week 1-2
advertisement

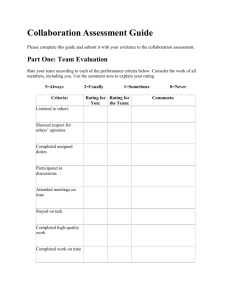
Introduction to J 3040 Media and Marketing Media Planning and Marketing Tonight we’re going to do several things You are going to take a quiz (not counted) to see how much you actually know about media. (20 minutes) I’m going to give you a broad overview of the course and point out some important things that you will need to know. I will point out We’re going to cover basic media terminology. I want you to know why this is important to you I want you to know basic media terms and verbiage I want you to know how terms relate to each other 5 of you are going to make mini presentations (10 minutes) Media Planning and Marketing Media is always changing World is speeding up New technologies available Number of media outlets expanding and contracting daily (radio, tv, publications, out of home opportunities, internet) Media Planning and Marketing The changes and new technology are totally reshaping the future of advertising. In addition to the technological changes, there is a complication of the changes in the way media is priced. The cost of advertising fluctuates up and down depending on supply and demand. Supply and Demand is one of the premises that most affects both media planning and marketing Media Planning and Marketing If you are a client, concerned with: Production Marketing Sales & Customer service Finance Research and Development Many other things Media Planning and Marketing If you are a Media Planner in an agency, this is how you fit into that picture: Account Planning-Account Supervisor and Account Executives Creative-Art Directors, Copy writers, Graphic designers, Producers Management/Finance-Management, accounting, Finance, Human Resources Marketing-*******Media planning, Media Buying, Research, traffic Media Planning and Marketing Media planners work with advertisers, with the ad media (TV, radio, internet, out of home vendors, etc.) and media buyers Media Planning is part of Marketing Can anyone tell the 4 P’s of Marketing? Product, Price, Place and Promotion Media Planning is part of Promotion***important Within promotion there is a mix of sales promotion, direct marketing, Public Relations, publicity and media advertising Media Planning and Marketing Within the promotional Mix falls Salespeople Telemarketing Catalog, literature, manuals Trade shows, seminars, training Direct mail and sales promotion PR and Publicity Media Advertising Media Planning and Marketing All these things combined go into reaching your target audience and determining how much it will cost to reach each contact Media planning is a small part of the big picture, but it’s a very important part of that picture. WHY? MONEY As media planners, you are holding a clients investments, trust and future in your hands. Media Planning and Marketing Advertising Media Mix Who What Where When How KNOW THIS. Probably the most important thing you will learn in this class. Your media plan will have to address each of these. Media Planning and Marketing Media plan is A blueprint for media buying A Road map… Shows How an advertising budget will be used to buy media that will reach prospective consumers with greatest effectiveness at lowest cost. Where you are now and how you will get to where you want to be What the best means of delivering ads to prospective buyers of product is. Media Planning and Marketing Going back to Who, What, Where, When, How: What this means: Who are the prospects? How many prospects are there? How many times should they be reached? In which medium? When should we reach them? Where should we reach them? How much should we spend? Media Planning and Marketing 4 Rules of vehicle selection (TV, radio, print, etc.) Optimize reach and frequency Minimize cost Avoid waste Stay within budget Media Planning and Marketing Media Planning Grounded in marketing Must have a marketing objective An advertising objective A Media objective There are trade offs-Effective advertising vs Efficient advertising Receptive audience vs Relevant audience Primary contact vs recent contact Media Planning and Marketing Media Planning is based on scientific research It is also based on inspired application of an informed media planners personal judgement So much of research is flawed and flakey and this means it is of the upmost importance for media planners to know as much as they can about as many different medias and the pros and