12. Academic Bio Cellular Respiration WebQuest
advertisement

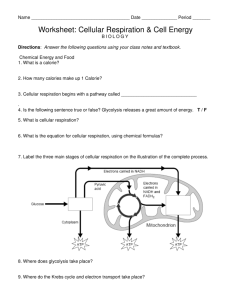
Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: ___________ CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION WEBQUEST Part I: Stages of Glycolysis Site Link: http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/glycolysis.html Site 1 is designed to show you exactly what goes on during glycolysis. Watch the video to answer Steps 1-3. Pay particular attention to the role of the energy molecules (ATP & NADH) as both reactants and products. STEP 1: STARTING GLYCOLYSIS Draw/label what happens in step one on the picture to the right and explain what is going on in your own words below. STEP 2: SPLITTING OF GLUCOSE Draw/label what happens in step two on the picture to the right and explain what is going on in your own words below. STEP 3: ENERGY GENERATION Draw/label the end result of step three on the picture to the right and summarize what happens below. 1 Acad Bio Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: ___________ Part II: The (Energy) Cost of Glycolysis Site Link: http://henge.bio.miami.edu/mallery/movies/glycolysis.mov Watch the video once through first. Then watch it again and answer the question below. WHY IS IT THAT ALTHOUGH WE MAKE 4 ATP, THERE IS ONLY AN OVERALL GAIN OF 2 ATP? Show your science knowledge and explain your answer below. Part III: Cellular Respiration Overview Site Link: http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/cellularrespiration.html The animation on this site will show you an overview of the process of cellular respiration. Watch the animation (don’t be afraid to click on the “subtitles” button) and answer the following questions. THE BIG PICTURE 1. How does cellular respiration compare to photosynthesis? Write your answer below. Also draw visual representations for the equation of each. 2 Acad Bio Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: ___________ GLYCOLYSIS 1. Where in the cell does glycolysis take place? 2. What is an outcome of glycolysis? 3. What is the net ATP yield of glycolysis? Explain this in terms of input and output. THE KREBS CYCLE 1. What molecules is Acetyl-CoA made from? 2. What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH? 3. After the Krebs cycle, where have all of the carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule gone? 4. What is the function of NADH? 5. Why is an increase in the number of mitochondria beneficial for aerobic exercise? ELECTRON TRANSPORT 1. What is the function of the electrons carried to the chain by NADH and FADH2? 2. What is a concentration gradient? What molecule/particle has a gradient set up for the transport chain? 3. What is the purpose of the proton gradient in the electron transport chain? 4. What happens to the electron transport chain if oxygen is lacking? 5. What is the overall purpose of cellular respiration? 6. How does cyanide block the function of the electron transport chain? 3 Acad Bio Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: ___________ Part III: Using Fermentation to Make Root Beer Site: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/fankhauser/Cheese/ROOTBEER_Jn0.htm Read the directions on the site for making root beer and answer the questions below. 1. What type of organism is yeast? Bacteria animal plant fungus? (circle one) 2. The “carbonation” found in the root beer comes from what molecule? 3. Why is it impossible for you to make homemade root beer using a sugar substitute? 4. Many times on the page the author cautions you to “be careful of explosions” by putting the bottle in the refrigerator rather than leaving it out. A) What product of alcoholic fermentation would cause the pressure build-up and possible explosion? B) Why would putting the bottle in the fridge prevent the explosion from occurring? Hint: Yeast are living organisms. Part IV: Using Fermentation to Make Yogurt Site: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/Fankhauser/Cheese/yogurt_making/YOGURT2000.htm Read the directions on the site for making yogurt and answer the questions below. 1. What type of fermentation is occurring when making yogurt? 2. The ________________ _________________ lowers the___________, makes it ___________, causes the milk protein to _____________________ and acts as a ______________________ since pathogenic(disease-causing) bacteria cannot grow in acid conditions. 3. What three things must you have in order to make good yogurt? 1. 2. 3. 4 Acad Bio