Lesson 8.3
advertisement

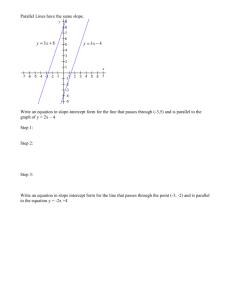
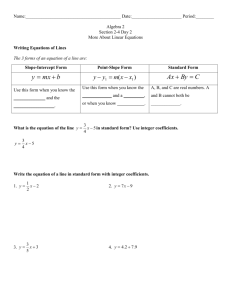
Academic Content Standards Patterns, Functions, and Algebra Standard 8th Grade 1. Relate the various representations of a relationship; i.e., relate table to graph, description and symbolic form. • 4. Extend the uses of variables to include covariants where y depends on x. • 6. Describe the relationship between the graph of a line and its equation, including being able to explain the meaning of slope as a constant rate of change and y-intercept in real-world problems. Academic Content Standards Patterns, Functions, and Algebra Standard 8th Grade • 13. Compute and interpret slope, midpoint and distance given a set of ordered pairs. • 15. Describe and compare how changes in an equation affects the related graphs; e.g., for a linear equation changing the coefficient of x affects the slope and changing the constant affects the intercepts. • 16. Use graphing calculators or computers to analyze change; e.g., interest compounded over time as a nonlinear growth pattern. Solve the following equation for “y”. Solve the following equation for “y”. 3 y x2 4 You just put the equation in slope-intercept form!!! 3 y x2 4 5.3 Equation of Lines Objectives: 1. Discover the slope intercept form of the equation of a line. This graph shows the relationship between degrees Celsius and degrees Fahrenheit. This is the graph of : 9 f c 32 5 9 y x 32 5 To convert from C to F, pick some degrees Celsius to convert: 9 f c 32 5 Let’s say you want to convert 16°C to °F. Find 16°C on the x axis 9 f c 32 5 Go straight up from 16° to the line. 9 f c 32 5 16 °C = 61°F 9 f c 32 5 From the line, go to the “f” axis. This is equal to 16°C in Fahrenheit! 16 °C = 61°F 9 f c 32 5 16°C is equal to almost 61° Fahrenheit You plug 16°C into the equation and see what you get. 9 f c 32 5 f 28.8 32 9 (16) f 32 5 1 f 60.8 You will now be asked several questions about the graph of: 9 f c 32 5 37 3°C= ___°F Plug 3°C into the equation and see what you get. 9 f c 32 5 f 5.4 32 9 (3) f 32 5 1 f 37.4 48 9°C= ___°F 107.6 42°C= _____°F 5 42°F= _____°C 38 100°F= ____°C Complete the chart and calculate the slope of the line. x y -2 -4 -1 -1 0 2 1 5 2 8 Compare your calculated slope with the equation of the line. Do you see a relationship? 3 1 x -2 3x+2 -4 -1 -1 The Slope Formula 0 2 1 5 •y2 - y1 x2 - x1 Compare your calculated slope with the equation of the line. Do you see a relationship? The slope is the 3 number in 1 front of the x -2 -1 1 0 “x”. 2 5 3x+2 -4 -1 When an equation is in slope-intercept form: Now look at the graph of each line. Look at where the graph crosses the “y” axis. What is the significance of this number in the equation? This is the yintercept (where the graph crosses the “y” axis. When an equation is in slope-intercept form: Slope-Intercept Conjecture: y=mx+b What is the equation of the line in slope-intercept form? 3 m = 4 b = -2 3 y x2 4 What is the equation of the line in slope-intercept form? 2 m = 5 b =3 2 y x3 5 What is the equation of the line in slope-intercept form? 1 m = 2 b = 4 1 y x4 2 Graph the equation…. First calculate the slope and y-int. 2 y x4 3 2 m = 3 b = -4 Plot the y-intercept. 2 y x4 3 2 m = 3 b = -4 Apply slope from y-intercept. 2 y x4 3 2 m = 3 b = -4 Draw line through two points. 2 y x4 3 2 m = 3 b = -4 Graph each equation: 7 y x 1 8 7 m = 8 b = 1 Graph each equation: y=-4x+6 m = -4 b = 6 True or False. The slope of 2 the line below is 5 . True or False. The yintercept of the line is -4. True or False. The equation of the line is: 2 y x4 5 Homework Page 275 #’s: 15-45 odds