cons of each. Media Planning and Marketing Planning procedures Analysis of marketing situation-marketing strategy Advertising creative strategy…do they want TV or out of home, or internet. This has tremendous influence over media plan Media Plan Objective-targets, reach, where Strategy-media selection, national/spot, radio, internet Tactics-vehicle selection, # ads, position Media Planning and Marketing Media Classification Traditional: Television, newspaper, magazines, radio Non-traditional: Interactive, computer, kiosk, telephone, Viral marketing Coupons/DM Third Party: shopping bags, statement stuffers Event In-store Place-based: transit, bus shelters, transportation, stores, stadium, or any outdoor media Media Planning and Marketing Medium VS Vehicle-know this Medium: A class of carriers Television Radio Newspapers Magazines Internet In-store Media Planning and Marketing Vehicle: an individual carrier within a medium Dallas Morning News, Denton RecordChronicle, New York Times, 60 Minutes, Wheel of Fortune, CSI, ER, People magazine, Time, Vogue, Google, American Airlines Arena in Dallas Media Planning and Marketing Medium Newspaper Vehicle NYT Ad unit 4 col. By 12 inches Magazine Time 4 color/full page Television News :30’s, :60’s Radio KPLX-F :30’s, :60’s Media Planning and Marketing Media Objectives, Strategy and Tactics Media Objective A goal which focuses on the target audience Who? How many? When? Where Media Planning and Marketing Media Strategy Actions to meet the objective Specific target audience Reach and frequency Media Mix (SOV) National vs Local Media Planning and Marketing Media Tactics The very specific activities required to implement the media plan Ad type Vehicle selection Timing and scheduling Media Planning and Marketing Example: Media plan for a Senior Health Care plan Objective: Reach 60 percent of target market with an average of three messages during the introductory month of the plan Strategy: Target to current users who are int the 55+ age category. Use 90/10 mix of daytime network and general editorial magazines Tactics: 2 x :30 second commercials per month on day time talk shows and soap operas Full-page 4 color ads in Modern Maturity and American Health Life Media Planning and Marketing Media can be confusing because there are so many terms to learn. Anything you do in advertising, you will have to interact with media. Understanding a few terms will allow you to know buzz words media planners, agencies and clients use. It will open up doors for you as you interview for jobs, as you interact with clients and with people in your departments. Media Planning and Marketing Media has a language all its own. Knowing what these words mean can and will open doors for you…even if you don’t go into media. Media touches every aspect of advertising and it is becoming more and more important because of the new technology and because so much money is involved. Media Planning and Marketing PUT ON BOARD Rating/GRP/TRP CPM/CPP Impressions Reach/frequency share MSA/DMA/TSA Intrusive SOV HUT/PUT/PUR FP/4c Boards showing flowchart insertion Efficiency effective qualitative quintile Standard Broadcast Calander Coverage BDI/CDI Media objectives, strategies, tactics Sampling circulation Gross impressions Seasonality Media Planning and Marketing Rating % of individuals or homes exposed to an advertising medium. Term generally used in TV and radio, but coverage (magazine) and showing (outdoor) are identical terms Example 6 volunteers TV TV TV TV TV Home Home Home Home Home 1 2 3 4 5 Grey’s Anatomy Grey’s Anatomy CSI MTV Videos Off Media Planning and Marketing 5 Homes total in this market Grey’s Anatomy = 2/5 or 40% This is a 40 rating CSI and MTV = 1/5 or 20%. This is a 20 rating In this example Greys has a 40 HH Rating. CSI and MTV have a 20 HH rating How many ratings? 