the circle with radius of 1 unit If r=1, =s 1 1 -1 s 1 x -1 s , in radians (rads) 1 Definition The radian measure of an angle is the distance traveled around the unit circle. Since circumference of a circle is 2 r and r=1, the distance around the unit circle is 2 Example Find the degree and radian measure of the angle in standard position formed by rotating the terminal side ½ of a circle in the positive direction. Leave your radian answer in terms of . Example Find the degree and radian measure of the angle in standard position formed by rotating the terminal side 5/6 of a circle in the negative direction. Leave your radian answer in terms of . Try This Find the degree and radian measure of the angle in standard position formed by rotating the terminal side 2/3 of a circle in the positive direction. Leave your radian answer in terms of . Solution 2 360 240 3 2 4 2 radians 3 3 Example 360° 2 rads 6.28 rads Example 45 (degrees) radians 4 .785 radians Example 90 (degrees) radians 2 1.57 radians Try This 180 3.14 rads rads Try This -180 - rads -3.14 rads Try This Do you see a pattern? 270 1 3 1 or 2 2 rads 4.71 rads Important Idea Radian measure allows the expansion of trig functions to model real-world phenomena where independent variables represent distance or time and not just an angle measure in degrees. Important Idea If a circle contains 360° or 2 radians, how many radians are in 180° Use to change rads to degrees Use to change rads • 180° degrees to rads 180° • rads Example Change 30° to radian measure in terms of . Try This Change 120° to radian measure in terms of . 2 rads 3 Try This Change 240° to radian measure in terms of . 4 rads 3 Example 3 Change radians to 4 degree measure. Example Change 2.356 radians to degree measure. (hint: radians are not always stated in terms of .) Try This 7 Change radians to 8 degree measure. 157.5° Try This Change -3.5 radians to degree measure to the nearest tenth. -200.5° Definition The quadrantal angles in radians 2 0 2 3 2 Definition The quadrantal angles in radians 2 0 2 3 2 Definition The quadrantal angles in radians 2 0 2 3 2 Definition 2 The quadrantal 0 angles in 2 radians The terminal side is on an axis. Definition Coterminal Angles: Angles that have the same terminal side. Important Idea In precal, angles can be larger than 360° or 2 radians. Example Find positive angles and negative angles that are coterminal with 30°. Important Idea To find coterminal angles, simply add or subtract either 360° or 2 radians to the given angle or any angle that is already coterminal to the given angle. Analysis 30° and 390° have the same terminal side, therefore, the angles are coterminal y 30° x y 390° x Analysis 30° and 750° have the same terminal side, therefore, the angles are coterminal y 30° x y 750° x Analysis 30° and 1110° have the same terminal side, therefore, the angles are coterminal y 30° x y 1110° x Analysis 30° and -330° have the same terminal side, therefore, the angles are coterminal y 30° x y -330° x With Mrs. Love How many angles can you find that are coterminal with a 30° angle and how do you find them? Try This Find 3 angles coterminal with 60° 420°,780° and -300° Try This Find one positive angle and two negative angle 3 coterminal with 2 radians. 7 5 and , 2 2 2 Try This Find two positive angle and one negative angle coterminal with 5 6 radians. 19 7 17 and , 6 6 6 Lesson Close In your own words and without looking at your notes, write a definition for: •Coterminal angle •Radian Practice 1.cws0-1/1-10 2. cws/11-27 (slides 1-37) (slides 38-63)