Lecture 34
advertisement

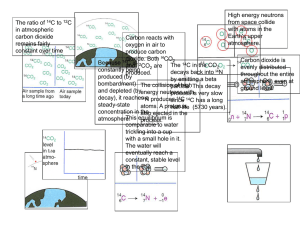
Outline: 4/16/07 Pick up leftover CAPA outside… Special seminar Wednesday pm Turn in Seminar reports – to me Today: Chapter 22 (cont’d) Nuclear Chemistry - Modes of decay - Half-life calculations Quiz #9 Please put away books & papers. Turn your paper over when done. Quiz #9 Please pass your quiz to the right… Nuclear Reactions: Types of radioactive decay: Alpha (a), Beta (b), and Gamma (g) fission, fusion, positron (b+), e- capture (EC)…. Natural vs. induced reactions: Worksheet #13 Balancing equations Worksheet #13 Start filling in the blanks: nuclear equation writing Remember: both top and bottom must balance on both sides of the equation (conservation of mass and charge!) Worksheet #13 (a) 1 + 235 = 131 + ____ 105 39 0 + 92 = 53 + ____ 105 Y 39 (b) 0 + ____ 14 = 14 7 = 6 -1 + ____ 14 N 7 (c) 60 = 0 + ____ 60 28 27 = -1 + ____ 60 Ni 28 Radioactive Decay: 1st order order decay : N = N0 e - k t Half-life: ln(N/N0) = - k t First ln(1/2) = - k t1/2 0.693 = k t1/2 t1/2 : a convenient way to refer to k e.g. 14C has k = 1.209 × 10-4 yr-1 ; what is its half-life? 0.693 = k t1/2 k = 1.209 × 10-4 yr-1 t1/2 = 0.683/k = 5730 yr e.g. : If 10.0 g of Kennewick Man bone has 34.6 dpm of 14C, and a present-day 10.0 g bone has 103.7 dpm, how old is Kennewick Man? N/N0 = e - k t or ln(N/N0) = - k t ln(34.6/103.7) = - k t t = 9080 yrs Decay calculations: • Where have you seen these before? Chapter 15 (pp. 627-630) = Kinetics PRACTICE! Worksheet #13 - Question 2 0.02% of 1000g = 0.2 g 14C 0.2 g 1mol/14g = 0.143 mol 14C 0.143 mol 14C 6.022e23 atoms/mol = 8.60e21 atoms 14C N/N0 = 7.65e20 / 8.60e21 = 0.0889 ln (0.0889) = - k t - 2.42 = - 1.209 × 10-4 yr-1 t t = 20,000 yr