80 (40 + 20 + 20) Media Planning and Marketing Now, lets assume 2 people in each HH Home Greys CSI MTV OFF Total Home 1 1 1 2 Home 2 2 2 Home 3 1 1 2 Home 4 2 2 Home 5 2 2 Total 3 1 2 4 10 Rating 30 10 20 Media Planning and Marketing In this example we have a total population of 10. Greys Anatomy has 3 out of 1- or 30% or a 30 rating. CSI has a1 out of 10, 10% or 10 rating. MTV has 2 out of 10 or 20% or 20 rating. With ratings, always drop the % sign Media Planning and Marketing Geography Population Men (in 1000’s) National (USA) Dallas Beaumont 90,000 900 500 100,000 1,000 600 10 10 10 8 8 8 Men delivery (in 1000’s) 9000 90 50 Women delivery (in 1000’s) 8000 80 48 Population Women (in 1000’s) Men Rating Women Rating Media Planning and Marketing In this example I’m showing that a 10 rating (Men) means different numbers of people depending on the market or population of the market. In the US, a 10 rating men would mean 9,000,000. In Dallas, 90,000 In Beaumont, 50,000. This could apply to TV, Radio, outdoor or any medium. TV and radio stations use ratings to determine a shows popularity. If a rating is high, the show generally stays on the air. If its low, often cancelled. Media Planning and Marketing A Rating is the most important broadcast term and advertisers use ratings to buy TV and radio programs to determine how many people will be reached by their message. A rating is always a % of a population. Buyers and sellers negotiate costs based on estimated ratings. If a rating is high (a popular show) the seller (station) can charge more money for the advertising because more people are watching the show. Media Planning and Marketing HUT=Households using Television =% of homes using TV at a given time of day. Get out little houses In the first 2 homes, they are viewing Greys Anatomy In the 3rd home they are viewing CSI In the 4th home they are viewing MTV The 5th home is not watching anything. Of the 5 TV homes, 4 are viewing TV. The HUT is 80%...4/5 Media Planning and Marketing Grey’s Anatomy = 40 rating (2/5 of 40% or 40 rating) CSI = 20 rating MTV = 20 rating Total ratings 80 HUT Media Planning and Marketing The same can be applied to radio, but the term is PUR (Persons using radio) When we are talking about People instead of Households, the term is PUT (People using Television) The difference comes from the populatoin base. Although 80% of the HOMES are using TV, the 5 of total people is less. Going back to our example of 2 people per Household, of 10 total people, IF only 1 person per Household is viewing in 4 of the 5 HH, the PUT (People using Television) is 40%...4 people viewing divided by a populatoin base of 10. Media Planning and Marketing The % always refers to the AVAILABLE UNIVERSE with a TV or radio in their homes…as opposed to the total population…although most people have TV’s in their home, not all do, so those people cannot be counted in the universe. Media Planning and Marketing Seasonality Hut levels vary by season…why? (weather, reruns, lifestyles holidays, work habits, writers strikes) Hut levels vary by geographic areas. TV useage levels generally lower in the moring, daytime and late night…why? (work, sleep) and lower in warm weather…why? (vacation)…interesting point is that usually when TV viewing is lowest, ratio listening is highest…In summer months, people are outdoors, at the beach, having barbeques, etc. Often take radio listening outdoors with them…changing with your generation…IPODS Media Planning and Marketing Terms HUT and PUT often interchangeable. But HUT really means Households using TV and PUT is people or persons using TV. Like HUT levels, PUT levels also vary and the variations are different from one group to another. Can anyone guess what group of people consistently watch more TV than any other group? Women…They watch more, but they also keep track more. Media Planning and Marketing Radio PUR levels also vary (please note there is not a term HUR for Households using radio) Adult listening is highest in what is called Drive time 6-10 A and 3-7 PM. Teen PUR is highest in PM drive (except in summer when teens not in school. Some stations still program to school being in and out of session. Media Planning and Marketing Radio times bought and sold in following time periods: M-F 6-10A AM Drive M-F10A-3P Midday M-F 3-7 P PM Drive M-F 7P-12M Evening M-SU 12m-6a Overnight Sat Same as above Sun Same as above Media Planning and Marketing Generally highest listening timeperiods are M-F 6-10 A and Sat 10a-3 PM. As stated before, when TV viewing is lowest, radio at highest (3rd quarter) because of weather, school and vacations. Media Planning and Marketing Next week I will review HUT/PUT and talk about SHARE, Gross Rating Points, Impressions and how they all relate to each other. We’ll do some in class exercises to make sure you understand what these terms mean. Now like to get to the mini media presentations. Dominique Brown Andrew Cantu Taylor McLelland Lauren Penn Sheila Tran next weeks assignment is on syllabus