Building Acadmic Vocabulary
advertisement
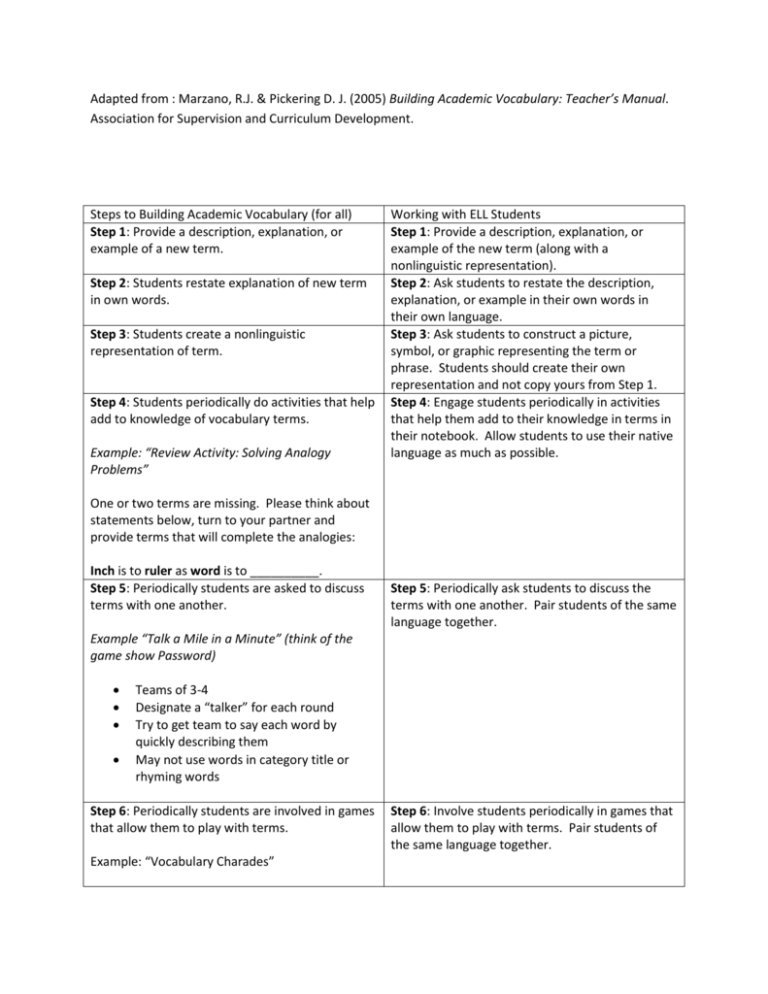
Adapted from : Marzano, R.J. & Pickering D. J. (2005) Building Academic Vocabulary: Teacher’s Manual. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Steps to Building Academic Vocabulary (for all) Step 1: Provide a description, explanation, or example of a new term. Step 2: Students restate explanation of new term in own words. Step 3: Students create a nonlinguistic representation of term. Step 4: Students periodically do activities that help add to knowledge of vocabulary terms. Example: “Review Activity: Solving Analogy Problems” Working with ELL Students Step 1: Provide a description, explanation, or example of the new term (along with a nonlinguistic representation). Step 2: Ask students to restate the description, explanation, or example in their own words in their own language. Step 3: Ask students to construct a picture, symbol, or graphic representing the term or phrase. Students should create their own representation and not copy yours from Step 1. Step 4: Engage students periodically in activities that help them add to their knowledge in terms in their notebook. Allow students to use their native language as much as possible. One or two terms are missing. Please think about statements below, turn to your partner and provide terms that will complete the analogies: Inch is to ruler as word is to __________. Step 5: Periodically students are asked to discuss terms with one another. Step 5: Periodically ask students to discuss the terms with one another. Pair students of the same language together. Example “Talk a Mile in a Minute” (think of the game show Password) Teams of 3-4 Designate a “talker” for each round Try to get team to say each word by quickly describing them May not use words in category title or rhyming words Step 6: Periodically students are involved in games that allow them to play with terms. Example: “Vocabulary Charades” Step 6: Involve students periodically in games that allow them to play with terms. Pair students of the same language together. Please stand. Using your arms, legs, and bodies, show the meaning of each term. Feldman and Kinsella (2005) suggest teachers must prioritize which unfamiliar words to teach and choose vocabulary that falls under the following categories: “big idea” words that get at the central concepts addressed in the text or lesson General academic words that are commonly used and applied across the content areas and grade levels Words that are specific to the subject area and are frequently taught to students at a particular age and at a particular proficiency level Words with multiple meanings Related words that might help students engage in academic discourse about the topic and ideas and/or themes associated with it. In order for students to benefit from their word knowledge, it is not enough for teachers to simply introduce new vocabulary and share definitions. Research shows there are several components of an effective vocabulary program: Regular opportunities to develop oral language (Nagy, 2005) A culture of promoting word consciousness (Nagy and Scott, 2000) Dynamic, explicit instruction of key words (Beck, McKeown, and Kucan, 2002) Guidance in independent word-learning strategies (Graves, 2000) Daily structured contexts for academic word use in speaking, writing, and assessment (Beck, McKeown, and Kucan, 2002) Students’ fluent reading of varied text (Cunningham and Stanovich, 1998) US History Academic Vocabulary English Abolition Allies Political (social, economic, cultural) conflict US involvement Expansionism Militarism Ratification Cultural diffusion Nativism Assimilation Political party Domestic (foreign) policy Spanish • abolición • Aliados • Políticos (social, económica, cultural) los conflictos • EE.UU. la participación • El expansionismo • militarismo • Ratificación • Difusión Cultural • nativismo • Asimilación • El partido político • Interno (extranjeros) la política Administration Legislature Judicial Economic development (programs, policies, systems) Gender roles Expansion Exploration Conquest Imperialism colonialism National identity Patriotism Americanism Treaties Agreements Tariffs Labor