anaphase
advertisement

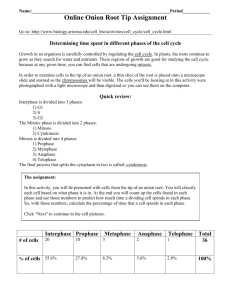
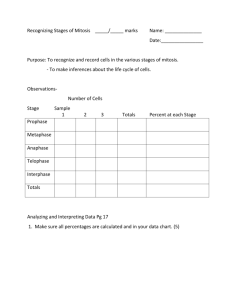
9.2 MITOSIS and CYTOKINESIS MAIN IDEA: Eukaryotic cells reproduce by MITOSIS and CYTOKINESIS WHAT YOU WILL LEARN -The events of each stage of mitosis -The process of cytokinesis READING Q’s NAME -What is one function of mitosis in a multicellular organism? -repair damaged cells -create new cells for growth / replacement READING Q’s LABEL -circle the picture that shows the sister chromatids being pulled to opposite ends of the cell ANAPHASE READING Q’s IDENTIFY -How are sister chromatids attached? -centromeres READING Q’s DESCRIBE -What happens to the chromatids during metaphase? -they line up along the equator of the cell READING Q’s IDENTIFY -What does the cell still need to do at the end of telophase? -cytoplasm divides--cytokinesis READING Q’s NAME -The cell structure that pinches the cytoplasm in half. animals -microtubules plants -cell plate READING Q’s IDENTIFY -What features in the figure can you use to identify this cell as a plant cell? -cell wall: cell dividing by forming a cell plate READING Q’s CREATE a “memory devise” to help you remember events that occur in each stage of MITOSIS by using the initials -- P –prepare/poles/pulling M –middle A –apart/away T –two/twin nuclei MITOSIS SONG http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pOsAbTi9tHw GROUP WORK: APPLICATION NOTES -COMPLETE application notes using GROUP knowledge/discussion from reading. REVIEW VOCABULARY DEFINE: life cycle -growth / development stages an organism goes through during its life MITOSIS IDENTIFY: two functions of mitosis in animals repair damaged cells 1-___________________ 2-__________________ growth of organism MITOSIS DESRCIBE: the stages of MITOSIS and the process of CYTOKINESIS NAME OF PHASE prophase (PREPARATION) metaphase (MIDDLE) Anaphase (APART/AWAY) telophase (TWIN NUCLEI) cytokinesis (CELLS CUT) DESCRIPTION (bulleted) -nuclear membrane/nucleolus disappear -chromatin coils to form chromosome -spindle apparatus forms from centrioles -chromosomes move to equator of the cell -centromeres spilt -sister chromatids pulled opposite sides -2 new nuclei formed -double membrane begins to form btwn them -cell’s cytoplasm divides/separates into 2 new identical cells MITOSIS LABEL: -the diagram of the stages of mitosis #13-16 -the structures pointed to using #17-20 METAPHASE sister chromatid ANAPHASE TELOPHASE PROPHASE G2 centromere spindle fibers centrioles MITOSIS SUMMARIZE: The function of each structure in mitosis part of chromosome spindle fibers attach to— PROPHASE/METAPHASE centromere-__________________________ tube-like structure/shorten & pull chromosome to opposite poles of cell--ANAPHASE microtubules-__________________________ attach and move chromosomes to middle of cell--METAPHASE spindle fibers-__________________________ help microtubules pull chromosomes motor proteins-__________________________ to poles of cell--ANAPHASE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-G-3BDlnK58 MITOSIS TRUE/FALSE: T _____1The nuclear membrane disintegrates during prophase. T _____2-Microtubules move chromatids to the poles of the cell during anaphase. F _____3-Chromosomes reach the poles of the cell during metaphase. anaphase T T _____5-Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers & line up along the equator of the cell during _____4-The cell’s chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase. metaphase. F _____6-the nucleus reappears during prophase. telophase F _____7-Centrioles are pulled apart during anaphase. sister chromatids T _____8-Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. T _____9-The shortest stage of mitosis is metaphase. _____10-The chromosomse decondense or unwind during telophase. T CYTOKINESIS COMPARE/CONTRAST: Cytokinesis in plant AND animal cells -CELL PLATE forms– -most of DNA -w/o proper -new cell wall life exist cell between daughter as doesn’t survive cells chromatin passed *accurately on -result in genetically identical daughter cells -CLEAVAGE FURROW forms-before division -microfilaments appear as short constrict dividing stringy structures cellin--nucleus PINCH into 2 new daughter cells SUMMARIZE Using a concept map, STAGES OF THE CELL CYCLE interphase GAP-1 synthesis GAP-2 MITOSIS cytokinesis prophase metaphase anaphase telophase -cell -cytoplasm -nuclear membrane -metaphase -nucleoli -poles