Matter
advertisement

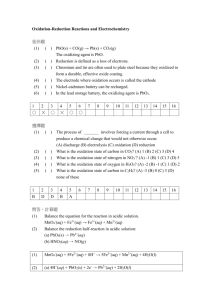
Redox reactions Oxidation Gain oxygen 2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s) Gain oxygen CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O() Loss electrons Mg(s) Mg2+(aq) + 2e- Reduction Loss oxygen 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO2(g) Gain electrons Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) Oxidation and Reduction Oxidation Reduction Gains oxygen Loses oxygen Loses electrons Gains electrons Oxidation number increases Oxidation number decreases Oxidizing agent Oxidizing agent A substance that causes oxidation is called an oxidizing agent. An oxidizing agent is a substance that gains electrons. oxidatio n 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO2(g) oxidizing agent Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) oxidizing agent Reducing agent Reducing agent A substance that causes reduction is called a reducing agent. A reducing agent is a substance that loses electrons. reduction 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO2(g) reducing agent Pb(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2ereducing agent Oxidizing agent and Reducing agent Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Undergoes reduction Undergoes oxidation Loses oxygen Gains oxygen Gains electrons Loses electrons Oxidation number decreases Oxidation number increases Oxidation numbers The oxidation number of an element is zero. oxidations numbers of N in N2, O in O2, S, Na, K, Cu are all zero. The oxidation number of an atom in ionic form is equal to the charge on the ion. oxidation number of iron in Fe3+ is +3 oxidation number of oxygen in O2– is –2 Oxidation numbers The oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound added together must be zero. MgO: Mg = +2, O = -2 KCl: K = +1, Cl = -1 ZnS: Zn = +2, S = -2 Oxidation numbers Some elements have fixed oxidation numbers in compounds all alkali metals (Group I) in compounds must be +1 Na in NaCl, K in K2SO4 hydrogen in most of its compounds +1 H in H2O, H in HCl, H in NH3 Exception: H in metal hydride e.g. H in NaH is -1 Oxidation numbers Some elements have fixed oxidation numbers in compounds all alkaline earth metals (group II) in compounds must be +2 Ca in CaCO3, Mg in MgCl2 fluorine in its compounds must be –1 F in NaF, F in HF Oxidation numbers Some elements have fixed oxidation numbers in compounds oxygen in most of its compounds –2 O in H2O, O in MgO Exception: O in peroxide e.g. O in H2O2 is –1 Oxidation numbers The sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in an ion is equal to the charge of the ion. OH-: O = -2, H = +1 NO3-: O = -2, N = +5 SO42-: O = -2, S = +6 NO2-: O = -2, N = +3 SO32-: O = -2, S = +4 Oxidation numbers Compounds Oxidation numbers HCl H = +1 Cl = -1 ZnO Zn = +2 O = -2 SO2 O = -2 S = +4 CO2 O = -2 C = +4 Na2Cr2O7 O = -2 Na = +1 Cr = +6 Oxidation numbers Compounds Oxidation numbers KMnO4 O = -2 K = +1 Mn = +7 H2SO4 O = -2 H = +1 S = +6 CuCO3 O = -2 Cu = +2 C = +4 Al2(SO4)3 O = -2 Al = +3 S = +6 NiCl2 Cl = -1 Ni = +2 Redox reactions Displacement reaction reduction 0 +2 +2 0 Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Reducing agent Oxidizing agent oxidation Redox reactions Metal with acid reduction 0 +1 +2 0 Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) Reducing agent Oxidizing agent oxidation The electrochemical series of metals The electrochemical series of metals Cu2+(aq) is lower than H+(aq) ion in the e.c.s., it is a stronger oxidizing agent and thus it discharges (reduces) more readily. The electrochemical series of non-metals OH-(aq) is higher than halides ions in the e.c.s., it is a stronger reducing agent and thus it discharges (oxidizes) more readily. Common oxidizing agents Common oxidizing agents Acidified potassium permanganate, KMnO4 Acidified sodium dichromate, Na2Cr2O7 Concentrated sulphuric acid, H2SO4 Dilute or Conc. nitric acid, HNO3 Halogens: Cl2, Br2, etc. Iron(III) ion, Fe3+(aq) Metal ions low in e.c.s. e.g. Ag+(aq), Cu2+(aq) Oxygen gas, O2(g) Common reducing agents Common reducing agents Metal high in e.c.s. e.g. K(s), Na(s) Hydrogen gas, H2(g) Carbon, C(s) and carbon monoxide, CO(g) Sulphur dioxide, SO2(g) and sulphite, SO32(aq) Iodide ion, I-(aq) Iron(II) ion, Fe2+(aq)