07-1-Definitions-to
advertisement

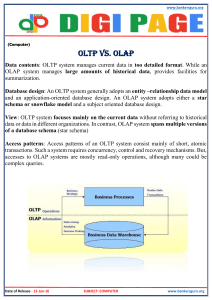
07-1-Definitions-to-learn Definitions or Pre Test Notes Data Warehouse A data warehouse is a separate relational database from the OLTP relational database that runs your day-to-day operations. The purpose is to provide business analysis ability to the company in a timely and meaningful manner that is not easily available from the OLTP system and the queries do no degrade the performance of the OLTP system. The data from the OLTP is used in the DW as well as other sources of data. Fact Table The Fact table is a very large table that holds keys and measures. The measures provide numerical analysis and the keys connect to dimension tables to provide the context or restrictions or textual description for analysis. Dimension Table A table that connects to a fact table by keys is called a dimension table. The dimension table contains descriptive text data for analysis purposes. Example Product name connects via product key to the fact table and through the keys to other dimension tables. Such analysis as Dales by month for a product is possible. Dimension tables answer the who, what where questions. Data Storage Methods - & advantages or disadvantages ROLAP MOLAP HOLAP Measures Types of Measures 1 2 Additive Semi-additive Non-additive Continuously valued OLAP - Online Analytical Processing - Software that allows users to easily analyse data online by manipulating the presentation of facts and dimensions. - By now you have seen a little of it OLTP - Online Transaction Processing - Software that processes business transactions such as order processing, visitor registration, support calls Document1 by rt -- 15 March 2016 1 of 3 Facts - Numeric values that represent - Amounts - Sales $ - Amt - Quantity on Hand) - Or events - Registration count Dimensions - Hierarchies that represent the perspectives a business can take of the facts - Time - Product - Geography - Customer RDBMS - Relational Database Management System - Software for building and managing databases using SQL (Standard Query Language) Data Mart - A targeted subset of a data warehouse to support a particular subject area or departmental requirement Cube - A multidimensional database (MDDB) pre-summarized (aggregation) for fast performance and easy slice-and-dice Slice-and-Dice - The action of changing dimensions to see information from a different perspective ROLL-UP - Aggregate on some dimension - Daily aggregates into weekly, monthly etc - Store data aggregates into stores in city, region, province, and country DRILL-DOWN - De-aggregate on some dimension - Getting at greater levels of detail CLIENTS - Query and reporting tools - Analysis tools DATA MINING - Discovering patterns of various forms by “mining” through the data - Client tools used to do mining - PowerPlay Document1 by rt -- 15 March 2016 2 of 3 E.T.L. Slowly Changing Dimensions How to solve – 3 ways Advantages and Disadvantages Surrogate Keys Advantage STAR SCHEMA SNOWFLAKE SCEMA Advantages and Disadvantages Example OLTP vs OLAP Example Factless Table Example Draw a visual of the Overall process from OLTP to Executive Grain Partitions Document1 by rt -- 15 March 2016 3 of 3