Vertebrate
advertisement

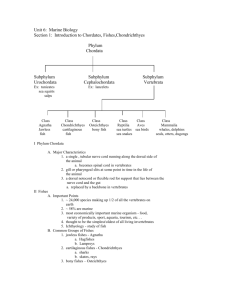
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Classes:
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes
Amphibia
Reptilia
Aves
Mammalia
Primitive organism:
Phylum: Chordata
amphioxus
Characteristics:
1. *Have a dorsal notochord, that becomes the spine.
2. An endoskeleton made of cartilage or bone.
3. Pharyngeal slits or gill pouches during development.
4. A dorsal nerve cord.
5. Post-anal tail
Subhylum: Vertebrata
Major Characteristic: have a backbone
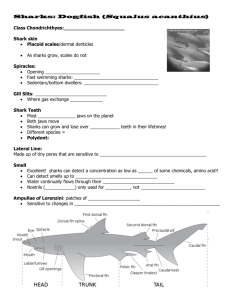
Class: Chondrichtyes
-
*Cartilaginous fish
from, “chondro-” (cartilage)
and “ichthyes” (fish)
skeleton made of cartilage.
have fins and scales.
breathe with gills.
Examples:
sharks, skates, and rays.
Class: Chondrichtyes
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
Ectothermic (cold-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of Cartilage
Circulatory System – 2 chambered heart
Reproduction – External fertilization, many eggs
*Dioecious = two distinct genders
Heterodontiformes - horn
sharks
Orectolobiformes - whale sharks
Rhincodon typus
Orectolobiformes –
nurse sharks
Ginglymostoma cirratum
Lamniformes - mackerel, mako, white sharks
Great White
Mako
Isurus oxyrinchus
Mako
Great White, Carcharodon carcharias
Carcharhiniformes requiem sharks
(blacktip)
Carcharhinus limbatus
blacktip shark
Carcharhiniformes - requiem sharks
(whitetip)
Triaenodon obesus
Carchariniformes – bull
sharks
Carcharhinus leucas
copyright FLMNH
Carchariniformes – tiger sharks
Galeocerdo cuvier
© George Burgess
Carchariniformes – basking sharks
Cetorhinus maximus
Superorder Squatinomorphi
– Squatiniformes-angel sharks
• bottom-oriented, enlarged
pelvic fins, spike-like teeth
Atlantic Angel Shark, Squatina dumeril
Spiny dogfish-Squalus acanthus
Squaliformes
dogfish sharks
Adipose spine
Pristiophoriformes - saw sharks
Myliobatiformes - sting rays
eagle & manta rays
butterfly rays
Rajiformes skates
Skate or Ray...what’s the
difference?
–
–
–
–
Skates (order Rajiformes)
pelvic fin divided into two lobes
stocky tail w/o stinging spine
enlarged, thorn-like scales ('bucklers') along the
midline of back
– males have rows of enlarged scales near the
eyes and wingtips
–
–
–
–
Rays (order Myliobatiformes):
one-lobed pelvic fin
whip-like tail, usually with stinging spine
no bucklers along back or tail
Pristiformes sawfishes
Torpediniformes - electric rays
Class: Osteichthyes
-
“BONY” fish
from, “osteo-” (bone) and
“ichthyes” (fish)
skeleton made of bone.
have fins and scales.
breathe with gills.
Examples:
bass, tuna, and catfish
bass
tuna
catfish
porcupine fish
salmon
Class: Osteichthyes
Class: Osteichthyes
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
Ectothermic (cold-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of BONE
Circulatory System – 2 - chambered heart
Reproduction – External fertilization, many eggs
*Dioecious
Class: AMPHIBIA
-
*Amphibians
means “double life”, part of life
spent on water and part on land
smooth, moist skin.
live near water
go through metamorphosis
no claws or scales.
Examples:
frogs, toads, newts, salamander
poison dart frog
bullfrog
Class: Amphibia
Cameroon toad
General Amphibians
Class: AMPHIBIA
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
Ectothermic (cold-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of BONE
Circulatory System – 3-chambered heart
Reproduction – External fertilization, eggs laid in water
*Dioecious
Class: REPTILIA
*Reptiles
- body covered w/scales or plates
- have lungs/scales & plates/claws
- 1st to use the amniotic egg.
- also use internal fertilization
Examples:
turtles, snakes, alligators, lizards
Burmese python
lizard
chameleon
cobra
Class: Reptilia
alligator
Class: REPTILIA
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
Ectothermic (cold-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of BONE
Circulatory System – 3-chambered heart
Reproduction – INTERNAL fertilization, AMNIOTIC egg
*Dioecious
Lizards
Komodo Dragon
Chameleon
Geckos
Horned Lizard
Frilled Lizard
Gila Monster
Class: AVES
-
*BIRDS
have wings and feathers.
most fly. Ex: penguin, ostrich,
emu
parents incubate eggs.
descended from dinosaurs
lightweight, hollow bones
Examples:
eagle, owl, cardinal, dove, quail
Class: AVES
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
ENDOTHERMIC (WARM-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of BONE
Circulatory System – 4-chambered heart
Reproduction – INTERNAL fertilization, AMNIOTIC egg
*Dioecious
Class: MAMMALIA
*Mammals
- have hair & mammary glands.
- give birth to live young
- have a diaphragm
Examples:
bats, whale, elephant, deer,
horse, human, monkey, rabbits
Class: MAMMALIA
CHARACTERISTICS:
Vertebrates
ENDOTHERMIC (WARM-blooded)
BILATERAL symmetry
Coelomate
Digestive System – COMPLETE
Skeletal System – made of BONE
Circulatory System – 4-chambered heart
Reproduction – INTERNAL fertilization, LIVE YOUNG
*Dioecious