USMLE Gross anatomy
advertisement

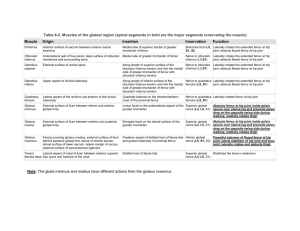
Upper limb Lower limb Lesions of the Brachial Plexus Fractures Erb-Duchenne’s Palsy Injury to C5-6 at Erb’s point Muscles paralysed – Deltoid, biceps, brachialis, barachioradialis Posture – waiter’s tip deformity Mechanism of injury : fall on shoulder or excessive pulling of head of new born during delivery 5 6 Injury to C8-T1 Muscles paralyzed – small muscles of hand Deformity Claw hand Mechanism : Sudden superior pull on upper 7 Symptoms: Clawed hand due to loss of innervation of Intrinsic muscle of the hand The characteristic clinical sign of radial nerve injury is wrist-drop. A midhumeral fracture may injure the radial nerve in the radial groove in the humeral shaft. Fracture is not likely to paralyze the triceps because of the high origin of the nerves to two of its three heads. SATURDAY NIGHT PALSY Radial Nerve Injury in Axilla: Mechanism: 1.Crutches pressing in axilla 2.Saturday night palsy! Main Effect: WRIST DROP Carpal Tunnel syndrome Common in computer professionals. Due to constant dorsiflexion of wrist while typing the keyboard 16 18 Clavicle Humerus Radius Scaphoid Junction of Medial 2/3rd and Lateral 1/3rd 21 Fracture of Surgical Neck of Humerus Damage to Axillary nerve and Post. Circumflex humoral Artery Fracture of Fracture of Mid Shaft Medial Humerus Epicondyle Damage to Damage to Radial Nerve Ulnar Nerve and Deep artery of Arm Fracture of Supracondylar part: Damage to median nerve and Brachial artery 22 Fall on Out stretched Hand Overall : Dorsal Displacement of Wrist and Hand Specifically: Dorsal and Proximal Displacement of Distal segment of fractured radius This is more common in older person 23 24 Nerve lesions in lower limb Injuries of hip, knee and ankle joint Injury Injury Injury Injury Injury Injury Injury Injury Injury to femoral nerve to obturator nerve to superior gluteal nerve to inferior gluteal nerve to sciatic nerve to tibial nerve to common fibular nerve to deep fibular nerve to superficial fibular nerve Weakness of hip flexion Iliopsoas, rectus femoris, and sartorius Knee extension Quadriceps femoris Loss of sensation over anterior thigh and medial leg and foot Loss of thigh abduction & medial rotation Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae Positive sign Trendelenburg Weakened hip extension Gluteus maximus Most noticeable when climbing stairs or standing from a seated position Footdrop and loss of eversion May cause sensory loss over lateral leg and dorsum of foot Causes Direct trauma as nerve passes superficially around neck of fibula Hip joint Knee joint Ankle joint Posterior dislocation Posterior tearing of joint capsule Dislocated femoral head lies on posterior surface of ischium Occurs in head-on collision Damage to Ischiofemoral ligament Complications Sciatic nerve may damage. Unhappy triad Anterior drawer sign Posterior drawer sign Anterior drawer sign: This injury causes the free tibia to slide anteriorly under the fixed femur. PCL ruptures allow the free tibia to slide posteriorly under the fixed femur. The lateral ligament is injured because it is much weaker than the medial ligament. The anterior talofibular ligament part of the lateral ligament is most vulnerable and most commonly torn during ankle sprains. During a football game, a player sustains a powerful blow to the lateral side of his weight-bearing leg. He experiences excruciating knee pain and is unable to walk. The three structures most likely to be injured are the Anterior cruciate and lateral collateral ligaments and the lateral meniscus Anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligaments and the medial meniscus Posterior cruciate and lateral collateral ligaments and the lateral meniscus Posterior cruciate and medial collateral ligaments and the lateral meniscus Posterior cruciate and medial collateral ligaments and medial meniscus