Learning and Accountability - The Carnegie Project on the
advertisement

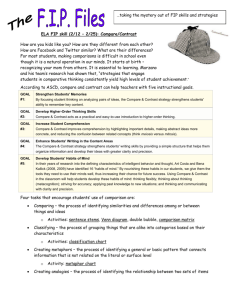
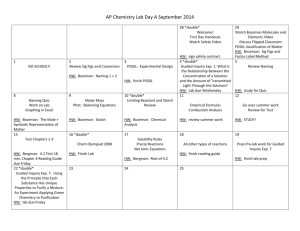
University of Central Florida EDA 7274 Learning and Accountability < Day, Time, Location> Spring Semester 2011 Dr. William Bozeman Office Office Hours Education Building, Suite 222, P.O. Box 161250, Orlando, FL 32816–1250 Monday and Thursday, 2:00 – 5:00 Email to make an appointment for other discussions. Office Phone (407) 823-1471 Email (prefer) bozeman@mail.ucf.edu Course Overview and Description The guiding purpose of this course is to provide a foundation for and understanding of three areas: (a) systems concepts, (b) technology applications, and (c) evaluation and data analysis techniques. Systems approaches provide the conceptual linkage between the purposeful but different activities of research and evaluation. Class activities relate to these topics as well as discussions of possible research leading to the doctoral dissertation. Learning Outcomes and Objectives Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills to: 1. To understand the role and importance of systems and systemic frameworks in planning, research, and evaluation. 2. To study and apply the concepts and principles of Breakthrough Thinking in planning and design. 3. To study and appreciate the applications of technology and data analysis to educational management and leadership. 4. To develop an understanding of analytics in educational decision making. 5. To develop an understanding of the importance of interpreting and communicating evaluation findings. Florida Principal Leadership Standards Instructional Leadership: High performing leaders promote a positive learning culture, provide an effective instructional program, and apply best practices to student learning, especially in the area of reading and other foundational skills. Learning, Accountability and Assessment: High performing leaders monitor the success of all students in the learning environment, align the curriculum, instruction, and assessment processes to promote effective student performance, and use a variety of benchmarks, learning expectations, and feedback measures to ensure accountability for all participants in the educational process. EDA 7274 / Spring 2011 W Bozeman Proposed National Standards: Advanced Certification for Educational Leaders Accomplished educational leaders drive, facilitate, and monitor the teaching and learning process. Accomplished educational leaders ensure equitable learning opportunities and high expectations for all. Text Creighton, T.B. (2007). Schools and Data (2nd Edition).Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press. Text (Recommended) Nadler, G. & Hibino, S. (1998). Breakthrough thinking. Rocklin, CA: Prima Publishing. Davenport, T.H. & Harris, J.G. (2007). Competing on Analytics. Boston: Harvard Business School Press. Course Requirements and Grading Strategy Each student is expected to complete all assignments and activities on schedule. Missing components will result in a grade of Incomplete. All examinations will be taken on the scheduled dates unless the professor approves prior arrangements. Students are expected to attend classes and be prepared to participate in discussions. Grades will be based on the professor's evaluation and will reflect the following weights: Exam Project Assignments Participation 25% 20% 35% 20% A+ (97-100) A (94-96) A- (90-93) B+ (87-89) B (84-86) B- (80-83) C+ (77-79) C (74-76) C- (70-73) Note: All assignments and papers are subject to review through turnitin.com Note: Students with disabilities who need reasonable modifications to complete assignments successfully, are encouraged to meet with the instructor as early in the semester as possible to identify and plan specific accommodations. Students may be asked to supply a letter from the Office of Student Disability Services. Note: According to UCF Golden Rule guidelines, academic dishonesty/cheating, which includes plagiarism, is a violation of student academic behavior standards and is subject to academic and/or disciplinary action. Within the College of Education, violations of this nature may also result in a fitness-to-teach evaluation. Students who plagiarize will receive an F in the course. The research paper must be turned in with a disk so that it can be submitted to turnitin.com. 2 EDA 7274 / Spring 2011 W Bozeman Calendar This calendar is a guide for your class preparation and planning. Please read the chapters identified prior to class so that substantial discussion and activity can take place. Changes to the calendar will develop as the semester proceeds depending upon the pace of the class and outside influences. Class Dates 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Topics Assignments Introductions; course overview and description; introduction to systems concepts (a) Study TC text (Ch 1), my paper draft, and BT handout; (b) Investigate possible student data sources Systems descriptions and systems planning Create a systems