Net Force
advertisement

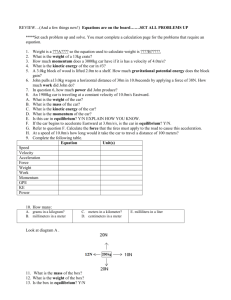
Daily Agenda for November 13th and 14th DO NOW: • With your partner, review Net Force Homework. Discuss your answers and how you arrived at your solutions. Homework due (Place in the Inbox please!) • Video Analysis (assignment from last week) Tonight’s Homework: • Read and Study Chapter 4 • Complete, check, & correct #1-7 on your POGIL (you’ll get this later in class today) Mechanical Equilibrium ( ME) Is when… The object is not changing its state of motion… so the object is not accelerating… and the net force on an object is zero. And there are 2 types of it… Static Equilibrium Dynamic Equilibrium If it is at rest. What does this mean? o Zero velocity o Zero acceleration If it is moving in a STRAIGHT LINE at a CONSTANT SPEED. What does this mean? o Constant velocity o Zero acceleration REMEMBER What is “N”? ◦ A “Newton” ◦ Named after Sir Isaac Newton ◦ It is a UNIT of force that we will learn more about NEXT class… What can you conclude MUST BE TRUE about Box 3? It’s in…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. S.E. D.E. M.E, but not enough info to say if it’s S.E. or D.E. None of the above - not in equilibrium at all! Not sure Mechanical Equilibrium ( ME) Is when… The object is not changing its state of motion… so the object is not accelerating… and the net force on an object is zero. And there are 2 types of it… Static Equilibrium Dynamic Equilibrium If it is at rest. What does this mean? o Zero velocity o Zero acceleration If it is moving in a STRAIGHT LINE at a CONSTANT SPEED. What does this mean? o Constant velocity o Zero acceleration 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. 1 person pushing with 5N + 1 person pushing with 10 N is equal to 1 person pushing with 15 N 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. 1 person pushing with 5N + 1 person pulling with 10 N is equal to 1 person pulling with 10 N 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. 2.1 Force Net Force The net force depends on the magnitudes and directions of the applied forces. What can you conclude MUST BE TRUE about this box? It’s in…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. S.E. D.E. M.E, but not enough info to say if it’s S.E. or D.E. None of the above - not in equilibrium at all! Not sure What can you conclude MUST BE TRUE about this box? It’s in…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. S.E. D.E. M.E, but not enough info to say if it’s S.E. or D.E. None of the above - not in equilibrium at all! Not sure Mechanical Equilibrium ( ME) Is when… The object is not changing its state of motion… so the object is not accelerating… and the net force on an object is zero. And there are 2 types of it… Static Equilibrium Dynamic Equilibrium If it is at rest. What does this mean? o Zero velocity o Zero acceleration If it is moving in a STRAIGHT LINE at a CONSTANT SPEED. What does this mean? o Constant velocity o Zero acceleration Take out Exit Slip Newton’s First Law! • For the next 3-5 minutes, discuss your responses with your partner/surrounding group. Make corrections! CHAPTER 4: Newton’s first law of Motion…inertia **DISCLAIMER** The information you are about to see does not represent the views, beliefs, or scientific facts held to be true by your teachers and the scientific community. Please remember that the views expressed are those of really old, REALLY dead scientists who made amazing contributions but weren’t always correct. WHO? Aristotle(Aριστοτέλης) WHERE? Greece WHEN? 4thCentury B.C. WHAT? Natural motion vs. violent motion; objects belong at rest unless experiencing a push or pull, or returning to rest Questions… a through d Any questions about the HW (#1-8)? WHO? Copernicus WHERE? Poland WHEN? 1473-1543 WHAT? Earth and other planets move around the sun; his ideas were so controversial that people persecuted him (De Revolutionibus) Questions… e Any questions about the HW (#9-13)? WHO? Galileo Galilei WHERE? Italy WHEN? Late Renaissance (1564-1642) WHAT? Need a force to KEEP an object moving ONLY if there is friction; objects resist change to states of motion (inertia); concerned with HOW not WHY things move Close-up view of Galileo’s Inclined Plane Bells Galileo’s Original Telescope Questions… Any questions about the HW (#14-16)? WHO? Sir Isaac Newton WHERE? England WHEN? December 25, 1642 - March 20, 1727 WHAT? 3 LAWS OF MOTION! AND Law of Universal Gravitation Newton’s Cradle (1600’s) Questions… f Any questions about Newton? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VupFD DrX0Rw#t=226 TASKS: CHECK and CORRECT your tests! You WILL see these questions again. If you don’t understand WHY an answer is what it is…ASK! Answers mean NOTHING if you don’t know how to get to them! TASKS: HW - #1-7 on POGIL (check/correct online) EXIT SLIPS: In IN BOX TESTS: Give to Mrs. Correia on way out the door Early Astronomers: Give to Mr. O’Connor on the way out the door Is this a mass, weight, or volume? Mass Weight Volume T Chart 2000 lb race car 2kg Discus 500ml Beaker What’s the BIG idea? What is the difference between Mass, Weight, and Volume? If I stood on a regular bathroom scale in outer space, what would it read? Does location affect my weight? POGIL- Moving Objects Work in groups of 4-5 You may work at a lab bench, but make sure you are able to see the projector Work efficiently on these problems! Whatever is not finished becomes homework! At each check in with a teacher. DO NOT GO AHEAD UNTIL YOU HAVE DONE SO. What do we know?? (Look at Page 3) What’s the BIG idea? What is the difference between Mass, Weight, and Volume? Mass: Quantity of how much matter is in an object. Units: g, kg, mg, etc. Weight: Measurement of force of gravity acting on an object. Units: pounds (lbs) Newtons (N) Volume: How much space an object takes up. Units: cubic cm, Liters (L), cubic meters What’s the BIG idea? If I stood on a regular bathroom scale in outer space (aka weightless environment), what would the scale read? What’s the BIG idea? Does location affect my weight? EXIT SLIP On a loose-leaf/scrap piece of paper, answer the following questions and place it in the inbox on your way out 1) 2) 3) TONIGHT’S HOMEWORK From the front of the classroom, please pick up Weight v. Mass Homework. There are dimensional analysis problems, you can do them! Look at the conversion sheet given on the first page.