●
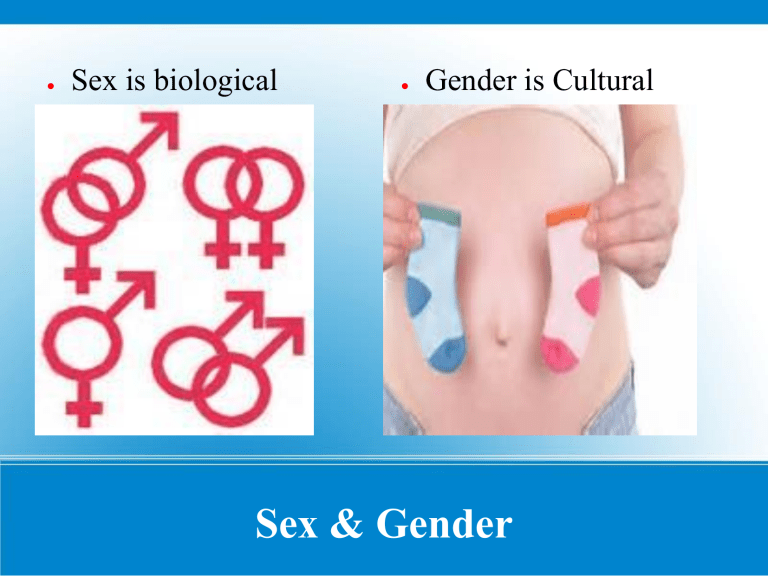
Sex is biological
●
Gender is Cultural
Sex & Gender
Inter-Sex Symbol
●
●
●
Sex is organized before birth
and is activated at puberty
Sex is Male, Female or
“other”
Inter-sex status means the
status of having physical,
hormonal or genetic features
that are:(a) neither wholly
female nor wholly male; or
(b) a combination of female
and male; or (c) neither
female nor male.
●
●
●
●
Gender describes the roles of
Males and Females
Gender traits differ from culture
to culture and can be shaped,
altered or changed over time
Gender makes us masculine or
feminine
Gender is an achieve status
because it must be learned
Sex VS Gender
●
Mammalian body plans are inherently female
●
Every Individual's body plan is a variation of the female body theme
●
●
●
–
Default (female)
–
Fully altered (male)
–
Partially altered (inter-sex)
Everyone falls on some point of the continuum from female (gynemorphic) to male
(andromorphic)
The sexual body plan is organized by the presence or absence of steroid hormones
during the “critical” period of development
Sexual systems are activated later by steroid hormones during puberty
Sex Explained
Males are physically altered females
Nature
●
●
Nurture
Organized before birth
●
Sexual behavior,
identity,and orientation
●
●
Natural instinct
●
Learned
Raised outside of the
natural gender
Chosen
Nature VS Nurture
●
●
Sex : the state of being male or female: men or male animals as a group or
women or female animals as a group: physical activity in which people
touch each other's bodies, kiss each other, etc. : physical activity that is
related to and often includes sexual intercourse
Gender :a subclass within a grammatical class (as noun, pronoun, adjective,
or verb) of a language that is partly arbitrary but also partly based on
distinguishable characteristics (as shape, social rank, manner of existence, or
sex) and that determines agreement with and selection of other words or
grammatical forms
–
the behavioral, cultural, or psychological traits typically associated with
one sex
Definitions
●
●
●
●
Stereotype: to believe unfairly that all people or
things with a particular characteristic are the same
Sociocultural : of, relating to, or involving a
combination of social and cultural factors
Theory is an explanation
Status is a category or position a person occupies
that is a significant determinant of how she or he
will be defined and treated
Definitions Continued
●
●
●
Role is the expected behavior associated with your
status
Androcentrism are male centered norms
Endogamy means to marry within the same social
class. Insuring that property and wealth are kept in
the hands of a few powerful families
Definitions continued
●
Our culture in the world is binary general....