matrix example UCF Library orientation Discussion of systems matrix as group activity (continued); systems planning Systems concepts (continued) Evaluation criteria, standards, and measures; validity and reliability; Excel applications; data analysis Identify and locate an article in a professional journal that is related to school administration as well as data-driven decision making in education. Develop a 100-word abstract and 100-word critique (a) Revise your systems matrix; (b) Excel assignment (a) Revise your systems matrix; (b) Excel assignment Exam Review Prepare Research and Systems Annotated Bibliography; Study TC Mid-term Exam text (Ch 2-3) 8 Review of Descriptive Statistics; Data-driven decision making 9 10 11 Data-driven decision making (cont’d) Study TC text (Ch 6) Study TC text (Ch 7) Data-driven decision making (cont’d); Hypothesis Testing and Inferential Statistics Study TC text (Ch 4) Data-driven decision making (cont’d); Correlational Research Study TC text (Ch 5) 12 Correlational Research (cont’d); CausalComparative Research Study TC text (Ch 8 & 11) 13 Evidence-based field research TBA 14 15 Exam Review Qualitative Research Final Exam 3 EDA 7274 / Spring 2011 W Bozeman FOR YOUR INFORMATION AND USE To be added IMPORTANT DATES — xx 20xx To be added WEB LINKS OF INTEREST ASCD www.ascd.org American Evaluation Association www.eval.org American Educational Research Association www.aera.net American Psychological Association www.apastyle.org Education Resources Information Center www.eric.ed.gov Florida Educational Research Association www.feraonline.org Library-Northern Michigan University www.nmu.edu/library/apastyle.htm#P1 Mid-continent Research for Education & Learning www.mcrel.org OWL Online Writing Lab - Perdue Univ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/ University Council for Educational Administration www.ucea.org 4 EDA 7274 / Spring 2011 W Bozeman References Bock, R.W. and Wolfe, R. (1996). A Review and Analysis of the Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System, Part 1. Nashville: Comptroller of the Treasury, Office of Education Accountability. Collins, J. (2005). Good to Great and the Social Sectors. HarperCollins. Davenport, T.H. & Harris, J.G. (2007). Competing on Analytics. Boston: Harvard Business School Press. Ercikan, K., & Roth, W. M. (2009). Generalizing from educational research: Beyond qualitative and quantitative polarization. New York: Routledge. Glass, G.V. (2008). Fertilizers, pills, and magnetic strips: The fate of public education in America. Charlotte: Information Age Publishing. Hunter, C. A., Ortloff, D. H., & Winkle Wagner, R. (2009). Bridging the gap between theory and practice in educational research: Methods at the margins. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. James, E. A., Bucknam, A., & Milenkiewicz, M. T. (2008). Participatory action research for educational leadership: Using data-driven decision making to improve schools. Los Angeles: Sage. Kidd, T. T., & Song, H. (2008). Handbook of research on instructional systems and technology. Hershey, PA: Information Science Reference. Lareau, A., Ranis, S. H., & Walters, P. B. (2009). Education research on trial: Policy reform and the call for scientific rigor. New York: Routledge. Mangin, M. M., & Stoelinga, S. R. (2008). Effective teacher leadership: Using research to inform and reform. New York: Teachers College Press. McMillan, J. H. (2008). Educational research: Fundamentals for the consumer (5th ed.). Boston: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon. Marzano, R. J. (2003). What works in schools: Translating research into action. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Nadler, G. & Hibino, S. (1998). Breakthrough thinking. Rocklin, CA: Prima Publishing. Noffke, S. E., & Somekh, B. (2009). The SAGE handbook of educational action research. Los Angeles: Sage. Reeves, D. B. (2004). Accountability for learning: How teachers and school leaders can take charge. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Reeves, D. B. (2006). The learning leader: How to focus school improvement for better results. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Reeves, D. B., Ed. (2008b). Ahead of the curve: The power of assessment to transform teaching and learning. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree. Schmoker, M. (2006). Results now: How we can achieve unprecedented achievements in teaching and learning. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Schreiner, C. (2009). Handbook of research on assessment technologies, methods, and applications in higher education. Hershey, PA: Information Science Reference. Senge, P. M. (2006). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization. New York: Doubleday/Currency. Van Horn, R. W. (2008). Bridging the chasm between research and practice: A guide to major educational research. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield Education. Young, M. D. (2009). Handbook of research on the education of school leaders. New York: Routledge. 5