Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
advertisement

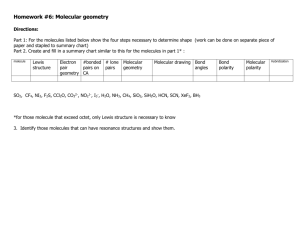
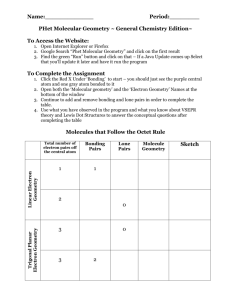
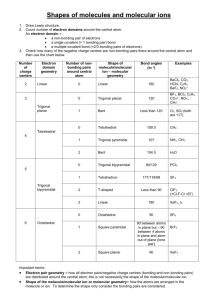
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories What determines molecular shape? Bond angles: e.g. CCl4 angle formed between two adjacent bonds on the same atom bond angle: ? Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories What determines molecular shapes? Lewis Structures => tell us how atoms are physically connected No information regarding the actual 3-D structure of molecules Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Repulsion of valence electrons => largest possible separation of atoms Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Model Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Different ways of depicting 3-D structure bond behind of the paper plane "Ball and Stick" "Spacefilling" bonds in plane of paper bond in front of the paper plane Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures show number of electron domains nonbonding pair Types of Electron Domains: ● nonbonding (or "lone") electrons ● single OR double OR triple bonding electrons => Bonding AND non-bonding electron pairs take up space bonding pair Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Molecular shape depends on electron domain geometry Lewis Structures tell us … ● ● where bonds (bonding electron pairs) are the location of nonbonding electrons } around the central atom Bonding AND non-bonding electron pairs take up space Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Possible Electron Domain Geometries: 180o 109.5o 120o Linear Trigonal Planar 90o 120o Tetrahedral 90o 90o Trigonal Bipyramidal Octahedral Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry 4 electron domains around central atom => electron domain geometry: Tetrahedral nonbonding pair bonding pair 3 non-bonding + 1 bonding electron domain Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry 4 electron domains around central atom => electron domain geometry: Tetrahedral F S F Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry 3 electron domains around central atom => electron domain geometry: Trigonal planar F F B F Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry 2 electron domains around central atom => electron domain geometry: Linear O C O Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry 3 electron domains around central atom => electron domain geometry: Trigonal planar O N O Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Lewis structures → electron domain geometry → molecular geometry Molecular Geometry depends on how many of the electron domains are actually bonds 4 electron domains: => electron domain geometry Tetrahedral 3 bonds, 1 nonbonding pair: => molecular geometry Trigonal pyramidal Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Bond angles can be distorted: 109.5 ● o 107 o 104.5 o nonbonding electron pairs occupy more volume than bonding pairs Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Bond angles can be distorted 125.3 111.4 o 125.3 ● o o multiple bonds occupy a larger volume than single bonds Volume Volume lone pairs => triple bonds => double bonds => single bonds Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Elements from the 3rd period onward.. have d -orbitals ● can have an expanded valence shell ● may have more than 4 electron domains surrounding them ● e.g. phosphorous: P: [Ne] 3s2 3p3 3s 3p 3d "expanded" valence shell Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Equatorial bond Axial bond Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains F TeF6 F F Te F F F electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains H3O + + electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains NO 2 O N O electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains SO3 electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains SCl2 Cl S Cl electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories # electron domains I SbI5 I I Sb I I electron domain geometry molecular geometry Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories The VESPR model can be extended to larger molecules e.g. glycine : predicted bond angles: ? ? ? Electron-domain geometry: ?