Chpt 9 a Glycolysis
advertisement

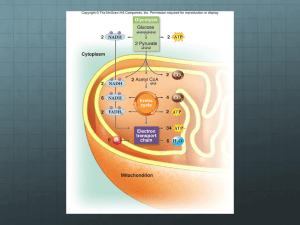
Chpt. 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Organic compounds store energy in their arrangement of CHEMICAL BONDS… Organic compounds store energy in their arrangement of BONDS… C C C C C C Organic compounds store energy in their arrangement of BONDS… Organic compounds store energy in their arrangement of BONDS… ENERGY is released!! It’s an AP Bio thing… you would understand! 2 e– + 2 H+ NAD+ 2 e– + H+ NADH H+ Dehydrogenase + 2[H] (from food) Nicotinamide (oxidized form) H+ Nicotinamide (reduced form NADH + NAD Lets get back to this… (becomes: ADP & Phosphate & E.) When an ATP molecule becomes phosphorylated the molecule loses a phosphate group. (becomes: ADP & Phosphate & E.) phosphorylated this kind of wor k! HOW?? How does ATP work? electrons have potential energy How does ATP work? electrons lose potential energy as they move toward more electronegative atoms from less electronegative ones. How does ATP work? the e- stored in food (in H atoms) is relocated… THE RELOCATION releases the energy. Redox Reactions = Redox Reactions = •transfer of electron(s) from one molecule to another. •ENERGY is released via. electrons… as they move closer to more electronegative atoms. Redox Reactions = Oxidation- Redox Reactions = Oxidationloss of electrons (reducing agent) Redox Reactions = Reduction- Redox Reactions = Reductiongains/accepts electrons (oxidizing agent) becomes oxidized (loses electron) becomes reduced (gains electron) LEO roars GER!! Electrons are removed from food … H H H via. H It transports with it energy that was stored 2 electrons & 1 proton move from hydrogen to oxygen they “ride” on the NAD+ “bus” NAD+ nicotinamide adenine NAD+ dinucleotide + NAD becomes reduced H e+ + NADH NAD+ 2 e– + 2 H+ NAD+ 2 e– + H+ NADH H+ Dehydrogenase + 2[H] (from food) Nicotinamide (oxidized form) H+ Nicotinamide (reduced form) Electrons move from hydrogen to oxygen (by the NADH “bus”) NADH NADH NADH molecules hold the stored energy that will be used later to make 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Respiration overview: 1. Glycolysis Respiration overview: 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle Respiration overview: 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs 3. eCycle Transport Chain Glycolysis: * Before glucose can be converted to ATP, it has to be broken down. Glycolysis: * Occurs in cytosol (cytoplasm) Glycolysis •Function - To split glucose and produce NADH and ATP. •Location - Cytoplasm. Glycolysis: * 2 phases: 1) energy investment Glycolysis: * 2 phases: 2) energy payoff Glycolysis: * Series of 10 steps * each step catalyzed by a different enzyme. Why not break down the glucose all at once?? "Glycolysis" strikes fear into many undergrad biology students because it presents them with an abstract series of reactions and molecules which are difficult to visualize and therefore incorporate into a coherant biochemical framework. Dr. Gregg Miami University Zoo 111 Fall 1983 That was MY professor Dr. Gregg Miami University Zoo 111 Fall 1983 Energy Investment Phase Energy Investment Phase 1 ATP 1)cell “spends” & gets 1 ADP & Glucose-6- phosphate Energy Investment Phase phosphate 2) Glucose-6- is rearranged to Fructose-6-phosphate “Presto… Chango … Re-Arrango!! Energy Investment Phase phosphate 2) Glucose-6- is rearranged to Fructose-6-phosphate Energy Investment Phase 3)Cell “spends” 1 more ATP & gets 1 more ADP 4) Energy Investment turns Phase into P - Fructose - P 5) Energy Investment Phase - P is P - Fructose broken down into 2 sugar molecules Glycolysis: Energy-investment phase 1)Cell “spends” 1 ATP & gets 1 ADP -> Glucose + P 2) Glucose + P is rearranged to Fructose + P 3)Cell “spends” 1 more ATP & gets 1 more ADP Glycolysis: Energy-investment phase- results: 4) P - Fructose - P 5) P - Fructose - P is broken down into 2 molecules P -c-c-c c-c-c -P G3P **2 ATP’s to 2 ADP’s** Energy Payoff Phase (2) G3Ps are dehydrogenated with (2) NAD+s Energy Harvest Phase becomes 1,3 bisposphoglycerokinase X2 Energy Harvest Phase A phosphate reacts with ADP to form ATP (X2) Energy Harvest Phase 3-phosphoglycertae formed (X2) Energy Harvest Phase “Presto… Chango … Re-Arrango!! Energy Harvest Phase PEP formed (X2) PEP Energy Harvest Phase Each PEP donates a P yielding 2 ATP’s (X2) & PYRUVATE (X2) PEP Energy Harvest Phase Glycolysis: Energy-payoff phase: 1) Cell constructs 4 ATP 2) Cell constructs 2 NADH Glycolysis: Energy-payoff phase-End result = C6H12O6 is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate = 2 net ATP’s produced = 2 NADH’s produced Glycolysis: End result = C6H12O6 is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate. = 2 ATP = 2 NADH