Darwin's 4 Principles of Evolution Overproduction
advertisement

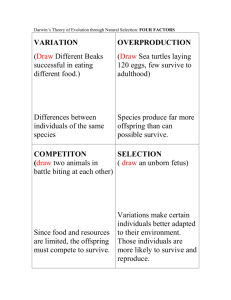
Warm-Up: Date 1/5-6 Session # Activity Page # Hidden Organism 24 Darwin’s 4 Principles 25 Can U Survive? Rock Pocket Mouse 26 1.Vocab definitions & images/examples 2.Can U Survive? •Sketch the organism that could be the result of the activity •Label the adaptations 8.L.4 Understand the evolution of organisms and landforms based on evidence, theories and processes that impact the earth over time. 8.L.4.1 Summarize the use of evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy to form the basis for biological classification systems and the theory of evolution 8.L.4.2 Explain the relationship between genetic variation and an organism’s ability to adapt to its environment TLW explain the principles of evolution by relating each principle to an element of a classroom activity, completing analysis questions after viewing a video, then illustrate the resulting evolved organism and explain each adaptation. Hidden Organism p. • You will have 1 minute to search the room for an organism that “lives” in the classroom. • Your are this organism’s predator. • The organism is shaped like this: • When you find it/them, TELL NO ONE! • Return to your seat and describe this activity and the adaptation of this species on p24of your notebook. Describe any other organisms you can think of with this type of adaptation. Geologic Time Scale records the evolution of life Unicellular organisms (1 cell) bacteria Multicellular organisms (2 or more cells) Simple plants ferns algae fish amphibians Flowering plants reptiles mammals Evolution of living organisms: process thru which species change over time, due to a change in genetic material that is passed thru generations. Two scientists with competing theories of evolution LAMARK •French •Animals acquired traits during their lifetime and passed them on to offspring •Lamark was wrong!! •Ex. Giraffes DARWIN Two scientists with competing theories of evolution LAMARK •French •Animals acquired traits during their lifetime and passed them on to offspring •Lamark was wrong!! •Ex. Giraffes DARWIN •British •Natural Selection: members of a species that are best suited to environment will survive and reproduce •4 principles to support Ex: Galapagos Isles Finch beaks Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution Activity 1 Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution Overproduction Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution Overproduction When plant or animal reproduces, it makes more offspring than actually survive and reproduce Ex Activity 2 Overproduction Variation Overproduction Variation •There are naturally occurring variations (differences) in traits due to different genetic material or due to mutations •Variations get passed on to offspring Overproduction Variation •There are naturally occurring variations (differences) in traits due to different genetic material or due to mutations •Variations get passed on to offspring Ex Activity 3 Flow Map shows order of events Overproduction Variation Adaptation Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution Overproduction Variation Adaptation • Inherited trait that gives an organism an advantage in its environment over other members of the species Ex Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution Overproduction Variation Adaptation Selection •Organisms with an adaptation will survive to reproduce and pass on the adaptation “Survival of the Fittest” Ex Relate the activity to the principles You saw Darwin’s 4 Principles of Evolution modeled during this activity. On your notes, specifically describe where in the activity you saw each of the 4 principles. Can you survive? Write an analysis of this activity which answers the following: – Why did some members of this species not survive? – What adaptations of different traits help some members survive while others did not? – Did all members without an adaptation die immediately? – What would happen to this species if the environment changed? Rock Pocket Mouse Evolution Isolation 2 populations of the same species are separated They can’t reproduce with each other Different mutations occur in each population Speciation evolution of a new species from an old one due to environmental changes. “SPECIATION IS DUE TO ISOLATION” Or “ISOLATION CAUSES SPECIATION” Kaibab squirrel (left) and Albert’s squirrel (right).