The Respiratory System
advertisement

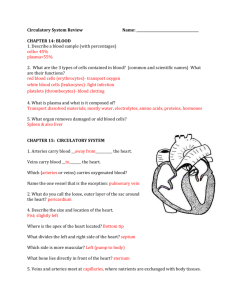
Daily Agenda 5/14/15: 1) Go over Notes: Respiratory System 2) Video: Into the Womb Objective: How does the respiratory system facilitate gas exchange? HW: 1) Work on and Study for Final Exam 2) Sign up for Norco College ID(by Monday) Page # Week 111 35 112 35 113-114 35 Activity Week 35 Daily Agenda Notes: Respiratory System Into the Womb Questions Points /5 /5 / 10 NOTES: CHAPTER 23 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1. Provide surface area for gas exchange between air and blood 2. Move air to and from exchange area of lungs 3. Protecting respiratory surfaces from dehydration, temperature changes and defending the respiratory system from invasion of pathogens 4. Producing sounds 5. Facilitating the detection of olfactory stimuli BREATHING AND RESPIRATION ARE THE SAME THING! NOT BREATHING Moving air in and out of the lungs RESPIRATION Chemical reaction that releases energy Two parts: upper ORGANIZATION respiratory system – nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and pharynx filter, warm and humidify incoming air cool and dehumidify outgoing air lower respiratory system – larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli Pathway of the Respiratory System Nose or mouth Pharynx Epiglottis (flap that prevents food from entering trachea) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Capillaries (take oxygen to body) NOSE AND NASAL CAVITY Brings air into the body through nostrils Nasal hairs in nostrils trap dust Nasal septum separates cavity into right and left halves NASAL CAVITY Warms & moistens air Glands that produce sticky mucus line the nasal cavity traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were not trapped by nasal hairs cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed PHARYNX passageway used by food, liquid, and air At the lower end of the pharynx is a flap of tissue called the epiglottis covers the trachea during swallowing so that food does not enter the lungs LARYNX “Voice box” The airway to which two pairs of horizontal folds of tissue, called vocal cords, are attached Sound production TRACHEA “Windpipe” Connects the larynx with the bronchi Lined with mucous membranes and cilia Contains strong cartilage rings BRONCHI Two short tubes that branch off the lower end of the trachea Carry air into the lungs. BRONCHIOLES Tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs Connect bronchi to alveoli ALVEOLI Tiny, thin-walled, grapelike clusters at the end of each bronchiole Surrounded by capillaries Where carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange take place http://mhln.com PLEURA Membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity DIAPHRAGM Muscle between the thoracic and the abdominal cavity that the body uses for breathing INSPIRATION (INHALATION) •Occurs because of air pressure differences between the env’t and the lungs •Rib muscles pull ribs up and out •Diaphragm muscle contracts to pull down the lungs •Tissue expands to force (pull) in air. EXPIRATION (EXHALATION) •Breathing out •Get rid of carbon dioxide •Rib muscles relax •Diaphragm muscle relaxes •Tissue returns to resting position and forces (pushes) air out http://mhln.com Breathing is controlled by the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata RELATIONSHIP TO DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Cellular respiration requires glucose and oxygen to release energy to the body C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy Oxygen is provided by the respiratory system Glucose is provided by the digestive system (glucose is made during photosynthesis) NON-RESPIRATORY MOVEMENTS Air Mechanism Movement Coughing Deep breath is taken, glottis is closed, and air is forced against the closure; suddenly the glottis is opened and a blast of air passes upward Sneezing Same as coughing, except air moving upward is directed into the nasal cavity by depressing the uvula Laughing Deep breath is released in a Function Clears lower respiratory passages Clears upper respiratory passages Expresses Crying Same as laughing Hiccupping Diaphragm contracts spasmodically while glottis is closed Yawning Deep breath is taken Speech Expresses sadness No useful function known Ventilates a larger proportion of the alveoli and aids oxygenation of the blood Air is forced through Vocal the larynx, causing communication vocal cords to vibrate; words are formed by lips, tongue, and soft Factors that affect breathing Factors Receptors Stimulated Response Effect Stretch Stretch receptors of tissues in visceral pleura, bronchioles, and alveoli Inhibits inspiration Low blood Chemoreceptors in pressure carotid and aortic (O2) bodies Increases alveolar ventilation Prevents over inflation of the lungs during forceful breathing Increases blood oxygen concentration High blood pressure Increases alveolar ventilation Decreases blood carbon dioxide Chemosensitive areas of the respiratory center