The French Revolution
advertisement

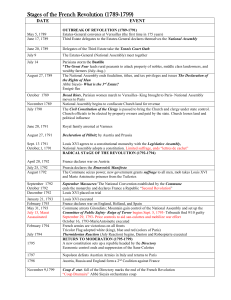
The French Revolution • Review – Louis XIV – The “Sun King” – The Enlightenment • How the French Government Worked – The Estates General • First Estate – Catholic Clergy – Accounted for 1% of population • Second Estate – Nobles – Accounted for 1% of population. • Third Estate (98% of population) – Bourgeoisie – Urban Workers (Sans-culottes) – Peasants King Louis XVI (1774-1793) and Marie Antoinette Problems faced by the royal family • King Louis XVI was good natured and generous but very indecisive • Marie Antoinette was 14 when she married Louis XVI – Charming & lighthearted, she was very unpopular because of her expensive tastes • Government was in debt, Louis had borrowed heavily to help finance the American colonists in their war against Britain • Nobles refused to pay taxes unless the king called a meeting of the Estates-General which had not met for 200 years • May 1st, 1789 – Louis XVI calls a meeting of the Estates General • Why? • Does it work? The Third Estate demands a new voting system but the First and Second Estate won’t agree. One vote for each estate Abby Sieyes, a leading clergyman, suggests that the Third Estate change its name to the National Assembly which will pass new laws and reforms in the name of the French people June 17, 1789 • June 17th, 1789 – Third Estate changes name to National Assembly • Why? • What do they do? – King Louis XVI’s reaction? Locked out of their meeting hall, they meet at an indoor tennis court and vow to give France a constitution The Tennis Court Oath June 20, 1789 • Louis XVI makes peace with the Third Estate by yielding to their demands • He orders the other Estates to join the Third Estate in a National Assembly • Concerned that he can not trust his troops he called in his Swiss troops for support • Parisians riot over bread prices • Parisians grow alarmed over the presence of the Swiss troops thinking the troops are there to harm them • Parisians take matters into their own hands • July 14th, 1789 – BASTILLE DAY in France – “The Storming of the Bastille” • Why? Parisians raided the Invalides (a military hospital) and obtained 30,000 muskets on the morning of July 14, 1789 The Bastille Storming of the Bastille Summer 1789 – Rumors of plots against peasants cause them to attack manor houses and destroy feudal records during the Great Fear Heads on pikes during the Great Fear Triumph of the Parisian Army and the People – guardsmen display the heads of troops who confronted the marchers • August 4th, 1789 – National Assembly adopts a new slogan. • “Liberty, Equality, Fraternity” Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen is adopted by the National Assembly Aug. 27, 1789 Parisian Women rioting over bread prices march to Versailles demanding the royal family move to Paris October 1789 The mob broke into the palace and ransacked the queen’s apartments Arrival of the royal family in Paris March 1791 •The New Constitution is finished. •The King reluctantly approved the Constitution and the Declaration of the Rights of Man. Sans-culottes dance around the liberty tree June 1791 - The royal family attempts to flee to Austria The return from Varennes (where they were captured) Louis’ reputation is irreparably damaged National Assembly gives power to the Legislative Assembly - September 1791 • 1791 - Legislative Assembly becomes divided. – Conservatives – Radicals – Moderates • 1792 War with Austria – Results of war? Radical Revolution Begins (Defense of National Security) 1792 • April 20 – Declaration of War on Austria • July 25 – Brunswick Manifesto - Prussian commander threatens to destroy Paris if revolutionaries harm the royal family King wears the revolutionary cap in an attempt to calm the Revolutionaries Radical mobs continue to threaten the royal family Attack on the Tulileries Palace August 10, 1792 King is arrested for encouraging foreign troops Marie Antoinette protects her husband and children as Louis is being arrested Royal family is imprisoned, August 10, 1792 Legislative Assembly September 21, 1792 • Set aside the Constitution of 1791 ending the limited Constitutional Monarchy • Declared the King deposed. • Elections are called for a National Convention to write a new constitution. Meeting of the National Convention National Convention Radical Jacobins George Danton M. Robespierre Moderate No definite views came to favor The Jacobins Conservative August 1792 - Danton and Marat set the revolution on a violent path with the help of the Paris mob Jacobin Club • The Jacobin club is a RADICAL political club • It’s members gave violent speeches • They demanded the King be removed and a republic set up. George Danton • Leader of the Paris Commune – devoted to the rights of the poor Jean Paul Marat • Radical leader of the Jacobin Club • Edited a radical newspaper • His fiery editorials called for “five or six hundred heads to be cut off to rid France of the enemies of the revolution Louis is tried and found guilty of treason The national razor Execution of Louis XVI January 21, 1793 1793-1794 Robespierre’s Reign of Terror Maximilien Robespierre The most powerful man on the Committee of Public Safety He was a merciless fanatic He was the Terror Get rid of all traces of France’s monarchy and nobility Committee of Public Safety Formed during the Summer of 1793 • Established by the Jacobins • Sought out enemies from within France – Decided who should be judged as an enemy of the Republic • Oversaw France’s defense – Well trained citizen army – All citizens were expected to help the war effort by serving in hospitals, collecting clothing, etc – Unified the nation Marie Antoinette’s Trial The Revolution devours it’s own children • Fellow revolutionaries such as Danton who challenged Robespierre’s leadership were executed in 1794 • Their crime – being less radical then Robespierre During the terror at least 3,000 people were executed in Paris. Historians believe as many as 40,000 were killed all together. Robespierre is arrested No one on the Committee is safe until Robespierre is removed from power Robespierre lays on a table in the office of the Committee of Public Safety Death of Robespierre – the Terror Ends July 28, 1794 The Directory - 1795 • Moderate leaders of the National Convention drafted a new constitution • Power was placed firmly in the hands of the upper bourgeoisie • It called for a two house legislature and an executive body of five men known as directors • They named Napoleon Bonaparte, a young general as commander of France’s army November 9th, 1799 - Napoleon stages a coup d'état and the Directory comes to an end