psychodynamic perspective beyond freud
advertisement

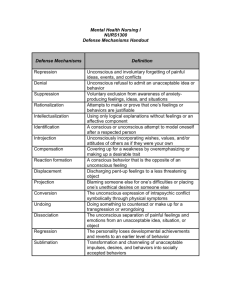
Psychodynamic theories Psychoanalysis (psychodynamic): • Unconscious thoughts & emotions are brought into awareness to be dealt with. • Psychological problems – the result of unconscious processes. • Bringing unpleasant unconscious thoughts into to consciousness, produces catharsis. Psychoanalytic methods of therapy (there are 4): • 1. Free Association – patient reports anything that comes to his/her mind. • The psychoanalyst listens for links & themes that might tie the patient’s fragmentary thoughts or remarks together. Dream analysis: • Dreams have two types of content: • Manifest content- actual events in dream. • Latent content – hidden message in dream. • Freud thought that each dream represents a form of wish fulfillment. The wish may be disguised, but it is always there. Transference • Feelings of love or other emotions (hatred) are expressed toward the therapist. • These feelings are actually unconsciously felt toward others; the patient is projecting these feelings onto the therapist. • This provides clues about the client’s feelings about these other people. Hypnosis • Hypnosis is a psychoanalytic therapeutic technique. • Supposedly reaches into the subconscious What are Criticisms of Freud’s theory?: • 1. Freud had no scientific data to support his theories. Theories aren’t scientific. • 2. Freud’s theories (unconscious mind, etc.) cannot be observed. • 3. Theory explains behavior (post-hoc) after the fact. • 4. Observations not representative of population (very sexist and not multicultural). What are Pros (good) of Freud’s theory • 1. childhood experiences are important in development. • 2. Information outside of awareness does influence us. • 3. Defense mechanisms—good descriptions of some of our behaviors. More psychoanalysts • Who was Carl Jung? He was a psychoanalyst who disagreed with Freud. • 1. collective unconscious • 2. archetypes Carl Jung • Less emphasis on social factors. • Focused on the unconscious. • We all have a collective unconscious: a shared/inherited well of memory traces from our species history. Carl Jung • Archetypes – certain symbols/literary characters that we all recognize • Ex: wise old man, witches, messiah Alfred Adler • Childhood is important to personality. • But focus should be on social factorsnot sexual ones. • Our behavior is driven by our efforts to conquer inferiority and feel superior. • Inferiority Complex (We strive to be superior) • Those that feel inferior develop an avoiding style of life • Everyone has an innate potential to cooperate with others • Environmental influences > biological influences Karen Horney - (Horn – EYE) • Also agreed with Alfred Adler on the importance of SOCIAL relationships during childhood (less of a focus on the unconscious) • Childhood anxiety is caused by a sense of helplessness; children need love and security • Opposed the concept of penis envy • Developed the concept of neurosis: a driving need for something or someone – Neurosis is normal- gives people something to strive for, however it can become abnormal when what we strive for (or are obsessed with) interferes with our daily life – Categories of neurosis: compliance (affection), aggression (power), withdrawal (independence) Psychodynamic testing • Projective tests ask subject to interpret a picture. Used only by psychoanalysts; are subjective. Ex. TAT, Rorschach Ink blot test TAT Thematic Apperception Test • A projective test which people express their inner feelings through stories they make about ambiguous scenes Thematic Apperception Test TAT Rorschach Inkblot Test • The most widely used projective test •A set of ten inkblots designed to identify people’s feelings when they are asked to interpret what they see in the inkblots. Rorschach Inkblot Test Rorschach Inkblot Test Rorschach Inkblot Test Rorschach Inkblot Test