1-Way ANOVA
advertisement

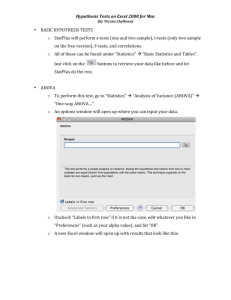
Lecture Overview on ANOVA Review hypothesis testing; inferential statistics z-test, t-test, independent & dependent t-test New Stuff Power – Ability to reject Ho ANOVA • • • • Analysis of Variance Done with 3 or more groups Playground Exercise Complete SPSS Example Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 2 Power Review: Hypothesis Testing Errors Wrongly rejecting Ho: Chance of Type I error: α Wrongly retaining Ho: Chance of Type II error: β Power Opposite of β Power = 1- β Ability to reject Ho (when Ho should be rejected). Researchers want Power! • Want ability to reject Ho; Show you were right to suspect a difference. • Want to show IV affects your DV. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 3 Error Areas α area (where we reject the Ho, β area (where we retain the Ho, and we shouldn’t) • beyond tcritical • under Ho and we shouldn’t) • inside tcritical • under Ha Ho: μ=55 Ha: μ>55 α α tc tc Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA β tc 4 Increasing Power #1: Increase Treatment: Increase difference between groups (μ’s) H0: μ=55 Reality: μ=57 H0: μ=55 Reality: μ=72 β β tc tc #2: Decrease Sampling Error: Decrease differences within groups. β β tc Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA tc 5 Examples of increasing power Rat Study: IV:Caffeine Level DV:Amt. Food Found Therapy Study: IV:Therapy (drug, talk, drug+talk, or control) DV: Improvement] #1 Increase Treatment Effect (Increase BG differences) Rat study 0,3,or 6 mg 0,10,or 20 mg Therapy study 10 therapy sessions 1 therapy session #2 Decrease Sampling Error (Decrease WG differences) Rat study Different strains of rats Same strain of rat Rats allowed to eat freely Rats all unfed for 24 hours Therapy study Diff. types of Therapy Same type of Therapy Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 6 1-Way ANOVA ANOVA Analysis of Variance 1-way means 1 Independent Variable (IV) Purpose: ANOVA allows hypothesis testing with 3+ sample means • Imagine study on interventions to help frosh make friends • Three IV levels: Standard courses, interactive courses, clustered courses. ANOVA uses F-test Strategy: Compare variability within group to variability between groups. F F is ratio between two values: Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA MS BG MSW G 7 ANOVA Playground (Download from Website) 1 Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 8 Matching Exercise Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 9 Draw Conclusions from Playground What does a large F mean? What two things will make F large? Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 11 Partitioning Variance Partition fancy word for “divide up” ANOVA partitions variance (MS means variance) Types of variance Total variance = MSWG + MSBG MSWG= sampling error (background noise) MSBG = sampling error + treatment (includes effect of Independent Variable) MS BG treatment error F MSW G error If just error F tends toward 1.0 If treatment effect F gets larger Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 12 Example of 1-way ANOVA Studying effect of caffeine on productivity Does caffeine help or hurt? IV: Level of Caffeine: 0, 10, 20 mg DV: Number of Food Pellets Found 0 mg 2 3 1 4 2 10 mg 1 2 3 1 2 20 mg 4 4 4 4 5 5 Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA Number of Food Pellets Found 13 SPSS Data Entry IV DV Label levels of IV so output is easier to read. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 14 SPSS Analysis Go to Analyze, Compare Means, & select One-way ANOVA Put DV here. Put IV here. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 15 SPSS Analysis, Part #2 Select this to get descriptive statistics like sample means & standard deviations. Gives you a line graph of the sample means Conducts “after the fact” test to compare all pairs of sample means. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA Alpha level still set to .05, just like it was with ttests. 