WellControll2
advertisement

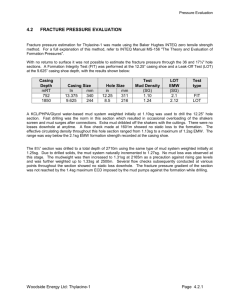
Petroleum Engineering 406 Lesson 3 Well Control Read • Well Control Manual – Chapter 7-8 • Homework 2 Due Jan. 30, 2001 Content • • • • • Equivalent Mud Weights - EMW Casing Seat Tests Kick Tolerance Differences in Kick Types Reaction of Gas in the Wellbore Equivalent Mud Weight • EMW - the total pressure exerted at a given depth expressed in ppg equivalent • EMW = Surf. Press./(0.052*TVDint)+MW – or • EMW = Total Press. /(0.052*TVDint) Equivalent Mud Weight • Examples: – KWM – ECD - Equivalent Circulating Density • ECD = Ann. Fric./(0.052*TVD)+OWM – Frac gradient – Pore pressure, etc Casing Seat Tests • We test casing seats to: – Determine max pressure that formation can withstand – Determine if we have a good cement job Casing Seat Tests • LOT - Leak-Off Test – Measure the fracture pressure at casing seat – or, Maximum pressure the formation can withstand prior to fracture EMW LeakOff Pr essure MW .052 * TVDshoe Fracture Initiation P r e s s u r e Leak-Off Fracture Extension Casing Test Volume pumped Casing Seat Tests • PIT - Pressure Integrity Test (FIT) – Determine if the casing seat can withstand a pre-determined pressure • Test Pressure = (EMW-MW)*0.052*TVDcasing seat Kick Tolerance • Maximum Casing Pressure - MCP • Maximum Allowable Annular Surface Pressure - MAASP, MASP • Maximum Casing pressure that the formation can withstand prior to fracture • = (EMW-MW)*0.052*TVDcasing seat Kick Tolerance • Maximum ppg kick - Maximum mud weight increase on a kick prior to formation fracture • =(EMW-MW)*TVDshoe/TVDwell • Assumes zero pit gain Kick Tolerance • Maximum Kick Volume Kick Types • Gas Kicks – Rapid expansion as gas circulated through choke – Mud gas separators and flare lines used – Gas migration problems – Higher SICP than others Kick Types • Gas Kicks, cont. – – – – Barite settling in OB mud Solubility of gas masks kick indicators Flammability of gas Slugging of gas at choke Kick Types • Oil Kicks – Flammable but not as explosive as gas – Density greater than gas-lower SICP – Very little expansion as kick reaches surface – But, there is almost always some gas present Kick Types • Water kicks – not flammable – very little expansion – lower SICP than gas or oil – But, there is still usually some gas present. Kick Types • Prediction kick types – Density of gas =1-2 ppg – Density of oil = 6-8 ppg – Density of salt water =8.6-9.0 ppg SICP SIDPP KickDensit y MW 0.052 height PitGain, bbl height Ann.Cap, bbl / ft Drillers Method • Pressure at Top of Kick-Px VB PB TX Z X MW 0.052 TB Z B v x vB B PB PFB D x 0.052 MW vX B B Px 2 4 2 1/ 2 Drillers Method • Surface Casing Pressure - CP – CP=Px-0.052*MW*x • Pressure at casing seat - Pseat – – – – Pseat=CP+0.052*MW*Dseat where the bubble is below the casing seat Pseat=PB-0.052*MW*(D-Dseat) where the bubble is above the casing seat Wait & Weight Method • Pressure at Top of Kick-Px B1 B VB PB TX Z X MW1 0.052 Px 2 4 v x TB Z B v B1 PB PFB B D'0.052 MW1 MW D x 0.052 MW1 vX 2 1 1/ 2 Wait & Weight Method • Surface Casing Pressure - CP – CP=Px-0.052*MW*x • Pressure at casing seat - Pseat – – – – – Pseat=CP+0.052*MW*Dseat where the bubble is below the casing seat Pseat=PB-(0.052*MW*D’) -[0.052*MW1*(D-D’-DSEAT)] where the bubble is above the casing seat Nomenclature Examples Surface Casing Pressure Ann. Press @ Various Depths Reaction of Gas in a Wellbore • Boyle’s Law • PV/ZT = nR – PV=constant • Charles’ Law – V/T=constant • Avagadro’s Law – PV=nRT • Real Gas Law – PV=ZnRT • P1*V1 = P2*V2 Z1*T1 Z2*T2 • V2 = P1*V1*Z2*T2 P2*Z1*T1 Reaction of Gas in a Wellbore • Circulating gas from wellbore • Given: – – – – – – Depth =16,000’ BHT =300oF BHP =12480 psi MW =15.0 ppg Surf. Temp =140oF Drilled up 1 cu.ft. of gas Reaction of Gas in Wellbore Reaction of Gas in Wellbore Gas Migration Gas Migration MASP