Integrated planning
advertisement

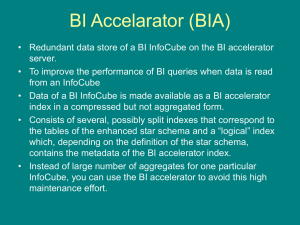
Integrated planning Understand integrated planning process Describe SAP integrated planning technology or tool (SAP-IP) Definition A formulaic process To define quantitative and actionable goals and objectives Using data and functions based on enterprise and interoperable standards Analogy From silo transactional systems to mySAP ERP From silo planning systems (e.g., all the Excel programs in various departments) to SAP-IP Pros and Cons of Spreadsheets Pros Small businesses Extremely individual requirements Short-term need Cons Process control Access protection Performance Complexity Consolidation Seasonal trend model Growing company Organizational changes SAP-IP architecture and tool Architectural components (Fig 9-4) Aggregation levels Plan data cache Planning data services Planning sequences Planning functions Which are defined in a planning model using Planning Modeler Role of Planning Modeler SAP NetWeaver Portal Enterprise Search UI s Knowledge Management Worklists Information Broadcasting can be embedded Composite Services & BAPIS Visual Composer Embedded Enterpris e Report Planning Layout BI App Ad Hoc Business Explorer Suite (BEx) Web Analyzer BIBIKit Web Application Designer Report Designer Data Sources Query Designer Planning Modeler Analytic Engine Operational Data Store Data Marts Data Warehouse PSA SAP Operational Data Non-SAP Operational Data 3rd-Party BI Data Data Flow Control / Process Chains VirtualProvider Monitoring / Administration BI Layer MS Excel Analyzer Web Services Open Hub Services InfoObjects / Master Data Meta Data Repository BI Consumer Services BI Consumer Services Collaboratio n SAP NetWeaver BI Data ODBO/XMLA SAP NetWeaver BI Accelerator Downstream System Near-Line Storage Basic planning components Data:Real-time InfoCubes Planning model: – Aggregation levels (slices of Infocube) – Data transformation: • input ready queries • planning functions (e.g. Copy, Formula) – Filter and variables to parameterize data selections and planning objects – Data protection mechanism: • Lock services • Authorizations • Data slices Basic Steps Planning Applications Combine queries to enter data with planning functions and thereby support planners in modifying the plan data. Functions can be used during data input (e.g., modifying the data by a percentage or distributing yearly values to months) and showing the effects of planned data (e.g., simulation of the income statement after entering planned sales volumes). Planning Applications (an example) • A combination of a query to enter sales volumes with a function for the determination of revenues based on a price list which was previously maintained centrally. • A query for yearly values and a planning function to distribute to months (e.g., seasonal) to facilitate the planning of sales volume on a monthly basis (with either yearly or monthly values being entered by • planners) Similar example Planning Modeler works with 5 tabs (e.g., Function: Formula) InfoProvider tab SAP-IP uses real-time InfoCubes To support write-back MultiProviders to supply static data Choose account-based over keyfigure-based models Aggregation levels tab Each plan uses a subset or slice of the real-time InfoCube As defined in the aggregation level ( a subset of the characteristics) Filter tab Planning data is further “selected” from the InfoCube through the various filters defined Including BEx variables, hierarchies, navigational attributes and dates Planning functions tab Data manipulations, transformations, and calculations are done via planning functions Use transaction and reference data Done in memory (plan data cache) Only committed to the InfoCube when data is saved (see the save button in the case study) Planning functions (basic) Data operations (delete, copy, repost) Characteristic relationships (delete invalid combinations, repost, generation combinations) Valuations (currency translation, unit conversion, revaluation) Planning functions (advanced) Distribution (of data over a planning hierarchy) Forecasting Formula (for custom-defined functions) using FOX language Planning sequences tab Grouping multiple manual or automated planning steps Into process chains for background processing Or for monitoring and control of planning via Status and Tracking (STS) Status and Tracking System Overview of Case Study