16 SPSS Output Descriptives FOOD_FND 0 mg 10 mg 20 mg Total N 5 5 6 16 Mean 2.40 1.80 4.33 2.94 Std. Deviation 1.140 .837 .516 1.389 Std. Error .510 .374 .211 .347 Min 1 1 4 1 Max 4 3 5 5 F Sample means from 3 groups, plus mean amount of food found overall. MS BG MSW G ANOVA Source of Variation Table FOOD_FND Between Groups W ithin Groups Total Sum of Squares 19.604 9.333 28.937 df 2 13 15 Mean Square 9.802 .718 F 13.65 Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA Sig. .001 17 Where does F come from? MSWG = SSWG/dfWG = Sum of Squares / degrees of freedom MSBG = SSBG/dfBG = Sum of Squares / degrees of freedom Degrees of freedom dfWG: NT – K dfBG: K-1 dfTOTAL: NT – 1 (Total # of subjects - # of groups) (# of groups – 1) (Total # of subjects – 1) Expectations: If I give you df and SS, you can calculate F You don’t have to get any SS by hand. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 18 SPSS Output –Post Hoc Test FOOD_FND No Sig. Diff. Between 0 & 10mg Student-Newman-Keuls GROUP 10 mg 0 mg 20 mg Sig. N 5 5 6 a,b Subset for alpha = .05 1 2 1.80 2.40 4.33 .270 1.0 4.5 4.0 Mean of FOOD_FND Means for groups in homogeneous s ubsets3.5 are displayed. a. Us es Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 5.294. Rats at 20 mg found 3.0 b. The group izes are unequal. The harmonic mean significantly more sfood 2.5 of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are than rats on 0 or 10 mg of not guaranteed. 2.0 caffeine. 1.5 0 mg 10 mg 20 mg GROUP Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 19 SPSS Output– Practical Significance ANOVA FOOD_FND Between Groups W ithin Groups Total Sum of Squares 19.604 9.333 28.937 df 2 13 15 Mean Square 9.802 .718 F 13.65 Sig. .001 η2 (“eta squared”) Effect size statistic – indicates % of variance explained Measures impact of IV on DV SS BG 19.604 .6775 SSTotal 28.937 2 We can explain 68% of the variance in how much food a rat finds if we know the level of caffeine. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 20 Hypothesis Testing Steps 1. Comparison: cf. three sample means. 2. Hypothesis: Ho: μ1= μ2 = μ3 3. Set-up: α= .05 , dfbg= K-1= 2, dfwg= NT-K = 16-3=13, Fcrit = 3.80 4. Fobt = 13.653 5. Reject Ho. Ha: Not all μ’s equal The hypothesis was largely supported. Rats found sig. more food on 20mg of caffeine (M=4.33) than on 0mg (M=2.40) or 10mg (M=1.80), F(2,13) = 13.653, p <=.05. Caffeine has a large effect on food finding behavior, accounting for about 68% of the variance, η2 = .6775. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 21 F-table df Between Groups df Within Groups Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 22 Lab #8: 1-way ANOVA TV Problem: The hypothesis was supported. Light TV users provided more community service (M = 6.13) than did moderate users (M = 4.00), who provided more than heavy users (M = 1.75), F(2,21) = 15.963, p ≤ .05. TV accounts for about 60% of the variance in community service, η2 = .6032. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 23 Follow-up Questions Q1: Variance within group? MSwg = 2.399 Q2: Variance between groups? MSbg=38.292 Q3: Replacing heavy scores with 4,5,4,5,6,5,4,3 would decrease the difference between groups because the heavy users would then difference less from the other groups. Q4: Decreasing between group differences (decreasing treatment) would decrease F. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 24 Problem #2: Post Hoc Explanation hours Student-Newman-Keuls commute 45 min commute 60 min commute 30 min commute 0 min commute Sig. a N 5 5 5 5 Subset for alpha = .05 1 2 1.20 1.60 2.40 2.40 3.40 .077 .068 Means for groups in homogeneous s ubsets are displayed. a. Us es Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 5.000. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 25 Problem #2: Post Hoc Explanation hours Student-Newman-Keuls commute 45 min commute 60 min commute 30 min commute 0 min commute Sig. a N 5 5 5 5 Subset for alpha = .05 1 2 1.20 1.60 2.40 2.40 3.40 .077 .068 Means for groups in homogeneous s ubsets are displayed. a. Us es Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 5.000. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 26 Problem #2: The hypothesis was supported. People commuting 0 minutes participated significantly more (M=3.4 hours) than people commuting 45 (M=1.2) or 60 minutes (M=1.6), F (3,16) = 7.256, p≤.05. Commuting accounted for a large amount of variance in community involvement, η2 = .5764. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 27 Follow-up Questions Q1: Variance within group? MSwg = .650 Q2: Variance between groups? MSbg=4.717 Q3: Replacing 30 minute commuting scores with 1,4,1,4,3 would increase the within group variability. Q4: Increasing sampling error would decrease F. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 28 Review Partitioning Study: Does alcohol affect reaction time? No Alcohol 10 2 Beers 4 Beers 15 20 20 25 15 15 30 30 10 20 40 14 23 26 μna=?? μ2b=?? Identify the treatment effect in this case. Explain how sampling error might arise. Sample Means μ4b=?? Population Means Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 29 One-Way ANOVA Part 2!! Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1way ANOVA 30 Review Partitioning Study: Does alcohol affect reaction time? No Alcohol 2 Beers What accounts for variability within groups? 4 Beers 10 15 20 20 25 15 15 30 30 10 20 40 What accounts for variability between groups? What’s the Formula for F? Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 31 Review Partitioning Study: Does alcohol affect reaction time? No Alcohol 2 Beers 4 Beers 10 15 20 20 25 15 15 30 30 10 20 40 If the alcohol content of the beers is not held constant, what happens? a. error increases b. error decreases c. treatment effect increases d. treatment effect decreases If the alcohol content of the beers is not held constant, what happens to F? a. increases b. decreases c. neither Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 32 Hypothesis Testing Steps 1. Comparison: cf. three sample means. 2. Hypothesis: Ho: μ1= μ2 = μ3 3. Set-up: α= .05 , dfbg=K-1=3-1=2, dfwg=NT-K=12-3=9, Fcrit = 4.26 Ha: Not all μ’s equal • now do one-way ANOVA on SPSS Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 33 SPSS Output - Charts Descriptives ALCOHOL ALCOHOL a St udent-Newman-Keuls N no alcohol 2 beers 4 beers Total 4 4 4 12 Mean 13.75 22.50 26.25 20.83 Std. Deviation 4.787 6.455 11.087 9.003 Std. Error 2.394 3.227 5.543 2.599 GROUP no alcohol 2 beers 4 beers Sig. N 4 4 4 Subset for alpha = .05 1 13.75 22.50 26.25 .118 Means for groups in homogeneous subs et a. Us es Harmonic Mean Sample Size = ANOVA ALCOHOL Between Groups W ithin Groups Total Sum of Squares 329.167 562.500 891.667 df 2 9 11 Mean Square 164.583 62.500 F 2.633 Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA Sig. .126 34 SPSS Output - Graphs 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 no alcohol GROUP Mean +- 2 SE ALCOHOL 40 30 20 10 0 N= 2 beers 4 beers 4 4 no alcohol 2 beers 4 4 beers GROUP Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 35 Hypothesis Testing Steps 1. Comparison: cf. three sample means. 2. Hypothesis: Ho: μ1= μ2 = μ3 3. Set-up: α= .05 , dfbg=K-1=3-1=2, dfwg=NT-K=12-3=9, Fcrit = 4.26 4. Fobt = 2.633 5. Retain Ho. Ha: Not all μ’s equal The hypothesis was not supported. The reaction times following no alcohol (M=13.75), two beers (M=22.50), and four beers (M=26.25) did not differ significantly, F(2,9) = 2.633, n.s.. Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 36 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset A 4 8 12 Bet. Group Varib: 5 9 10 4 9 11 MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: 5 8 12 L M H L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 37 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset B 8 4 10 Bet. Group Varib: 9 5 12 9 5 11 MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: 8 4 12 L M H L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 38 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset C 7 3 9 Bet. Group Varib: 10 6 13 7 6 10 MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: 10 3 13 L M H L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 39 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset D 7 6 7 Bet. Group Varib: 10 8 7 7 6 12 MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: 10 10 12 L M H L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 40 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset E 7 6 7 10 8 7 7 6 12 10 10 12 7 6 7 10 8 7 7 6 12 10 10 12 Bet. Group Varib: L M H MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 41 Numb. of Words Recalled: Dataset F Bet. Group Varib: L M H MSbg: _______ With. Group Varib: L M H MSwg: _______ MS BG F MSW G Dr. Sinn, PSYC301, The joy of 1-way ANOVA 42