The History of Measurement
advertisement

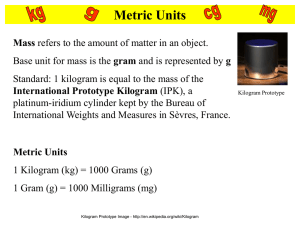
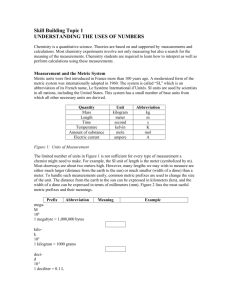
An accurate and consistent system of measurement is the foundation of a healthy economy. Without a consistent, honest system of measurement, World trade would be thrown into chaos. Throughout history, buyers and sellers have tried to defraud each other by inaccurately representing the quantity of the product exchanged. From ancient times to the present there has been a need for measuring things accurately. 1967 Surveyor 3 landed in an ancient crater known as the Sea of Tranquility and sent back data indicating it would be a suitable landing site for a manned mission. July 16, 1969 Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin became the first humans to set foot on the surface of the Moon. They traveled over 400,000 kilometers through space and landed within walking distance of the Voyager 3 craft with only 10 seconds of fuel remaining. Imagine what would have happened if NASA scientists had inaccurately measured the thrust of the Saturn V rockets, the mass of the payload, the distance to the Moon, the location of the Voyager 3 craft, the gravitational field of the Moon, the rate of fuel consumption, the speed of the Apollo 11 craft, the orbit of the Moon around the earth, the astronauts’ rate of oxygen consumption or the radio frequency of the communication gear!! Built pyramids by measuring the stones they cut using body dimensions Every worker could relate. Small distances = digits the width of a finger Longer distances = cubit the length from the tip of the elbow to the tip of the middle finger 1 cubit = 28 digits Romans built roads in paces 1 pace = 2 steps 1000 paces = 1 mile (mil is Latin for 1000) Danes seafaring people wanting to know the depth of water shipping channels Fathom = distance from the tip of the middle finger on one hand to the tip of the middle finger on the other Distances features were defined by the King’s body Yard = circumference of his waist Inch = distance between the knuckles of his thumb Foot = length of his foot Acre: The amount of land your ox could plow from sunrise to sunset. Hand: King Henry VIII said that it is equal to 4 inches. What is it used to measure today? The height of horses!!! Because every person’s body is different, using body parts as reference would cause every measurement to be inaccurate. As various cultures emigrated to England, they brought with them various measurement systems. Today, the English or Customary system reflects the variety of different measurement systems from which they originated. There are, for example many units in which distance can be measured in the Customary system, but bear no logical relationship to each other. 1 statue mile = 0.8688 nautical miles = 1760 yards = 320 rods = 8 furlongs = 5280 feet = 63,360 inches = 880 fathoms = 15,840 hands Unfortunately, most people have no idea what nautical miles, fathoms, hands, or furlongs are because they use only the more common measures of miles, yards, and inches. What is a better price for gasoline? Canada: $2.98/liter U.S.: $3.59/gal Therefore, we need a system that everyone uses!!!!!!!!!!! 1670 measurement system based on the decimal system proposed. 1791 metric system developed (metric is based on the French word for measure.) Prefixes were agreed upon Multipliers >10 = Greek Multipliers <10 = Latin 1960 an international conference was called to standardize the metric system. Scientists developed “Le Système Internationale d’Unités” more commonly known as the SI System. It is the modern version of the metric system Base 10 Simple Used by scientists worldwide Mandatory system of measurement in every country of the world except the U.S., Liberia, and Burma BASE UNIT QUANTITY SYMBOL meter length m *kilogram mass kg second time s Kelvin thermodynamic temperature K mole amount of substance mol ampere electric current A 1 meter = 0.001 kilometers = 1000 millimeters = 1,000,000 micrometers = 1,000,000,000 nanometers The meter was originally intended to be 1/10,000,000 of the earth’s meridian that passes through Paris. It is now defined as the distance light travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second. The kilogram is the only SI base unit to incorporate a prefix. The kilogram is the only unit still based on a single lump of stuff. All the other definitions can be reproduced with a high degree of accuracy in any laboratory with the proper equipment. 16 prefixes (NEED TO MEMORIZE 10) PREFIX Symbol Examples using prefixes giga- G Gg, Gm, Gs 1000000000 g = 1 Gg 109 mega- M Mg, Mm, Ms 1000000 g = 1 Mg 106 kilo- k kg, km, ks 1000 g = 1 kg 103 deka- da dag, dam, das 10 g = 1 dag 101 BASE UNIT BASE UNIT BASE UNIT BASE UNIT 100 deci- d dm, dg 10 dg = 1g 10-1 centi- c cm, cg 100 cg = 1g 10-2 milli- m mm, mg, ms 1000 mg = 1g 10-3 micro- g, m, s 1000000 g = 1g 10-6 nano- n ng, nm, ns 1000000000 ng = 1g 10-9 pico- p pg, pm, ps 1000000000000 pg = 1 g 10-12 Meaning Exponential Notation millimeter, centimeter microsecond, second kilogram, kilogram centigram deciliter milliliter deciliter, picometer, nanometer megaliter dekaliter megaliter, Give the name of each of the following quantities. millimeter ________________________ 0.001 m microsecond 0.000001 s ________________________ 0.01 g centigram ________________________ 1000 m kilometer _______________________ picoliter 0.000000000001 L _________________ megamole 1000000 mole______________________ 10-2 pedes 106 phones 101 cards 10-12 boos 10-6 phones