United States Government
advertisement

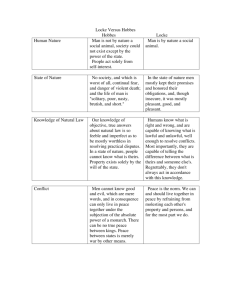
Principles of Government Key Terms state, nation, nation-state, consensus, sovereignty, government, social contract Find Out • What are the four main purposes of government? • How do various theories explain the origin of government? Principles of Government Understanding Concepts Public Policy Which policies of the government make your life better? Which do you think make life worse? Section Objective Identify the essential features of a state and describe the theories about the origin of government. In the last 50 years the number of countries in the world has more than doubled. In 2000, there were 196 independent countries, each with its own people and government. I. Essential Features of a State (pages 6–8) A. Population, the most obvious essential feature of a state. B. An area with fixed boundaries. C. Sovereignty, or absolute authority, within its territorial boundaries. D. A government which maintains order, provides public services, and enforces decisions that its people must obey. I. Essential Features of a State (pages 6–8) I. Essential Features of a State (pages 6–8) U.S. citizens sometimes complain about government, claiming it has too much power and control over their lives. Why do you think they feel this way? People usually complain about government when it affects them directly. II. Theories of the Origin of the State (page 8) A. The state evolved from the family group. B. One person or a group used force to establish its authority to govern the people. C. The rulers of the people were chosen by the gods to govern. D. The people gave the government its power to rule them, and in return the government had to respect the people’s rights. II. Theories of the Origin of the State (page 8) During World War II the government imposed hardships, such as the rationing of gasoline and food, on the U.S. population. Are such measures justifiable? Why or why not? When national security is threatened, strong measures are needed. III. The Purpose of Government (pages 9–11) A. Governments are needed to maintain social order by making and enforcing laws. B. Governments provide essential services for people, such as promoting public health and safety. C. Governments protect people from attack by other states and from internal threats such as terrorism. D. Governments pass laws that shape and control the nation’s economy in various ways. III. The Purpose of Government (pages 9–11) Do you think the government has too much or too little control over the economy of the United States? Answers will vary. Students should support their opinions with examples. Checking for Understanding 1. Main Idea In a graphic organizer similar to the one below, identify four major purposes of government and give an example of each. Answers might include: maintain social order—police and courts; provide public services—highways and firefighters; provide national security—army and navy; establish and regulate an economic system—banks and currency. Checking for Understanding Match the term with the correct definition. ___ A social contract A. theory that by contract, people surrender to the state the power needed to maintain order and the state, in turn, agrees to protect its citizens ___ C sovereignty B. an agreement about basic beliefs ___ E nation C. the supreme and absolute authority within territorial boundaries ___ D nation-state ___ B consensus D. a country in which the territory of both the nation and state coincide E. group of people united by bonds of race, language, custom, tradition, and, sometimes, religion Checking for Understanding 3. Identify Aristotle, Thomas Hobbes, John Locke. Aristotle, a scholar in ancient Greece, was one of the first students of government. He studied the polis, the ancient Greek city-state. Thomas Hobbes was one of the first to theorize on the social contract. John Locke wrote that people were naturally endowed with the right to life, liberty, and property. Locke believed that people had the right to break the contract when the government failed to preserve the rights of the people. Checking for Understanding 4. Summarize the divine right and social contract theories. The divine right theory holds that the state comes from a god and that rulers are descended from or chosen by a god. The social contract theory says people give power to the state so the state may preserve order and rights. Critical Thinking 5. Making Comparisons Thomas Hobbes and John Locke both subscribed to the social contract theory of government. Analyze their views of that theory. Both believed that people surrendered to the state the power needed to maintain order, but Locke believed that people had the right to break that contract when government failed to preserve the rights of the people. Hobbes did not believe they had that right.