2.1 Notes
advertisement

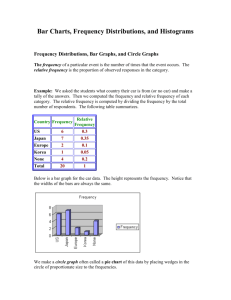
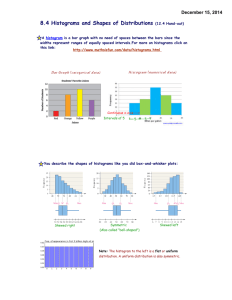
Chapter 2: Organizing Data 2.1 – Frequency Distributions, Histograms, and Related Topics 2.2 – Bar Graphs, Circle Graphs, and TimeSeries Graphs 2.3 – Stem-and-Leaf Displays Focus Problem “Say It With Pictures” • Read page 33 in text book • After this Chapter we will be able to… – Explain what a histogram is and when to use it – Differentiate common distribution shapes – Select appropriate graphs for given data sets – Order data and reveal distribution shape. 2.1 – Frequency Distributions, Histograms, and Related Topics Vocabulary • Frequency Table • Constructing a Frequency Table 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Decide how many classes you want Find class width Determine data range for each class Tally data and find frequency Find the midpoint for each class Determine class boundaries Constructing a Frequency Table 1. Decide how many classes you want – 5-15 classes 2. Find Class Width largest data value – smallest data value Desired # of classes (Round up to whole number) Constructing a Frequency Table 3. Determine data range for each class – Lower class limit: – Upper class limit: 4. Tally data and find frequency – Tally – Frequency Constructing a Frequency Table 5. Find Midpoint (class mark) of each class Lower class limit + upper class limit 2 6. Determine class boundaries (for graph) – Upper class boundary: – Lower class boundary: 7. (Extra) Find Relative Frequency (%) Class frequency Total of all frequencies Lets put it all together… Nurses on the eighth floor of Community Hospital believe they need extra staffing at night. To estimate the night workload, a random sample of 35 nights was used. For each night, the total number of room calls to the nurses station on the eights floor was recorded as follows: 68 60 69 71 83 58 90 86 71 71 92 95 70 46 74 18 84 82 75 63 101 77 102 80 86 85 73 86 62 100 90 37 88 70 87 Histograms and Relative-Frequency Histograms Procedure: 1. Make a frequency table 2. Place class boundaries on horizontal axis and frequencies/relative frequencies on vertical axis 3. Draw bars (touching) Histograms and Relative-Frequency Histograms Histogram Relative-Frequency Histogram Histograms and Relative-Frequency Histograms Distribution Shapes • Symmetrical: • Uniform/Rectangular: • Skewed Left / Skewed Right (Tails): • Bimodal: Guided Exercise #1 (if time) • With table partners, turn to page 40-41 – Cover answers – Discuss answers • Check – Whole group clarification Checkpoint Organize raw data using a frequency table Construct histograms and relative frequency histograms Recognize basic distribution shapes: Uniform Symmetric Skewed Bimodal Interpret graphs in the context of the data setting Homework • Read Pages 34-42 – Take notes on what we have not covered • Do Problems – Page 43-47 (1-10) try 11-13 (dotplots) • Not multiple choice! • Check odds in back of book • Read and preload 2.2 information – Notes/vocab