notes
advertisement

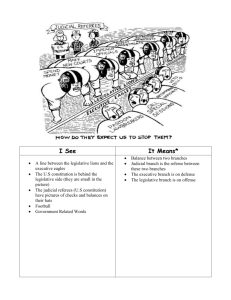
• The first government & constitution of USA • • Lasted a decade (’77-’87) STRUCTURE: • weak central gov’t – opposite of Parliament. • 1 Branch of gov’t (Legislative) • • • made up of 13 members, one from each state. Passing laws required 9 of 13 yes votes. Amending Articles required all 13 states. • Land Ordinance of ’85 – set up boundaries and developed area into townships • • • 6x6 miles = 36 square miles per town Provided for government & education NW Ordinance of ’87 – set up a formula for territories to become new states • • Needed to have a republican gov’t At least 60,000 people Weakness No power to tax Result No Money No Executive Branch No enforcement of laws 1 house Legislature 1 vote / state unequal representation No Judicial Branch disputes not settled problems in interstate relations Weakness No Regulation of commerce Result Economic quarrels NO foreign trade No power to maintain army NO DEFENSE Power in the States No Unity Voting consent or change Impossible to make laws • • Economic depression hurt businesses and individuals after the Rev. War. States issued own money, developing inflation making it worthless. • • • Farmers can’t pay any of their debt. Farmer’s lost property for lack of payment. Shays Rebellion in MA leads to change • • • Farmers, led by Daniel Shays attacked courthouses in MA Want to stop the judges from taking properties away. Rebellion stopped by militia, not national government! • • Causes the elite in other states to worry that other revolts could sprout up. The Articles didn’t give national gov’t power to stop this from happening. • More power had to be given to the national gov’t • • May ‘87 in Philadelphia, PA to address the Articles… They end up changing the gov’t Two plans lead the way • NJ plan – small state plan – wanted equal (2) representation in a unicameral legislature • VA plan – BIG STATE PLAN – wanted population of ea. state to set representation in a bicameral legislature. • • AKA The CT Plan – brought big & small state plans together to form the new government. Bicameral Legislature: • • • • 3/5 compromise: Deals with slave population and total population count. • • • US Senate – reps based on equality (every state has 2) US House of Representatives – reps based on population Slave states (south) want slaves counted in total pop = more reps Free states (north) rather taxes paid on slaves than reps count Compromise ends with 3/5 of state slave pop counting • every 5,000 slaves – 3,000 is counted to the white population. • • States were not willing to give up all of their power. US Constitution sets up a Federalist government that has shared powers between the National and State govt’s. • Each gov’t has unique powers as well as shared. NATIONAL • Declare War • Maintain armies STATE SHARED • Elections • Local gov’ts • Enforce Laws • Regulate Trade • Business within a state • Collect Taxes • Marriage laws • Admit new states • Borrow Money • Public safety • Coin money • Establish courts • Foreign policy • Provide for public welfare • • Legislative (laws), Executive (Pres), and Judicial (Court) Multiple branches of gov’t provide for a Separation of Power between the different branches. • • No one branch can become more powerful than another. Checks and Balances so that each branch could prevent the other two from greed. Executive Branch Checks Legislative: Judicial: Adjourn Congress Appoint Judges Veto Bills Legislative Branch Checks Executive: Judicial: Reject appointments Amendments Reject treaties Impeach Justices Withhold funding Impeach Override veto Judicial Branch (Supreme Court) Checks Executive: declare executive actions unconstitutional Legislative: declare laws unconstitutional