union Diplomacy International relations Conflict/strife Migration Progressivism Discrimination Equal rights Civil rights Civil liberties Reconstruction Reform Industrialization Civilization Democracy Communism Capitalism Socialism Ideology Programs (policies) Stalemate Disarmament Isolationism Laissez-faire Quota Consumer Assembly line Age (era, period, circa) Manifest destiny • Administración • Legislatura • Judicial • El desarrollo económico (programas, políticas, sistemas) • Los roles de género • Expansión • Exploración • Conquista • El imperialismo • colonialismo • La identidad nacional • Patriotismo • El americanismo • Tratados • Acuerdos • Tarifas • Trabajo de la Unión • Diplomacia • Relaciones internacionales • Conflicto / conflictos • Migración • El progresismo • Discriminación • La igualdad de derechos • Derechos civiles • Libertades Civiles • Reconstrucción • Reforma • La industrialización • civilización • Democracia • comunismo • El capitalismo • socialismo • ideología • Programas (políticas) • Estancamiento • Desarme • El aislacionismo • El laissez-faire • cuota • Consumidor • Línea de montaje • Edad (época, período, circa) • Destino Manifiesto • Sufragio • Prohibición • Urbano • Rural • Sociedades • Cambio demográfico (evolución de la población) • La esclavitud (esclavitud, bajo contrato) • aparcero • compromiso • Instituciones • Movimiento (s) • Constitución • Reforma • Mecanizado (-ción) • La unidad nacional • La urbanización • La corrupción política • Asuntos de Interior (nacionales, mundiales, nacionales, internacionales) • auge económico (o nada) • Bienestar Suffrage Prohibition Urban Rural Societies Demographic shift (population trend) Slavery (enslaved, indentured) Sharecropper Compromise Institutions Movement(s) Constitution Reform Mechanized (-ization) National unity Urbanization Political corruption Affairs (national, world, domestic, international) Economic boom (or bust) Welfare Abolition Allies Political (social, economic, cultural) conflict US involvement Expansionism Militarism Ratification Cultural diffusion Nativism Assimilation Political party Domestic (foreign) policy Administration Legislature Judicial Economic development (programs, policies, systems) Gender roles Expansion Exploration Conquest Imperialism colonialism National identity Patriotism Americanism Treaties Agreements Tariffs Labor union Diplomacy International relations Conflict/strife Migration Progressivism Discrimination Equal rights Civil rights Civil liberties Reconstruction Reform Industrialization Civilization Democracy Communism Capitalism Socialism Ideology Programs (policies) Stalemate Disarmament Isolationism Laissez-faire Quota Consumer Assembly line Age (era, period, circa) Manifest destiny Suffrage Prohibition Urban Rural Societies Demographic shift (population trend) Slavery (enslaved, indentured) Sharecropper Compromise Institutions Movement(s) Constitution Reform Mechanized (-ization) National unity Urbanization Political corruption Affairs (national, world, domestic, international) Economic boom (or bust) Welfare Words in Questions “foundational” – Understands why the Bill of Rights is considered a foundational document in American history. “Took root” and “reshaped” – Understands how the values and institutions of European economic life took root in the colonies and how slavery reshaped European and African life in the Americas. “involved in shaping” – Understands the causes of the American Revolution, the ideas and interests involved in shaping the revolutionary movement, and reasons for the American victory. “impact” – Understands the impact of the American Revolution on politics, economy, and society. “rise” and “reflected” – Understands the rise of the American labor movement and how political issues reflected social and economic changes. “at home and abroad” – Understands the causes and course of World War II, the character of the war at home and abroad, and its reshaping of the US role in world affairs. “struggle” – Understands the struggle for racial and gender equality and for the extension of civil liberties. “viewpoints and perspectives” – Understands the historical viewpoints and perspectives for arguments for and against the New Deal.