Get your GEEK on AHG 2012_FInal
advertisement

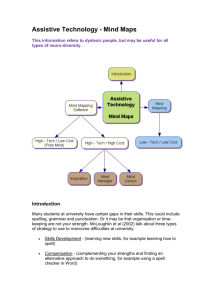
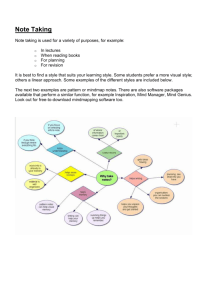
Embrace Your Inner Geek Accessing Higher Ground 2012 Wink Harner Mesa Community College and Heidi Scher University of Arkansas w Get Your GEEK On! “O O O”AT for Newbies: w Out-of-the-Box Obvious Obscure Key Learning Outcomes AT DISCOVERY - By the end of this workshop you will be able to identify: Out-of-the-Box: I opened it this morning, not sure what it does, but all the parts are there. Obvious: I can see you have short fingers. Is typing difficult? Dragon Naturally Speaking might be a good option. Obscure: Ooooo, I wonder if I could use my ) smartphone for that? Are You… • New to the field of disability service provision? • Feeling overwhelmed and confused by AT? • Feeling “technology-challenged”? • Wondering how to start with confidence as: The NEW ADAPTIVE TECHNOLOGY SPECIALIST w WELCOME! It’s your first day on the job, and this is what your staff says to you: “Welcome! We’re so glad you’re here.” What you hear: “So, we heard you were an AT specialist. Great. Tell us everything you know.” What you tell yourself: “I know enough to get out of the road.” ) A Natural Reaction w Uh oh. This does NOT look good! I’d better “Get my GEEK on” and get out of the road! Newbies’ Knowledge • Newbies need basic knowledge of software/adaptive technology applicable in key, mainstream areas. Remember: • AT isn’t about disability • AT IS about removing barriers and the ability to accomplish tasks! ) Key, Mainstream Tasks & Resources 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. w Manipulating/accessing print materials Writing Communication (aural or visual) Simple scanning & screen reading software Web resources & listservs for quick research Publisher, textbook, and alt-text resources Web-based solutions and online resources Free & fee AT for LD Community & state resources Out-of-the-Box Basics - 1 • Check the device to see what’s built-in!! • Operating systems’ accessibility options • Available on iOS, Windows, Android ) Out-of-the-Box Basics - 2 • Computer screen access - screen reader - magnification w Out-of-the-Box Basics - 3 • Input data – – variety of sticky key, – one-handed keyboard type programs, etc. from: http://www.onehanded keyboard.com/ ) Out-of-the-Box Basics - 4 • Writing on the computer – dictation software, – spelling (online or not), – off-the-shelf options that can also work w Out-of-the-Box Basics - 5 • Communication access – captioning, – transcription services, – VRS (video relay service), – Skype (for simple interactions) • Organizing/planning Mindmapping – does it hurt? ) Mindmapping Painless, Helpful & Even Fun! ) Mindmapping Example for Students • Live demonstration - FreePlane ) Mindmapping - Example ) Mindmapping - Example ) Obvious w 1. Scanning & screen reading software: OpenBook 2. Reading, writing & study tools: Read&Write Gold, WYNN, Kurzweil, 3. Screen reading software: Natural Reader, Adobe Reader, JAWS, MAGic, ZoomText 4. Mind mapping (organization & brainstorming): Inspiration 5. Captioning (video): Camtasia, MAGPie 6. Educational transcription: C-Print, Typewell 7. Use of iPhone & SmartPhone technology + free apps! Obscure w • Scan & read tools: Play Books • Screenshot reader • Reading, writing & study tools: Balabolka, TextAloud • Screen reading software: NVDA • Dictation: (for smartphones – Remote Bluetooth for Android) [DNS website, scan barcode, click activate] • Note cards, flash cards, calendars, tasks, mind-mapping [organization & brainstorming] (FreePlane, MindJet, iMindMap), etc. Out of the Cloud Web resources Listservs for quick research Publisher/textbook & alt text resources Web-based solutions & online resources (ex: effective GOOGLE search) Exploring resources in your community/state - PEPNET, AHEAD, TAP Projects, Bridge for Independent Living resources, etc. w Out of the Cloud BRILLIANT! SensusAccess is a self-service solution that automates the conversion of documents into a range of alternative formats including Braille, mp3, Daisy and e-books. The service can also be used to convert otherwise inaccessible documents such as image-only PDF files or scanned images into more accessible formats. SensusAccess is intended as a self-service solution for print-impaired students at universities and colleges and complements the accessibility services usually offered by educational institutions. The service can also be used by faculty to convert lecture notes and other educational material into accessible formats. • http://www.sensusaccess.com/ w Four Parts 1. Meeting With The Student: Using task-oriented approach to demonstrate how AT can help 2. AT Discovery Guidance for the newbie and for students 3. Identifying Resources 4. Networking & Sharing Resources ) Meeting With The Student Case Study #1 w Joe comes to Disability Resources. He