Summary notes
advertisement

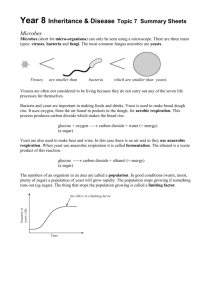
Our Living World 3 Summary Notes East Lothian Council Contents 1. What are microbes? ..............................................................................................2 a. What parts of a cell are found in microbes? ...................................................2 b. How do microbes reproduce? ..............................................................................3 2. How are diseases spread? ....................................................................................3 a. How can the spread of disease be prevented? ...............................................3 b. Vaccinations .............................................................................................................3 3. Flu...............................................................................................................................4 4. HIV ............................................................................................................................4 5. HPV ............................................................................................................................4 6. MRSA ........................................................................................................................4 7. Using bacteria to make yoghurt and cheese ....................................................4 8. What can yeast do for us? ...................................................................................4 a. Microbes and bread making .................................................................................5 b. Immobilising Yeast .................................................................................................5 9. Are Biological Washing Powders Effective? ....................................................5 10. Designing experiments ......................................................................................5 1 1. What are microbes? Microbes (sometimes called microorganisms) are all around us. They are in the air, on our skin and in the food we eat. There are five types of microbes. 1. Bacteria 2. Viruses 3. Fungi 4. Algae 5. Protozoa Microbes have many different roles to play in our lives. Some are very useful while others are harmful. Microbes are tiny living things which can only be seen with a microscope. Bacteria can cause diseases such as cholera, sore throats and food poisoning. Some bacteria are useful, for example they allow us to make yoghurt and we need them in our gut to keep us healthy. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria. They are harmful and cause diseases such as flu, chicken pox and colds. Fungi include moulds such as those which grow on old bread. Some skin diseases are caused by fungi, like athletes foot and ringworm. Yeast is a type of fungus and is used in brewing and baking. a.What parts of a cell are found in microbes? Part of cell Do fungi have Do bacteria this part? have this part? Cell membrane Cell wall Cell nucleus 2 Do viruses have this part? b. Bacteria reproduce by diving in two. Viruses reproduce in living cells. Fungi can reproduce by budding (where a parent yeast cell forms a growth on its surface, which eventually pinches off) or by producing spores (like seeds - they can be carried on the wind or rain, spreading the fungus to new places). Bacteria and fungi need temperature, food, water & time to grow. The world is not over-run with microbes because conditions are rarely perfect for them to grow in. 2. How do microbes reproduce? How are diseases spread? Through the air e.g. when someone who has a cold sneezes without covering his/her mouth. Through the skin – e.g. touching an infected person can spread viruses that cause chicken pox and measles. Through the digestive system e.g. food can be infected by dirty hands. Through the reproductive system e.g. HIV can pass from one person to another during sexual intercourse. a.How can the spread of disease be prevented? Wash your hands thoroughly after going to the toilet and before handling food. Cook food thoroughly and eat it whilst it’s still hot. Use a condom when having sexual intercourse. Cover your nose when you sneeze and your mouth when you cough. Get immunized. If you’re sick, stay at home until you’re better. b. Vaccinations Vaccinations involve dead or weakened microbes being injected into the body. These make the body produce antibodies so that the body’s defences are ready if the disease ever attacks. 3 3. Flu Flu is an infectious and common viral illness spread by coughs and sneezes. It causes a sudden high temperature, headache and general aches and pains, tiredness and a sore throat. You can also lose your appetite, feel nauseous and have a cough. It is highly infectious. There is no cure for flu, however there is a vaccination available that can help to prevent its spread. 4. HIV HIV is a virus which attacks the immune system, and weakens your ability to fight infections and disease. It's most commonly caught by having sexual intercourse without a condom. There is no cure for HIV. 5. HPV The human papilloma virus (HPV) is the name given to a family of viruses. Some types of HPV can cause warts or verrucas. Other types are associated with cervical cancer. The HPV virus is very common and is easily spread by sexual activity. All girls aged 11 to 13 are offered HPV vaccination as part of the NHS childhood vaccination programme in Scotland. The vaccine protects against cervical cancer. 6. MRSA MRSA is a type of bacterial infection that is resistant to a number of widely used antibiotics. This means it can be more difficult to treat than other bacterial infections. MRSA infections are more common in people who are in hospital or nursing homes. It enters the body through an open wound. 7. Using bacteria to make yoghurt and cheese Bacteria are used to make yoghurt and cheese. They thicken milk and cause it to sour. Different sorts of microbes make different sorts of cheese. 8. What can yeast do for us? Yeast is used in the brewing industry to make beer and wine. The name of this process is fermentation. Fermentation is carried out by microorganisms to produce energy for their growth and reproduction. Alcohol and carbon dioxide are produced if no oxygen is present. 4 a.Microbes and bread making Bakers add yeast to dough to make it rise. Yeast feeds on sugar in the dough and produces bubbles of carbon dioxide. This process is called fermentation. The bubbles makes the dough swell. During the baking of the bread, the yeast is killed and fermentation stops. b. Immobilising Yeast Yeast can be immobilised in jelly beads. This technique is used in industry because it is easier to separate the yeast from the end product and the yeast can be reused. Immobilised yeast is used to make Kefir, which is a slightly alcoholic milk drink which originated in Eastern European countries. 9. Are Biological Washing Powders Effective? Enzymes are used in biological washing powders. They break down stains so that the stain is removed. Non-biological washing powders do not have enzymes in them, but are kinder to skin. 10. Designing experiments In an experiment, the independent variable is the thing you are investigating e.g. in an experiment investigating the effect of exercise on heart rate, the independent variable is exercise. You usually only have one independent variable in an experiment, so you can be sure of the effect its having. The dependent variable is the thing you measure in an experiment e.g. in an experiment investigating the effect of exercise on heart rate, the dependent variable is heart rate. A control is a copy of the experiment where you don’t change the independent variable. For example, in an experiment investigating the effect of exercise on heart rate, a control could be doing no exercise. A control makes sure that it’s the independent variable that causing the effect on the dependent variable. 5