striation
advertisement

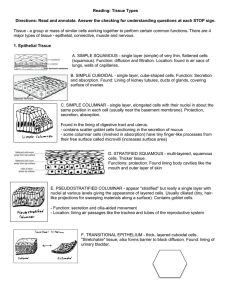
Tissues • Definition? • Histology- study of tissues within the body systems • Classified based on: – Embryonic development – Intercellular space • Four Tissue Types EPITHELIAL TISSUE Very Little intercellular space material Derived from all three embryonic layers Regeneration?? Arranged in sheets with a basement membrane Exposed surface (internal or external) Function Protection Cover internal and external surfaces Secretion and absorbtion (Glands) Classified by shape of cells and number of layers EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE SQUAMOUS Single layer Squamous shape Lining of body cavity, lungs, blood vessels EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE CUBOIDAL Single layer Cuboidal shaped Kidney tubules, glands EPITHELIAL TISSUE SIMPLE COLUMNAR Single layer Columnar shape Lining of digestive tract Modified by presence of cilia EPITHELIAL TISSUE STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS Multi layer Outer most layer- squamous cells Inner- cuboidal or columnar Lining of mouth, esophagus, skin EPITHELIAL TISSUE PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR One layer Appears stratified Respiratory tract Glands • One cell or a group of specialized epithelial cells to secrete substances into ducts, the surfaces or blood – Exocrine • Example- sweat or salivary glands – Endocrine • Example- hormones CONNECTIVE TISSUE Abundant extracellular material Derived from the mesoderm Matrix (dominant part) Fiber, cells in liquid, gel, or solid matrix Highly vascular Function Bind and/or support other tissue Store nutrients CONNECTIVE TISSUE Tendons Dense fiberous Abundant, well organized fiber CONNECTIVE TISSUE ADIPOSE TISSUE Loose connective Semisolid matrix Store large droplets of fat BLOOD Lymph Liquid, fluid matrix Sometimes in different category RBC- Red Blood Cells WBC- White Blood Cells CONNECTIVE TISSUE CARTILAGE Chondrocytes Small cavities- lacunae Dense, solid elastic matrix Ear, nose CONNECTIVE TISSUE BONE Osteocytes Solid, rigid matrix Hardest CT Impregnated w/ calcium salts MUSCLE TISSUE Derived from mesoderm Little intercellular matrix, fibers close together Cells have ability to contract Function Locomotion Other body movement Pg 156-157,162; slides 161 SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE Voluntary movement Typically attach to bone Long and cylindrical Transverse striation Each fiber is multi-nuclear MUSCLE TISSUE SMOOTH Involuntary movement Nonstriated Predominant Long, spindle shape Single nucleus Internal organs MUSCLE TISSUE CARDIAC Striations Involuntary One nucleus Deep center Heart muscle NERVE TISSUE Derived from ectoderm Little intercellular matrix Cells very high ability to Respond to stimuli Transmit impulses Two types: Neurons and Neuroglia NERVE TISSUE NEURON Cell Body(3) Dendrites (5) Axon(1) List of intercellular matrix • Least to most – Epithelial – Muscular – Nervous – connective