reports difficulties associated with ADD/ADHD such as: • Taking class notes • Unable to complete tasks/tests • Distractibility • Disorganization Case Study #1: Joe Joe relates the following areas of difficulties: 1. Class notes - he writes down everything or very little as he can’t write & listen 2. Reading Assignments - doesn’t complete readings (has to re-read, is slow, doesn’t comprehend/remember what’s been read, gets distracted by the ‘eye-candy’ layouts on book pages) 3. Test - rarely finishes, runs out of time ) Joe 4. Distractions - gets distracted by others in class when they finish testing 5. Organization – he struggles with getting organized for the semester & completing large projects on time 6. Learns best by hands-on approach ) Tools for Tasks w Difficult Tasks Useful Tools 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Note taking tools (sync audio recording with notes taken) – apps, hardware 2. Required reading materials in alternate format (fullDAISY, accessible PDF) 3. AT to read tests aloud 4. Mindmapping organization (apps, software) Taking class notes Completing readings Completing tests Distractions Getting organized Meeting With The Student Case Study #2 Cindy is referred to you directly from Disability Services. • Standard-size text print is not large enough for her to read. • Seeing the board and demonstrations in class are difficult. ) Roll Play Case Study #2 • Here’s how we roll…. ) KISS When Talking With Students Three Main Areas to Discuss with Students 1. Student’s Strengths 2. Opportunities 3. Areas for Growth ) Strengths, Opportunities, Areas of Growth ) Know What You Don’t Know • Do not be afraid of new stuff – It does not bite, chase you, or jump out from behind trees (well, it might sometimes). • Embrace the geek within yourself (and others) • Identify what you don’t know – Helps you with opening doors to discover new technology & techniques! – (It’s OK to admit you don’t know yet!) • Continuously build your resources and tools to help in your learning process w Group Practice w Meeting With The Student Case Study #3 Rob is a returning vet. He reports having a trouble with memory recall as well as PTSD episodes. ) Meeting With The Student Case Study #4 ) Marcia has limited use of her hands and arms. She needs to be able to: • have good notes from lectures, • provide answers to tests, • use a computer, • access class materials (books, handouts, etc) during classes “Get Your GEEK On“ Sunglasses here! w Start hunting for resources! AT DISCOVERY: Guidance for the Newbie & for Students ) • AT demonstrations “bring the AT home” to students – better understanding of how/why to use AT • Provide handout of technology options – Students won’t remember all the details so give them a reference • List multiple options at different price points – Options exist & aren’t always expensive – Sometimes combo of free/inexpensive options can be as useful as higher-cost options • Ask students for feedback regarding what they use and why they like it Embrace Your Inner Geek & GO! Learn how to use the technology! After you find it, however simple or complicated it may be, make sure you learn how to use it or find someone who does. - Get training (familiarity) - Offer a variety of different types of training to the students w Into the Classroom • Unfamiliar with the classroom or how a student might use technology appropriately & effectively? – Make time for field trips to classes! • Request permission to attend class(es) as a technology assessment observer. • Take good notes. w – A LiveScribe Pen or Bamboo tablet are good tools to take notes in the classroom. – Both allow for sketches & drawings to help assess needs. Mission Possible Team Activity Challenge, should you choose to accept: Search and locate resources to overcome barriers and reach intended goal ) Mission Possible Example: Reaching the Goal • Goal = Accomplishing reading assignments • Barrier = hard-copy print – Example questions to ask student: • How do you understand things best? • What makes reading easier? • What have you tried? • Does it help if you read out loud to yourself? • Resources & resolutions w Team Report: Mission Accomplished What resources and resolutions did your team find? ) Discovering & Sharing Resources • Don’t limit yourself to AT-specific information only – Resources can be found in unexpected places! • Professional support organizations • State & national entities • Conference contacts • Listservs & Websites • DSS, AT, Technology, Sales, “Deals of the day”, Teaching, etc. w Teach Others! Campus resource: your college/university’s faculty resource center Engage them in training others by offering websites, blogs, wikis & workshops on the technologies ) Thank You! Wink Harner Heidi Scher Mesa Community College Center for Educational Access University of Arkansas foreigntype@cox.net hascher@uark.edu