●
this means that they support two genders only
–
●
●
Male and Female
In the US “other” are hidden, unaccepted or misunderstood and are expected
to adapt or assimilate to their environment.
*However some cultures does in fact recognize more than two genders.
India (Hijras)
Tahiti (Mahus)
Native American's (Berdache)
●
●
Gender independent children do not abide by the prescribed gender norms.
When people don't abide by society gender rules they are labeled as sissies,
gays, bisexual, transsexual, or natures experiment
Gender Facts
●
Gender roles are taught when they are infants
–
●
Gender roles are established
Socialize “Men as Men” and “Women as Women”
–
Do not cross gender boundaries
Gender Facts Continued
Images of gender and sex conflict
●
Family
●
Peers
●
School
●
Mass Media
●
Teachers
●
Caregivers
Sources of Learning Gender
Functionalist emphasize on the value consensus or the shared
values and their relation to social change
●
Husband “Instrumental task”
●
Money maker
●
Decision maker
●
Economic supervision
●
Wife “Expressive task”
●
Provide affection
●
Emotional Family Support
●
Domesticate
Functionalist Perspective
Conflict Theory unlike functionalist, who believe that
social order is combined through value consensus, assert
that it is preserved involuntary through the exercise of
power one social class holds over the other
Gender division inside the household
●
Male Control
●
Dominance
●
Dependent on women
Conflict Perspective
Karl Marx (1818-1883) believed that conflict theory is
based on the assumption society is a stage on which
struggles for power and dominance are acted out.
The struggles are between the social classes
competing for control.
Conflict Continued
Feminist perspective advocates empowerment to exert the ability for women to
have control over their own destiny. They feel that women are disadvantaged
by race, class, sexuality and are not helpless victims. They actually possess
agency, the power to adapt and thrive in a difficult situation.
●
Advocate Social change
●
Gender equality
●
Viewed as equal to men
●
Male dominance causes oppression
Feminist Perspective
Cognitive development theoretical explanations for gender socialization
contrast sharply with social learning theory.
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) interest in how children gradually develop
intelligence, thinking, and reasoning laid the foundation for cognitive
development theory.
●
●
The mind matures through interaction with the environment
Cognitive theory stresses a child's active role in structuring and
interpreting the world
●
By age 3 children begin self identity
●
By age 6 gender constancy is in place
●
A girl knows that she is a girl and will remain a girl
Cognitive Development Theory
●
●
●
This is a promising and important subset of
cognitive development theory
Schema are cognitive structure that are used to
understand the world, interpret perception, and
process new information
Consistent with cognitive development theory,
before a schema is created to process gender related
information children must be at the cognitive level
to accurately identify gender
Gender Schema Theory
●
Aggressive
●
Proud
●
Disorganized
●
Courageous
●
Confident
●
Independent
●
Ambitious
●
Selfish
●
Logical
Characteristics of Men
●
Easy Going
●
Demanding
●
Strong
●
Head of Household
Characteristics of Men Continued
●
Emotional
●
Sensitive
●
Affectionate
●
Patient
●
Romantic
●
Moody
●
Thrifty
●
Manipulative
●
Possessive
Characteristics of women
Left to Right: Woman in the kitchen cooking, Man at the bar
Woman standing over a Man, and a independently sexed person
●
●
●
●
What gender stereotypes does the previous images
portray?
How do they each influence conceptions of gender?
Do you wish for your child to be a particular sex and
why?
How do you think society view gender?
–
Example...unequal in workplace, religion, virtues,culture
etc.
Discussion
Dictionary.com
Lindsey, Linda L., Gender Roles A Sociological Perspective (4th Edition)
Money, John; Ehrhardt, Anke A. (1972). Man & Woman Boy & Girl. Differentiation and
dimorphism of gender identity from conception to maturity. USA: The Johns Hopkins
University Press. ISBN 0-8018-1405-7
References







