File
advertisement

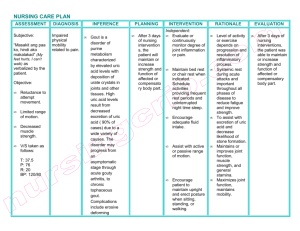
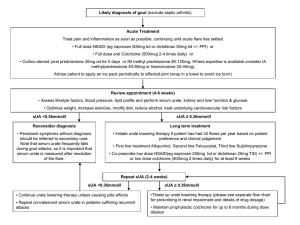
ANTI-GOUT DRUGS GOUT A familial metabolic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of acute arthritis due to deposits of monosodium urate in joints & cartilage. GOUT Treatment aims to: Relieve acute gouty attacks - Colchicine, NSAIDs, corticosteroids Prevent - - recurrent gouty episodes Uricosuric agents Allopurinol CLASSIFICATION of antigout drugs 1. 2. 3. 4. Colchicum alkaloids Colchicine Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Naproxen, indomethacin, phenylbutazone, ibuprofen Uricosuric agents Probenecid, sulfinpyrazone Urate synthesis inhibitors Allopurinol COLCHICINE An alkaloid (colchicum autumnale) Relieves pain & inflammation of gouty arthritis in 12-24 hrs MOA inhibits the polymerization of tubulin (a structural protein necessary for motility) - inhibits leukocyte migration reduces the phagocytosis of urate crystals by leukocytes Adverse Effects Diarrhea - bloody Nausea, vomiting & abdominal pain Hair loss Bone marrow depression Peripheral neuritis Myopathy Acute intoxication: burning throat pain, bloody diarrhea, shock, hematuria Fatal ascending CNS depression NSAIDs: Anti inflammatory ( inhibiting urate crystal phagocytosis) & analgesic effects Indomethacin is most commonly used NSAID- uricosuric All NSAIDs except aspirin, salicylates & tolmetin URICOSURIC AGENTS PROBENECID SULFINPYRAZONE Organic acids MOA inhibit the reabsorption of uric acid in the proximal part (S2) of the nephron may also reduce secretion of uric acid into the nephron (proximal tubule), but reduction of reabsorption is the dominant (& therapeutic) effect Adverse effects Gastrointestinal irritation Rash Nephrotic syndrome with probenecid Aplastic anemia ALLOPURINOL Standard of care therapy in the intercritical period Reduces total uric acid body burden MOA Allopurinol is converted to alloxanthine by xanthine oxidase Inhibits the production of less soluble uric acid by xanthine oxidase from more soluble xanthine & hypoxanthine Pharmacokinetics 80-90% absorbed after oral administration short half-life(1-2hours),but metabolite alloxanthine (oxipurinol) has a half-life of about 15 hours Adverse effects Acute attacks of gouty arthritis (prophylactic treatment with NSAIDs or colchicine) GI intolerance Peripheral neuritis Necrotizing vasculitis Bone marrow depression Aplastic anemia Hepatic toxicity, Interstitial nephritis Allergic skin reactions-exfoliative dermatitis Cataract formation Interactions Inhibits the metabolism of 6mercaptopurine and azathioprine so their dosage must be reduced by 75% Prolongs t1/2 of warfarin & probenecid (inhibits metabolism) May enhance the bone marrow toxicity of cytotoxic drugs (cyclophosphamide) Caution: Safety in children & during pregnancy has not been established FEBUXOSTAT Recently approved first non-purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase Safe in renal disease as highly metabolized to inactive metabolites in the liver GLUCOCORTICOIDS INTERLEUKIN-1 INHIBITORSanakinra – under investigation Thank u!



![06Gout_-_Copy[1].](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005758926_1-0d7c6513b0c82c14c18839741770ea53-300x300.png)



