Exercise 4 Cell Cycle – Mitosis
advertisement

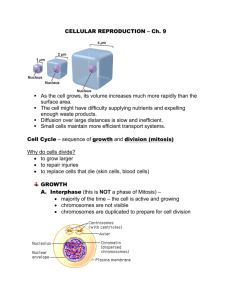
Objectives 1) Name three parts of the cell cycle. 2) Name four major parts of mitosis. 3) Identify important parts of a dividing cell. The cell cycle has three major parts: 1. 2. Interphase Mitosis (Mitosis has four major sub-parts) (Karyokinesis) 1) Prophase 2) Metaphase 3) Anaphase 4) Telophase 3. Cytokinesis Interphase Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Characterized by: 1. Intact nuclear envelope 2. Visible nucleolus 3. Although you can’t tell it, the cell’s DNA and other cell components are undergoing a process called replication (duplication process); chromosomes become doublestranded. 4. Three sub-phases: G1, S, and G2 Mitosis = Karyokinesis Prophase Condensed chromosomes (chromatin fibers) Characterized by: 1. Disappearing nuclear envelope and nucleolus 2. Chromosomes (46* in each human cell) coil and condense *23 pairs of chromosomes 3. Spindle fibers (microtubules) form and chromosomes become attached by way of centromeres 4. Newly formed centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell Mitosis = Karyokinesis Metaphase Characterized by: 1. Chromosomes align across the “equator” or metaphase plate 2. Centrioles stop at opposite ends of the cell 3. Spindle apparatus is fully formed Spindle apparatus Centrioles Metaphase plate Centrioles Mitosis = Karyokinesis Anaphase Centrioles Centrioles Shortening microtubules (spindle fibers) Characterized by: 1. Spindle fibers (microtubules) shorten and separate the chromosomes at the metaphase plate 2. In the human cell, 46 singlestranded chromosomes move in opposite directions toward each pole Can you name structures in the dividing cell? single-stranded chromosome centromere centrioles spindle fiber (microtubule) Mitosis = Karyokinesis Telophase Characterized by: 1. Cleavage furrow forms 2. Nuclear envelopes begin to form around two daughter nuclei 3. Chromosomes decondense 4. Spindle disappears cleavage furrow daughter nuclei Cytokinesis (Division of cytoplasm and contents into two cells) This figure represents an overview of the cell cycle.