IAS 16: Property, Plant & Equipment Accounting
advertisement

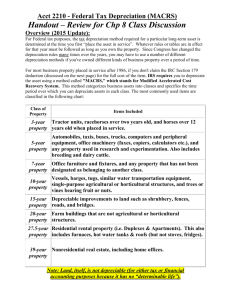
IAS 16 Governments awards an amount to a entity specifically for the purchase of an asset Government grant is recognised as either: ◦ Deferred income; or ◦ By deducting the grant in arriving at the carrying amount of the asset Repayment of government grant accounted for as a change in accounting estimate Grants relating to income to be presented separately as ‘other income’ Same recognition principles Excludes day-to-day servicing of the asset (recognise as an expense) Asset acquired in state of disrepair – subsequent expenditure to restore the item to be capitalised Each item of PPE depreciated separately Depreciable amount allocated on a systematic basis over the item’s useful life Depreciable amount is determined after deducting the residual value Depreciation charge recognised as an expense, unless it is included in the carrying amount of another asset (entity uses one asset to construct another asset) Depreciation begins when the item is ready/available for use Depreciation ceases when the asset is classified as held for sale & derecognised Useful life is estimated after considering: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Expected usage Expected physical wear & tear Technical or commercial obsolescence Legal or similar limits on the use of the asset Land usually not depreciated Buildings are depreciated because they have a limited life Depreciation methods selected based on the expected pattern of consumption of future economic benefits embodied in the asset Depreciation method is to be reviewed at least annually at the financial year-end Change in depreciation method = change in accounting estimate = only current & future periods are adjusted (prospective adjustment) Useful life & residual value to be reviewed at least once a year at the financial year-end Depreciation does not cease when asset becomes temporarily idle, unless classification of asset changes to ‘held for sale’ Fair value – price that would be received to sell an asset in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date Carrying amount – amount at which asset is recognised after deducting any accumulated depreciation & accumulated impairment losses PPE measured at revalued amount less subsequent accumulated depreciation & accumulated impairment losses Frequency of revaluations varies depending on volatility of changes in fair value Class of PPE can be carried under this model only if fair value can be measured reliably Item revalued – entire class to which asset belongs shall be revalued. Item of PPE to be derecognised upon disposal Gains or losses on disposal – difference between the disposal proceeds and the carrying amount of the asset & included in profit or loss for the period Disposal proceeds measured at fair value of consideration received PPE presented as separate line item in SOFP Accounting policies note ◦ Depreciation methods for each class of PPE ◦ Useful lives of each class of PPE ◦ Accounting policy adopted for government grants Note to profit & loss for the year: ◦ ◦ ◦ Gain or loss on disposal Impairment loss Depreciation allocated by class of PPE Note to PPE (per class of assets): ◦ Measurement basis (historical cost or revaluation) ◦ Cost & accumulated depreciation at the beginning & end of the period ◦ Reconciliation of carrying amount at the beginning and end of the period Additions Assets classified as held for sale Increases/decreases resulting from revaluations & impairments Impairment losses Depreciation Restrictions on title Expenditures capitalised during construction Revalued items of PPE: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Date of revaluation Whether or not an independent valuator was used The depreciated historic cost of each revalued class Revaluation Reserve (statement of changes in equity) – detailing movements for the period