Periodic Properties
advertisement

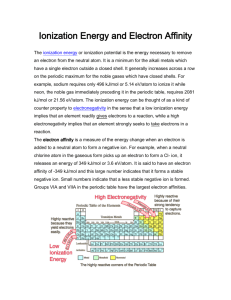
Periodic Properties Atomic Size - the size of the atom decreases as you move from the left side of the chart to the right side of the chart; the size of the atom increases as you move down a column in the chart a. adding additional orbitals causes the size of the atom to increase as you move down the chart b. adding additional protons in the nucleus and additional electrons to the same orbital causes the atom to contract as you move across a row Periodic Properties Ionization energy - the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the neutral atom; electrons are always removed from the highest energy orbital first. Removal of electrons creates positive ions called CATIONS Ionization energy increases as you move from left to right in a row of the periodic chart Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom as you move down a column Ionization energy follows the same pattern as atomic size. Why might this be the case? Periodic Properties Electronegativity - the attraction that an atom has for an additional electron. Linus Pauling invented this scale in 1953 and assigned a value of 4.0 to F electronegativity increases from left to right in a row in the periodic table electronegativity decreases from top to bottom in a column in the periodic table Noble gases are not included in electronegativity. Periodic Properties Electron Affinity - the energy given off when an electron is added to an atom creating a negative ion called an ANION electron affinity increases from left to right in a row in the periodic table electron affinity decreases from top to bottom in a column in the periodic table Noble gases are not included in electron affinity. Periodic Properties Metallic character - metallic character might be described as the ability to give up an electron; the easier an element looses an electron, the more metallic that element is. Metallic character decreases as you move across a row in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements are on the left side Metallic character increases from top to bottom in a column in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements will be found at the bottom of the chart. Periodic Properties Smallest atom - He Largest atom - Fr Smallest ionization energy - Fr Largest ionization energy - He Least metallic character - He Most metallic character - Fr Least electronegative element - Fr Most electronegative element - F Types of Elements • Metals • Nonmetals • Semimetals (metalloids)