carl jung - Bowmanville High School
advertisement

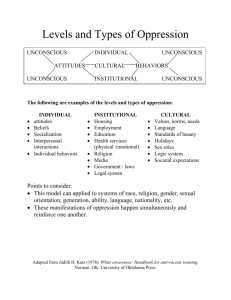
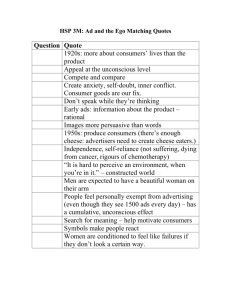
By: Christina & Alannah • Jung emphasized the importance of balance and harmony. He cautioned that modern people rely too heavily on natural science and logical positivism and would benefit from integrating spirituality and appreciation of unconscious realms. •Swiss psychiatrist, an influential thinker and the founder of analytical psychology. • Although he was a theoretical psychologist and practicing clinician, much of his life's work was spent exploring other areas, including Eastern and Western philosophy, alchemy, astrology, sociology, as well as literature and the arts. • Studied dreams, art, mythology, world religion and philosophy. • He is best known for his theories of the Collective Unconscious, including the concept of archetypes, and the use of synchronicity in psychotherapy. • personal unconscious. • In Jungian psychology, a part of the unconscious mind, shared by a society, a people, or all humankind, that is the product of ancestral experience and contains such concepts as science, religion, and morality. In other words, someone who shares personality and actions within a family doing the same stuff and not realizing there actions. • repressed part of mind: in Jungian and related forms of psychotherapy, a section of somebody's unconscious mind that contains impulses, fears, and memories that have been repressed • Your unconscious mind makes you think you forgot about something tragic that happened but you repressed it all your life so you don’t realize what you are doing when you do the same thing, so you are repeating your fears. Ex: if you get attacked by your dad and he beats you at a young age, but you grow up and “forgive” him, when you have kids you are likely to beat them and not know why you are doing so, doctors will try and blame it on your dads past but you will deny because you say you forgave him, too scared to face your fears. • Jung developed a personality typology that has become so popular that some people don't realize he did anything else! It begins with the distinction between introversion and extroversion. • Introverts are people who prefer their internal world of thoughts, feelings, fantasies, dreams, and so on. They keep to themselves usually really shy and don’t socialize. • Extroverts prefer the external world of things and people and activities. • They are usually very out going and socialize with everyone. Jung's theory divides the psyche into three parts. The first is the ego, which Jung identifies with the conscious mind. Closely related is the personal unconscious, which includes anything which is not presently conscious, but can be. The personal unconscious is like most people's understanding of the unconscious in that it includes both memories that are easily brought to mind and those that have been suppressed for some reason. • There are some experiences that show the effects of the collective unconscious more clearly than others: The experiences of love at first sight, of deja vu and the immediate recognition of certain symbols and the meanings of certain myths, could all be understood as the sudden conjunction of our outer reality and the inner reality of the collective unconscious. Boeree, George C. personality theories. N.p., 2006. Web. 30 Apr. 2010. <http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/jung.html>. "collective unconscious." answers.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 Apr. 2010. <http://www.answers.com/topic/collectiveunconscious>. magee, bryan. The story of philosophy. New York: dk publishing, 2001. N. pag. Print.