Sample CRQs Primate city - Sewanhaka Central High School District
advertisement

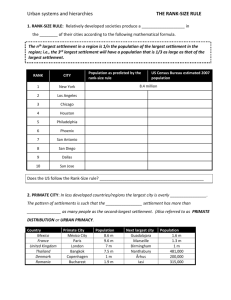
Primate city: cities that are more than 2x the size of the next largest city AND exert social, political, and economic dominance Rank-size rule: Sizes of cities are in proportion to one another. If x is the largest city, then the second largest will be ½ x and the third largest will be 1/3 x. According to the statistics for the populations of Mexican cities, Mexico has a primate city since Mexico City is more than twice as large as the next largest city of Guadalajara. Mexico does not follow a rank-size rule in the population distribution of its cities. Large market for goods and services Can benefit from the advantages of agglomeration Can offer high end goods and services because of larger threshold population Creates global trade networks (primate cities can compete on global scale and attract foreign investment plus gravity model shows high degree of interaction among cities with high populations) Unequal distribution of wealth and/or power Brain drain – migration of educated people to primate city Unequal distribution of education, entrepreneurship, opportunities Disproportionate effect of disaster in the primate city on the entire country Hard for people who are not in the primate city to access essential services such as hospitals. Using contemporary examples, explain how each of the following has contributed to the development of national identity and the strengthening of a state. Economic development Relocation of a state’s capital China Any of the How this Asian Tigers helps national identity… • Since Deng Xiaoping, • Used the international • Strong economy China has trade approach to creates jobs, supports incorporated increase their a sense of well being, capitalism into their economic and supports economy development confidence in • As of 2001, China • Have focused on leadership and loyalty joined World Trade skilled labor, to state Organization (WTO) electronics, and • Economic prosperity • Has allowed foreign clothing helps to hide other investment into their • Rapid growth of problems the country country economy may be experiencing • Relocation of factories • National pride to China has provided reinforces national citizens with jobs identity Brazil Nigeria How this helps national identity… • Relocated capital from • Relocated capital from • Strengthens the state Rio de Janeiro to Lagos to Abuja and provides stability Brasilia in order to • Since Nigeria is relocate population to comprised of so many a central area ethnic groups, there • Helps develop the has been constant interior which was conflict mostly uninhabited • Capital was relocated • Break ties with to a central location to colonial past accommodate (importance of cities different ethnic along the coast to groups provide to Portugal) Nigeria: A Case Study for Language Conflicts 493 languages 3 main languages Hausa (15%) Yoruba (15%) Igbo (15%) 55% speak one of the other 490 languages Using contemporary examples, explain how each of the following may detract from the development of national identity and weaken a state. Ethnicity Transportation/infrastructure Yugoslavia Nigeria How this hurts national identity… • Ethnic tensions between Serbs, Croats, and Bosnian Muslims led to genocide during the 1990s • Ethnic tensions between Hausa, Igbo, and Yoruba has led to constant violence and fighting • Ethnic tension weakens loyalty to the state • Tension between ethnic groups can lead to balkanization, separatism, devolution, etc. • Placement of political boundaries without regard to ethnic territories leads to problems Chile Democratic Republic of Congo How this hurts national identity… • Elongated state therefore poor communications • Weak government and • Poor transportation rebel groups have infrastructure deterred the contributes to maintaining of isolation and a sense infrastructure of separation • Size or shape of a state may hinder development Discuss THREE ways in which the concept of core- periphery relations helps explain the development of the urban systems shown above. Be sure to use evidence from both maps to support your conclusions. Primate city in Argentina vs. Rank-Size Rule in Germany Argentina is a semi-peripheral country and city populations are not evenly distributed. The map shows that Buenos Aires is a primate city and population is therefore centered there. This can sometimes be an indicator of lower development since it often leads to unequal distribution of goods and services with Buenos Aires being dominant. In addition, Buenos Aires is in a coastal position because it was set up by Europeans looking to exploit the resources of Argentina. This demonstrates a peripheral position in the world. Germany on the other hand follows more of a rank-size distribution of population. City populations are more evenly distributed which shows more even development throughout the country thereby demonstrating their position as a core country. Roads systems also help demonstrate core-periphery relations In Argentina there are less roads and they are all focused toward getting goods to their primate city of Buenos Aires. This again demonstrates that Argentina was set up to be more export oriented which shows their dependence on other countries buying their goods. Lack of infrastructure in general shows a lack of development. In Germany, roads are more evenly distributed throughout the country showing its higher levels of development and status as a core country. Germany can afford to pay for the building and maintaining of transportation systems. They are not focused on just one city because they have a more mature and integrated economy.