Chapter 1 - Routledge
advertisement

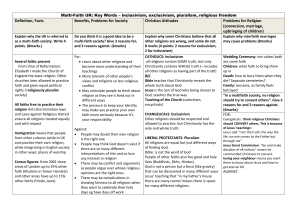
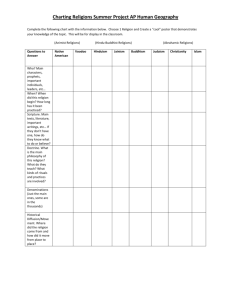
Religious diversity and pluralism Religious views in focus Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Christianity Islam Atheism Agnosticism Religious relativism Religious pluralism Religious inclusivism Religious exclusivism Explanation: one world religion is correct and all others are mistaken; salvation (or nirvana, or moksha, etc.) is found only through this one religion. (p. 26) Explanation: only one world religion is fully correct, but other world religions participate in or partially reveal some of the truth of the one correct religion; it is possible, however, to obtain salvation (or nirvana, or moksha, etc.) through other religions. (p. 26) Explanation: ultimately all world religions are correct, each offering a different path and partial perspective vis-à-vis the one Ultimate Reality. (p. 26) The Blind Men and the Elephant parable. (p. 31) Explanation: while each religion can be regarded as “true” and “effective” for its adherents, there is no objective or tradition-transcending sense in which we can speak of religious truth. (p. 26) Criteria Logical consistency Coherence of overall system Consistency with knowledge in other fields Reasonable answers to fundamental questions Existential plausibility Religious tolerance is best understood as recognizing and respecting the religious beliefs and practices of others (p. 41) A paradigm shift from rejecting to understanding Tolerance doesn’t affirm that everyone is right, but does realize that everyone is significant Which of the six approaches to religious diversity do you find most persuasive, and why? Can one hold to exclusivism or inclusivism and also be religiously tolerant? What would tolerance mean in these cases? Do you believe that it is possible to compare rival religious systems in such a way that one can objectively assess their plausibility? (Explain your answer.)