Writing And Balancing Equations
advertisement

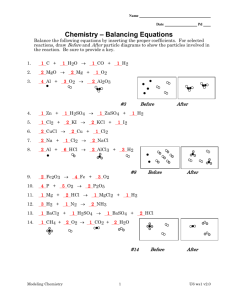
Writing And Balancing Equations Chemistry Dr. May The Road To Writing Sentences Know the alphabet Know vowels and consonants Know how to spell words Know the meaning of words Know sentence structure Know capitalization and punctuation The Road To Writing Equations Know the atomic symbols Know oxidation numbers of elements Know the charge on polyatomic ions Be able to create the correct formulas Identify the reactants and products Balance the equation The Language of Equations Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + 2 H2O The equation above is like a sentence The compounds Ca(OH)2, H2SO4, CaSO4, and H2O are like correctly spelled and chosen words The elements Ca, O, H, and S are like the letters of the alphabet Equations in English Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + 2 H2O One molecule of calcium hydroxide plus one molecule of sulfuric acid yields one molecule of calcium sulfate plus two molecules of water. Equations Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 On the left, Zn and HCl are reactants On the right, ZnCl2 and H2 are products The arrow () means “yields” The up arrow () indicated a gas product The 2 in front of HCl is a coefficient The small 2 to the right of H is a subscript “Skeleton” Equation Identify the reaction Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to give zinc chloride and hydrogen gas Determine the correct formulas and write the “skeleton” (unbalanced) equation Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Coefficients A coefficient placed before a formula multiplies every atom in that formula by that number 2 H2SO4 2 H2SO4 means 2 molecules of sulfuric acid but also 4 H atoms, 2 S atoms, and 8 O atoms Conservation Of Mass A balanced equation contains the same number of each kind of atom on each side of the equation The balanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass Balance The Equation Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Count atoms of each element on each side Balance each element by placing whole numbers (coefficients) in front of each formula as needed Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Write Equation Calcium hydroxide reacts with sulfuric acid to give calcium sulfate and water Calcium = Ca+2 Hydroxide = OH1 Hydrogen = H+1 Sulfate = SO42 Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + H2O Balance Equation Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + HOH Count atoms on both sides 1Ca, 2OH, 2H, 1SO4 1Ca, 1OH, 1H, 1SO4 Balance the water Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + 2 HOH Write Equation Aluminum hydroxide plus sulfuric acid gives aluminum sulfate plus water Aluminum = Al+3 Hydrogen = H+1 Hydroxide = OH1 Sulfate = SO42 Al(OH)3 + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2O Balance The Equation Al(OH)3 + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 1 Al, 3 OH, 2 H, 1 SO4 2 Al, 3 SO4, 1 H, 1 OH 2 Al(OH)3 + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + HOH HOH 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 2 Al(OH)3 + 2 H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 6 HOH HOH Write The Equation Propane burns to produce carbon dioxide and water C 3H 8 + O2 CO2 + H2O The above skeleton equation must be balanced Balance The Equation C3H8 + O2 CO2 + First balance the carbons C3H8 + O2 3 CO2 H2O + H2O + + 4 H2O 4 = 10 Next balance the hydrogens C3H8 + O2 3 CO2 6 Finally balance the oxygens C3H8 + 5 O2 2 x 5 = 10 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Chemical Equations Chemical equations are the short hand description of a chemical reaction It tells us: The reactants and products The formulas of the reactants and products The number of molecules of reactants and products The number of atoms of each element The number of moles of each substance The End This presentation was created for the benefit of our students by the Science Department at Howard High School of Technology Please send suggestions and comments to rmay@nccvt.k12.de.us